Apache facts for kids
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 111,810 alone and in combination | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Texas, Oklahoma, Mexico, Coahuila, and Tamaulipas | |
| Languages | |
| Apache, Jicarilla, Plains Apache, Lipan Apache, Mescalero-Chiricahua, Western Apache, English, and Spanish | |
| Religion | |
| Native American Church, Christianity, traditional tribal religion | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Navajo, Dene, Tarahumara |
The Apache are a group of Native American tribes who share similar cultures. They live in the Southwestern United States. These indigenous peoples of North America speak a Southern Athabaskan language. This language is similar to others spoken in Alaska and western Canada.
Long ago, Apache peoples lived across a wide area. This included eastern Arizona, northern Mexico, New Mexico, west and southwest Texas, and southern Colorado. Their lands had high mountains, green valleys, deep canyons, deserts, and the southern Great Plains.
The Apache tribes were known as strong and skilled warriors. They fought against the Spanish and Mexican peoples for many years. They also fought the U.S. Army in the 1800s. Even though they were powerful, the Apache tribes spoke seven different languages. Their cultures were not always united.
The Apache way of life has changed since European settlers arrived. Today, some Apache groups live in Oklahoma and Texas. Others live on reservations in Arizona and New Mexico. Some Apacheans have moved to big cities. Others work in farm labor in places like Southern California. The main Apache groups today include the Navajo, Western Apache, Chiricahua, Mescalero, Jicarilla, Lipan, and Plains Apache.
Contents
How Apache People Organized Their Communities
All Apache groups lived in large family units. These were like big family groups living close together. When a couple got married, they would join the bride's family. They would build a home nearby. This helped create large, close-knit family groups.
Several of these large families worked together as a "local group." A chief led each local group. The chief was the closest thing to a leader in Apache cultures. Chiefs were chosen based on their good character and leadership skills.
What Kind of Homes Did Apache People Live In?
Apache people lived in three main types of homes, depending on where they lived:
- The teepee was used by Apache groups who lived on the plains.
- The wickiup was a round, 8-foot-tall (2.4 m) frame made of wood. It was held together with yucca fibers and covered with brush. Wickiups were common for Apache groups in the highlands.
- The hogan was a structure made of earth. It was used in desert areas. Hogans helped keep the Apache cool in the hot weather of northern Mexico.
What Did Apache People Eat?
Apache people got their food from four main ways:
- hunting wild animals,
- gathering wild plants,
- growing plants, and
- trading with or sometimes attacking neighboring tribes for food.
For example, the Western Apache diet was about 35–40% meat and 60–65% plant foods. The types of food eaten varied among Apache tribes. This was because they lived in different environments.
How Did Apache People Hunt?
Hunting was mostly done by men. However, sometimes women helped, especially with smaller animals like rabbits. Boys were also allowed to hunt rabbits.
Hunting often involved special preparations. These included fasting and religious ceremonies. Medicine men performed these rituals before and after a hunt. Many Apache shared about half of their hunted meat with other hunters and those in need at the camp.
Before Europeans brought guns, the main hunting weapon was the bow. Hunters used different strategies depending on the animal and the land. They used animal disguises, whistles, and chased prey.
Most Apache tribes hunted deer. Other animals hunted depended on where the tribe lived. These included pronghorns, cottontail rabbits, squirrels, wapiti (elk), and buffalo (for those near the plains). Some Apache cultures did not eat certain animals like bears, fish, or snakes.
What Wild Plants Did Apache People Eat?
Women usually gathered plants and other foods. However, men helped with heavy tasks, like gathering large agave plants. Many plants were used for food, medicine, and religious ceremonies.
Agave and yucca were important plants for most Western Apache groups. They used as much of these plants as possible. Several types of cactus also grew in the southwest. These included saguaro and prickly pear.
Despite the dry climate, many fruits and berries grew where the Apache lived. These included cholla fruits, wild grapes, juniper berries, raspberries, and strawberries.
Apache cultures also used nuts, seeds, roots, and grasses. They harvested acorns, pinyon nuts, walnuts, and pecans. They also gathered seed grasses for flour and sunflower seeds. Vegetables and herbs like chili peppers, onions, and sage were also part of their diet.
Did Apache People Grow Crops?
Of all the Apache tribes, the Navajo did the most crop cultivation. Some Apache tribes did not grow crops at all.
What Did Apache People Wear?
When the Apache hunted, they used as much of the animal as they could. This included the hide for clothing and shoes. The Western Apache decorated their clothing with seed beads. They used thin lines and diagonal stripes of colorful glass beads. They made buckskin shirts, ponchos, skirts, and moccasins. These were often decorated with beautiful beadwork.
How Did Apache People Interact with Others?
The Apache traded with European and American settlers. They found that they could use European and American goods.
The Apache had clear differences between raiding (for goods) and war (for revenge). Raiding involved small groups looking for specific items, like horses. War involved larger groups, often family members, fighting back for wrongs done to them.
Mexican settlers did not like it when their livestock was stolen. This led to conflicts with the Apache.
Interesting Facts About the Apache
- Before European settlers came, most Apache were nomads. This means they moved from place to place.
- The name Apache came from an enemy tribe, the Zuni. It means "enemy."
- Apache children played like most children. However, they started doing chores and riding horses at a young age.
- The Apache had many religious ceremonies. These involved singing, chanting, and dancing.
- Apache men were trained for combat and war from childhood.
- Many Apache did not cut their hair. They believed it would bring bad luck.
- Storytelling is very important in Apache culture.
- Basket weaving is one of the Apache's oldest forms of art.
- Some Apache groups played a fiddle made from agave stalks.
- In the late 1800s, the Apache fought battles against the United States government.
- Cochise and Geronimo are two famous Apache leaders.
Images for kids
-
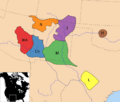
Apachean tribes, c. 18th century:
- WA: Western Apache
- N: Navajo
- Ch: Chiricahua
- M: Mescalero
- J: Jicarilla
- L: Lipan
- Pl: Plains Apache
-
Kathy Kitcheyan, chairwoman of the San Carlos Apache
-
Essa-queta, Plains Apache chief
-
Young Jicarilla Apache boy, New Mexico, 2009
-
Apache rawhide playing cards c. 1875–1885, collection of NMAI.
-
The Coronado Expedition, 1540–1542
See also
 In Spanish: Apache para niños
In Spanish: Apache para niños