Idaho facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Idaho
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
The Gem State (official), The Potato State
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Esto perpetua (Latin for "Let it be perpetual")
|
|||
| Anthem: "Here We Have Idaho" | |||
Location of Idaho within the United States
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| Before statehood | Oregon Territory, Washington Territory, Idaho Territory | ||
| Admitted to the Union | July 3, 1890 (43rd) | ||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Boise | ||
| Largest county or equivalent | Ada | ||
| Largest metro and urban areas | Boise | ||
| Legislature | Legislature | ||
| • Upper house | Senate | ||
| • Lower house | House of Representatives | ||
| Judiciary | Idaho Supreme Court | ||
| U.S. senators | Mike Crapo (R) Jim Risch (R) |
||
| U.S. House delegation | 1. Russ Fulcher (R) 2. Mike Simpson (R) (list) |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 83,571 sq mi (216,444 km2) | ||
| • Land | 82,644 sq mi (214,046 km2) | ||
| • Water | 927 sq mi (2,399 km2) 1.11% | ||
| Area rank | 11th | ||
| Dimensions | |||
| • Length | 479 mi (771 km) | ||
| • Width | 305 mi (491 km) | ||
| Elevation | 5,000 ft (1,520 m) | ||
| Highest elevation | 12,662 ft (3,859 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 713 ft (217 m) | ||
| Population
(2024)
|
|||
| • Total | |||
| • Rank | 38th | ||
| • Density | 23.63/sq mi (8.33/km2) | ||
| • Density rank | 44th | ||
| • Median household income | $74,900 (2023) | ||
| • Income rank | 31st | ||
| Demonym(s) | Idahoan | ||
| Language | |||
| • Official language | English | ||
| Time zones | |||
| primary | UTC−07:00 (Mountain) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−06:00 (MDT) | ||
| Idaho Panhandle | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) | ||
| USPS abbreviation |
ID
|
||
| ISO 3166 code | US-ID | ||
| Latitude | 42° N to 49° N | ||
| Longitude | 111°03′ W to 117°15′ W | ||
| Dance | Square dance |
|---|---|
| Bird |
|
| Fish | Cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii) |
| Flower | Syringa (Philadelphus lewisii) |
| Tree | Western white pine (Pinus monticola) |
| Insect | Monarch butterfly (Danaus plexippus) |
Idaho is a state located in the western part of the United States. It is part of the Mountain West region. Idaho shares a border with British Columbia in Canada to the north. It also borders six U.S. states: Montana, Wyoming, Nevada, Utah, Washington, and Oregon.
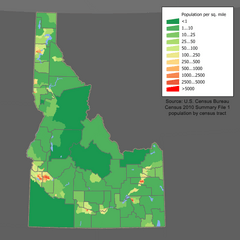
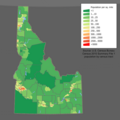
The capital and largest city in Idaho is Boise. Idaho is the 14th largest state by land area. It has about 1.8 million people, making it one of the less populated states.
For thousands of years, native peoples lived in the Idaho area. In the early 1800s, Idaho was part of the Oregon Country. This area was claimed by both the U.S. and the British Empire. In 1846, the Oregon Treaty made it officially U.S. territory. Idaho became a separate territory in 1863. On July 3, 1890, Idaho became the 43rd U.S. state.
Idaho is part of the Pacific Northwest. It has many different geographic and climate regions. The northern part, called the Idaho Panhandle, is connected to Eastern Washington. This area uses the Pacific Time Zone. The rest of the state uses the Mountain Time Zone. Southern Idaho includes the Snake River Plain, where most people live and farm. Idaho is very mountainous, with parts of the Rocky Mountains. The United States Forest Service owns about 38% of Idaho's land. This is the highest amount for any state.
Idaho's economy relies on manufacturing, farming, mining, and tourism. Many science and technology companies are in Idaho. The state is also home to the Idaho National Laboratory. This is a large Department of Energy facility. Idaho grows many farm products. It is most famous for its potatoes, which make up about one-third of the U.S. potato crop. Idaho's official nickname is the "Gem State."
Contents
- The Name of Idaho: What Does it Mean?
- Idaho's Past: A Look at History
- Idaho's Amazing Geography
- How Idaho's Government Works
- People and Population in Idaho
- Idaho's Economy: How People Make a Living
- Energy in Idaho
- Transportation in Idaho
- Education in Idaho
- Sports and Recreation in Idaho
- Idaho in Movies and Pop Culture
- Images for kids
- See also
The Name of Idaho: What Does it Mean?
