Vitamin B5 facts for kids
Pantothenic acid is a very important vitamin that your body needs to work properly. It's part of the B vitamins group and is also known as vitamin B5. Think of it like a tiny helper that makes sure many important jobs get done inside you! It's a special kind of molecule that comes from something called beta-Alanine, which is a building block for proteins.
Contents
What is Vitamin B5?
Vitamin B5 is a water-soluble vitamin. This means it dissolves in water. Your body doesn't store large amounts of it. Instead, any extra vitamin B5 usually leaves your body through urine. This is why you need to get it regularly from the foods you eat.
Why is Vitamin B5 Important?
Vitamin B5 plays a key role in many body functions. It helps turn the food you eat into energy. This energy is what powers your muscles, brain, and every cell in your body. Without enough vitamin B5, your body would struggle to get the energy it needs.
It also helps make and break down fats. These fats are important for building cell membranes and for storing energy. Vitamin B5 is also involved in making hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that control many processes in your body.
How Vitamin B5 Helps Your Body
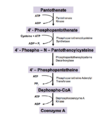
- Energy Production: Vitamin B5 is a crucial part of a molecule called Coenzyme A (CoA). CoA is like a central hub for many chemical reactions. It helps your body use carbohydrates, fats, and proteins for energy.
- Making Red Blood Cells: It helps your body make red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body.
- Healthy Skin and Hair: Some studies suggest vitamin B5 can help keep your skin healthy. It might also play a role in hair growth and strength.
- Nervous System Support: It helps keep your nervous system working well. Your nervous system sends messages between your brain and your body.
- Stress Response: Vitamin B5 supports the adrenal glands. These glands produce hormones that help your body respond to stress.
Where Can You Find Vitamin B5?
Vitamin B5 is found in almost all foods. This is why its name, "pantothenic," comes from the Greek word "pantothen," meaning "from everywhere." You can get it from a wide variety of foods.
Good Food Sources of Vitamin B5
- Meats: Chicken, beef, and liver are excellent sources.
- Fish: Salmon and tuna contain good amounts.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, mushrooms, avocados, and sweet potatoes are rich in B5.
- Grains: Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and whole wheat bread.
- Legumes: Lentils and split peas.
- Dairy: Milk and yogurt.
- Eggs: A good source of many vitamins, including B5.
Cooking and Vitamin B5
Since vitamin B5 is water-soluble, some of it can be lost during cooking. Especially if foods are boiled in a lot of water. Steaming or stir-frying can help keep more of the vitamin in your food.
What Happens if You Don't Get Enough?
It's very rare for people to not get enough vitamin B5. This is because it's found in so many different foods. However, if someone had a very poor diet, they might experience a deficiency.
Signs of Vitamin B5 Deficiency
Symptoms of not getting enough vitamin B5 can include:
- Feeling tired or weak
- Headaches
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Trouble sleeping
- Stomach problems like nausea or cramps
These symptoms are usually mild and go away once enough vitamin B5 is consumed.
History of Discovery
Vitamin B5 was first discovered in 1933 by a scientist named Roger J. Williams. He found it was a growth factor for yeast. Later, scientists learned how important it was for humans and animals too. Its role in energy production was a big discovery that helped us understand how our bodies work.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Vitamina B5 para niños
In Spanish: Vitamina B5 para niños