Raspberry facts for kids
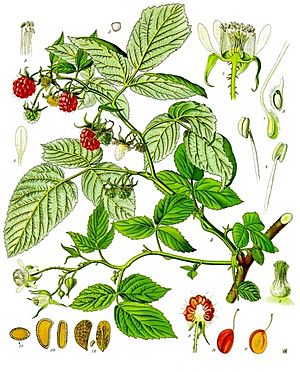
A raspberry is a tasty fruit made of many small parts joined together. It looks a bit like a blackberry, but a raspberry is hollow inside. There are many different kinds, or species, of raspberry plants. Only a few of them grow fruit that you can buy in stores. People also use the leaves of raspberry plants, fresh or dried, to make herbal teas. Raspberries are usually red when they are ready to eat. They are also used to make juices. Raspberries are a very popular fruit in many places around the world.
Contents
Raspberry Plants
Raspberry plants often grow in open fields or in forest areas where trees have been cut down or where there has been a fire. When grown by people in places with mild, wet weather, they are easy to take care of. They can spread quickly if they are not trimmed back.
You can buy two main types of raspberry plants:
- Summer-bearing plants: These plants produce fruit once a year, in the summer.
- Ever-bearing plants: These plants produce fruit twice. They give fruit in the fall of their first year and again in the summer of their second year.
Raspberry plants grow new stems, called stalks, every year. These stalks live for two years. The fruit grows on these stalks.
Types of Raspberries
The raspberries you usually find in stores come from plants that are a mix, or hybrid, of two types: the European red raspberry (Rubus idaeus) and the American red raspberry (Rubus strigosus). Sometimes, you can find black raspberries (Rubus occidentalis). There are also purple raspberries, which are a mix of these types. These three main types belong to the same group of raspberries.
Other types of raspberries include:
- Rubus crataegifolius (Korean raspberry)
- Rubus gunnianus (Tasmanian alpine raspberry)
- Rubus leucodermis (Whitebark, Western, Blue, or Black raspberry)
- Rubus parvifolius (Australian native raspberry)
- Rubus phoenicolasius (Wine raspberry or Wineberry)
- Rubus rosifolius (West Indian raspberry)
- Rubus ellipticus (Yellow Himalayan Raspberry)
- Rubus strigosus (American raspberry)
Some other raspberry types that are a bit different include:
- Rubus arcticus (Arctic raspberry)
- Rubus deliciosus (Boulder raspberry)
- Rubus nivalis (Snow raspberry)
- Rubus odoratus (Native Flowering raspberry)
- Rubus sieboldii (Molucca raspberry)
How We Use Raspberries
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 220 kJ (53 kcal) |
|
11.94 g
|
|
| Sugars | 4.42 g |
| Dietary fiber | 6.5 g |
|
0.65 g
|
|
|
Protein
|
1.2 g
|
| Vitamins | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Thiamine (B1) |
3%
0.032 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
3%
0.038 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
4%
0.598 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
7%
0.329 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
4%
0.055 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
5%
21 μg |
| Choline |
3%
12.3 mg |
| Vitamin C |
32%
26.2 mg |
| Vitamin E |
6%
0.87 mg |
| Vitamin K |
7%
7.8 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Calcium |
3%
25 mg |
| Iron |
5%
0.69 mg |
| Magnesium |
6%
22 mg |
| Manganese |
32%
0.67 mg |
| Phosphorus |
4%
29 mg |
| Potassium |
5%
151 mg |
| Zinc |
4%
0.42 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 85.8 g |
|
Link to USDA Database entry
|
|
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Raspberry Fruit
People grow raspberries to sell as fresh fruit. They are also processed into frozen fruit, purée, juice, or dried fruit. These are used in many foods, like raspberry pie. In the past, raspberries were only available in midsummer. But now, thanks to new ways of growing and transporting them, you can find raspberries all year long.
Raspberry Leaves
Raspberry leaves can be used fresh or dried to make herbal tea. This tea has a slightly sharp taste. In some traditional practices, raspberry leaves are used for certain health reasons. However, there is no strong scientific proof that they work as medicine.
Images for kids
-
European Rubus idaeus raspberries on the plant
-
Raspberries from Serbia
See also
 In Spanish: Frambuesa para niños
In Spanish: Frambuesa para niños