The exact meaning of the name "Idaho" is still a bit of a mystery. In the early 1860s, the U.S. Congress was thinking about creating a new territory. A politician named George M. Willing suggested the name "Idaho."
Willing claimed the name came from a Shoshone word. He said it meant "the sun comes from the mountains" or "gem of the mountains." However, it was later found that no such word existed in Shoshone. Willing then said he made up the name after meeting a girl named Ida. Because the name seemed made up, Congress decided to call the area Colorado Territory in 1861. But by then, a town in Colorado was already named Idaho Springs, Colorado after Willing's idea.
In the same year, a county called Idaho County was created in Washington Territory. This county was named after a steamship called Idaho. The steamship was launched on the Columbia River in 1860. It is not clear if the ship was named before or after Willing's story came out. Later, part of Washington Territory, including Idaho County, became the Idaho Territory in 1863. This territory eventually became the state of Idaho.
Idaho's Past: A Look at History
Humans might have lived in the Idaho area as far back as 14,500 years ago. In 1959, scientists found old tools and arrowheads at Wilson Butte Cave near Twin Falls. These are some of the oldest items found in North America. The main American Indian groups in the area were the Nez Percé in the north and the Northern and Western Shoshone in the south.
In 2019, archaeologists found an even older site at Cooper's Ferry in western Idaho. Evidence there suggests people lived in the area 15,300 to 16,600 years ago. This was even before the Beringia land bridge was fully formed. The tools found there are similar to ones found in Japan. This suggests that the first people might have come to North America by boat along the Pacific coast.
Early French-Canadian fur trappers also explored Idaho. You can still see their influence in names like Nez Percé, Cœur d'Alène, Boisé, and Payette. These names appeared before the Lewis and Clark expedition.
Idaho was part of the Oregon Country. Both the United States and Great Britain claimed this land. In 1846, the U.S. gained full control. From 1843 to 1859, Idaho was under the control of the Provisional Government of Oregon. When Oregon became a state in 1859, Idaho was part of the Washington Territory.
Between 1849 and 1863, parts of Idaho were included in the Oregon Territory, Washington Territory, and Dakota Territory. The new Idaho territory in 1863 included present-day Idaho, Montana, and most of Wyoming. The Lewis and Clark expedition traveled through Idaho in 1805 and 1806. They mostly followed the Clearwater River.
The first non-Native American settlement was Kullyspell House. It was built in 1809 by David Thompson for fur trading. The first permanent communities were started by Mormon pioneers in 1860. Lewiston became the first official town in 1861. Many Chinese immigrants came to Idaho early on. By 1870, they made up about 28.5% of the territory's population.
Idaho became a state in 1890. This happened after some challenges as a territory. For example, the capital was moved from Lewiston to Boise. Also, there were disagreements about laws for some groups.
Idaho was hit hard during the Great Depression. Prices for Idaho's main crops dropped sharply. For example, potatoes that sold for $1.51 in 1919 cost only ten cents in 1932. Farmers' incomes fell greatly.
In recent years, Idaho has grown beyond farming and tourism. Science and technology industries are now very important. They make up over 25% of the state's total income. This is more than farming, forestry, and mining combined.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Idaho's hospitals became very busy. The state had one of the lowest vaccination rates in the country in late 2021.
Idaho's Amazing Geography
Idaho shares borders with six U.S. states and one Canadian province. Washington and Oregon are to the west. Nevada and Utah are to the south. Montana and Wyoming are to the east. Idaho also has a short border with British Columbia in Canada to the north.
Idaho's landscape is rugged and beautiful. It has some of the largest untouched natural areas in the U.S. For example, the Frank Church-River of No Return Wilderness Area is huge. It is the largest continuous protected wilderness in the continental United States. Idaho is a Rocky Mountain state. It has many natural resources and scenic spots. You can find snow-capped mountains, rushing rivers, large lakes, and deep canyons. The Snake River flows through Hells Canyon, which is the deepest gorge in the United States. Shoshone Falls is taller than Niagara Falls.
The most important river in Idaho is the Snake River. It is a major branch of the Columbia River. The Snake River starts in Yellowstone in Wyoming. It flows through the Snake River Plain in southern Idaho. Then it turns north and leaves the state near Lewiston. Other important rivers include the Clark Fork, the Spokane River, and many rivers that feed into the Snake River. These include the Clearwater River, the Salmon River, the Boise River, and the Payette River.
The Port of Lewiston is located where the Clearwater and Snake Rivers meet. It is the farthest inland seaport on the West Coast. Ships can travel 465 miles from the Pacific Ocean to Lewiston.
Most of Idaho's people live in the Snake River Plain. This is a valley that runs across southern Idaho from east to west. Major cities like Boise, Meridian, Nampa, Caldwell, Twin Falls, Idaho Falls, and Pocatello are in this valley. The plain was an easy path through the Rocky Mountains for settlers traveling west on the Oregon Trail. Many chose to settle here instead of risking the difficult route further west. The western part of the plain is called the Treasure Valley. The central part is known as the Magic Valley.
Idaho's highest point is Borah Peak. It is 12,662 feet (3,859 meters) tall. This peak is in the Lost River Range north of Mackay. The lowest point in Idaho is 710 feet (217 meters) high. This is in Lewiston, where the Clearwater River joins the Snake River. The Sawtooth Range is one of Idaho's most famous mountain ranges. Other ranges include the Bitterroot Range, the White Cloud Mountains, and the Salmon River Mountains.
The Salmon-Challis National Forest is in the east-central part of the state. This area is known as the Idaho Cobalt Belt. It has a 34-mile (55 km) long rock formation. This formation contains some of the largest cobalt deposits in the U.S.
Idaho has two time zones. The dividing line is about halfway between Canada and Nevada. Southern Idaho, including the Boise metropolitan area, Idaho Falls, Pocatello, and Twin Falls, are in the Mountain Time Zone. Areas north of the Salmon River, like Coeur d'Alene and Lewiston, are in the Pacific Time Zone. Less than a quarter of Idaho's population and land area are in the Pacific Time Zone.
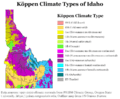
Idaho's Climate: Weather Across the State

Idaho's climate changes a lot from one area to another. Even though the state's western border is about 330 miles (530 km) from the Pacific Ocean, the ocean still affects Idaho's weather. This is especially true in winter. During winter, there are more clouds, humidity, and rain or snow. This ocean influence makes winters milder. Temperatures are not as low as you might expect for a northern state with high elevations. In the panhandle, moist air from the coast brings a lot of rain and snow. This creates a North American inland temperate rainforest.
The ocean's influence is weakest in eastern Idaho. Here, the weather patterns are often reversed. Summers are wetter, and winters are drier. Also, the temperature differences between seasons are much greater. This shows a more dry continental climate.
Idaho can get hot, but temperatures rarely stay above 98°F (37°C). The exception is Lewiston, which is the lowest point in the state. Lewiston also gets very little snow. Hot summer days are made more comfortable by low humidity and cooler evenings. For most of the state, the biggest daily temperature changes happen in the summer. Winters can be cold, but long periods of very bitter cold below zero are unusual. Idaho's highest temperature ever was 118°F (48°C). This was recorded in Orofino on July 28, 1934. The lowest temperature ever was -60°F (-51°C). This happened at Island Park Dam on January 18, 1943.
| Monthly normal high and low temperatures for various Idaho cities. (°F) | ||||||||||||
| City | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boise | 38/24 | 45/27 | 55/33 | 62/38 | 72/46 | 81/53 | 91/59 | 90/59 | 79/50 | 65/40 | 48/31 | 38/23 |
| Lewiston | 42/30 | 47/32 | 55/36 | 62/41 | 72/48 | 79/54 | 91/61 | 90/60 | 80/52 | 63/42 | 49/35 | 41/30 |
| Pocatello | 33/16 | 38/19 | 49/27 | 59/33 | 68/40 | 78/46 | 88/52 | 88/51 | 76/42 | 62/33 | 45/24 | 33/16 |
| Orofino | 38/25 | 46/28 | 55/32 | 64/38 | 72/44 | 80/50 | 89/54 | 90/53 | 79/45 | 63/36 | 46/31 | 37/26 |
| ' | ||||||||||||
Idaho's Lakes and Rivers



Idaho has many beautiful lakes and rivers. Here are some of the most important ones:
- Clark Fork River
- Alturas Lake
- Bear River
- Bear Lake (Idaho–Utah)
- Boise River
- Clearwater River
- Hayden Lake
- Henry's Lake
- Kootenai River
- Lake Cascade
- Lake Cleveland
- Lake Coeur d'Alene
- Lake Lowell
- Lake Walcott
- Pend Oreille - This is the largest lake in Idaho.
- Little Redfish Lake
- Lucky Peak Lake
- Moyie River
- North Fork Clearwater River
- Pack River
- Payette Lake, (McCall)
- Pettit Lake
- Priest Lake
- Perkins Lake
- Portneuf River
- Redfish Lake
- Salmon River
- Sawtooth Lake
- Snake River - This is the longest river in Idaho.
- Stanley Lake
- St. Joe River
- Warm Lake
Protected Natural Areas in Idaho
Idaho has many protected natural areas. These include national parks, reserves, and state parks. They help protect Idaho's beautiful landscapes and wildlife.
National Parks, Reserves, and Historic Sites
- Salmon-Challis National Forest
- California National Historic Trail
- City of Rocks National Reserve
- Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve
- Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument
- Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail
- Minidoka National Historic Site
- Nez Perce National Historical Park
- Oregon National Historic Trail
- Yellowstone National Park
- Pacific Northwest National Scenic Trail
National Recreation Areas
- Hells Canyon National Recreation Area
- Sawtooth National Recreation Area
National Wildlife Refuges and Wilderness Areas
- Bear Lake National Wildlife Refuge
- Camas National Wildlife Refuge
- Deer Flat National Wildlife Refuge
- Frank Church—River of No Return Wilderness Area
- Grays Lake National Wildlife Refuge
- Kootenai National Wildlife Refuge
- Minidoka National Wildlife Refuge
National Conservation Areas
- Snake River Birds of Prey National Conservation Area
Idaho State Parks
Idaho also has many state parks for people to enjoy:
- Bear Lake State Park
- Bruneau Dunes State Park
- Castle Rocks State Park
- City of Rocks National Reserve
- Coeur d'Alene Parkway State Park
- Dworshak State Park
- Eagle Island State Park
- Farragut State Park
- Harriman State Park
- Hells Gate State Park
- Henrys Lake State Park
- Heyburn State Park
- Lake Cascade State Park
- Lake Walcott State Park
- Land of the Yankee Fork State Park
- Lucky Peak State Park
- Massacre Rocks State Park
- McCroskey State Park
- Old Mission State Park
- Ponderosa State Park
- Priest Lake State Park
- Round Lake State Park
- Thousand Springs State Park
- Three Island Crossing State Park
- Trail of the Coeur d'Alenes
- Winchester Lake State Park
How Idaho's Government Works
Idaho's government is set up like the U.S. national government. It has three main parts: the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The state's laws are written in the Idaho Code and Statutes. The state constitution requires the government to have a balanced budget.
The State Legislature: Making Laws
Idaho has a bicameral legislature. This means it has two parts: the Senate and the House of Representatives. Lawmakers are elected from 35 different areas. Each area has one senator and two representatives.
Idaho's lawmakers work part-time. This means being a legislator is not their only job. They usually meet for a set period, but they can extend the session if needed. Senators and representatives both serve two-year terms. Elections for the legislature happen every even-numbered year.
Since 1960, the Republican Party has mostly controlled both parts of Idaho's legislature. However, Democratic lawmakers are often elected from cities like Boise and Pocatello.
The Executive Branch: Leading the State
The governor of Idaho leads the executive branch. The governor serves a four-year term. Governors are elected during the midterm elections, not in the same year as the U.S. president. Idaho is one of 13 states where there are no limits on how many terms a governor can serve.
Other important elected officials include the Lieutenant Governor, Secretary of State, Treasurer, Attorney General, and Superintendent of Public Instruction. These officials also serve four-year terms.
The Judicial Branch: Interpreting Laws
The highest court in Idaho is the Idaho Supreme Court. There is also an intermediate appellate court called the Idaho Court of Appeals. This court hears cases that are sent to it by the Supreme Court. The state also has District Courts that serve seven different judicial areas.
People and Population in Idaho
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 14,999 | — | |
| 1880 | 32,610 | 117.4% | |
| 1890 | 88,548 | 171.5% | |
| 1900 | 161,772 | 82.7% | |
| 1910 | 325,594 | 101.3% | |
| 1920 | 431,866 | 32.6% | |
| 1930 | 445,032 | 3.0% | |
| 1940 | 524,873 | 17.9% | |
| 1950 | 588,637 | 12.1% | |
| 1960 | 667,191 | 13.3% | |
| 1970 | 712,567 | 6.8% | |
| 1980 | 943,935 | 32.5% | |
| 1990 | 1,006,749 | 6.7% | |
| 2000 | 1,293,953 | 28.5% | |
| 2010 | 1,567,582 | 21.1% | |
| 2020 | 1,839,106 | 17.3% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 1,964,726 | 25.3% | |
| Source: 1910–2020 2023 |
|||
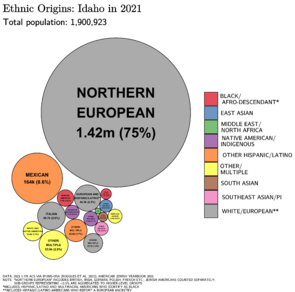
In 2021, Idaho's population was about 1,900,923 people. This was a 21% increase since the 2010 U.S. census. In 2018, the population was about 1,754,208. This was an increase of over 186,000 people since 2010. Many people have moved to Idaho from other states. Also, many people have moved to Idaho from other countries. The main countries people come from are Mexico, Canada, the Philippines, China, and Germany.
Idaho's population grew by 17.3% from 2010 to 2020. This was the second fastest growth rate of any state.
Nampa, located west of Boise, became the state's second largest city in the late 1990s. Its population grew from under 29,000 in 1990 to over 81,000 by 2010. Meridian, between Nampa and Boise, also grew a lot. It went from under 10,000 residents in 1990 to over 75,000 in 2010. It is now Idaho's third largest city. Other cities like Caldwell, Coeur d'Alene, Post Falls, and Twin Falls also saw big population increases.
From 1990 to 2010, Idaho's population increased by over 560,000 people. The Boise metropolitan area is the largest in Idaho. Other large metro areas include Coeur d'Alene, Idaho Falls, Pocatello, and Lewiston.
| Racial composition | 1970 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White or European American | 98.1% | 94.4% | 90.1% | 89.1% | 82.1% |
| Indigenous | 0.9% | 1.4% | 1.4% | 1.4% | 1.4% |
| Asian | 0.5% | 0.9% | 0.9% | 1.2% | 1.5% |
| Black | 0.3% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander |
— | — | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.2% |
| Other race | 0.2% | 3.0% | 4.2% | 5.1% | 5.6% |
| Two or more races | — | — | 2.0% | 2.5% | 8.3% |
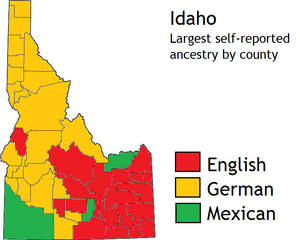
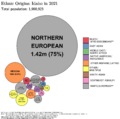
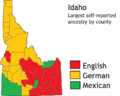
In 2017, about 12.2% of Idaho's population was of Hispanic or Latino origin. The largest ancestry groups were German (17.5%), English (16.4%), and Irish (9.3%). Most white residents in Idaho have ancestors from the United Kingdom, Germany, Ireland, France, Italy, or Poland. There are also smaller numbers of Native Americans, Asians, and African Americans.
Idaho has five federally recognized Native American tribes. These include the Shoshone-Bannock, Shoshone-Paiute, Coeur d’Alene, Kootenai, and Nez Perce tribes.
Religion in Idaho

Religious self-identification, per Public Religion Research Institute's 2022 American Values Survey Protestantism (37%) Mormonism (24%) Catholicism (9%) Jehovah's Witness (2%) Unaffiliated (26%) New Age (3%)
According to a 2022 survey, about 72% of Idaho's population identifies as Christian. About 26% say they are not religious. And 3% follow New Age beliefs. Among Christians, 37% are Protestant, 24% are Mormon, and 9% are Catholic.
The largest religious groups in Idaho are The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) and the Catholic Church. Many people also identify as non-denominational Protestants.
Languages Spoken in Idaho
English is the main language spoken in Idaho. Other languages spoken by smaller groups include Spanish and various Native American languages.
Idaho's Economy: How People Make a Living
In 2023, Idaho's total economic output was $118.8 billion. The average income per person was about $59,035.
In 2016, there were over 562,000 jobs in Idaho. There were also over 45,000 businesses.
Important industries in Idaho include food processing, wood products, machinery, and electronics manufacturing. Mining for silver and other minerals is also important. Tourism is a big part of the economy too. The world's largest factory for barrel cheese is in Gooding, Idaho. This cheese is used to make processed cheese.
Hewlett-Packard has a large factory in Boise. It has been there since the 1970s. This factory mainly produces LaserJet printers.
Idaho has a state gambling lottery. From 1990 to 2006, this lottery gave $333.5 million to Idaho's public schools and higher education.
Taxes in Idaho
The Idaho State Tax Commission collects taxes in Idaho. The state personal income tax is a flat 5.8%. Idaho residents can get tax credits for taxes paid to other states. They can also get credits for donations to Idaho schools and some non-profit youth facilities.
The state sales tax is 6%. Some local areas might add a small extra sales tax, up to 6.5%. Sales tax applies to buying, renting, or leasing goods and some services. Food is taxed, but prescription drugs are not. Hotel and motel stays are taxed at a higher rate (7% to 11%). The sales tax was first introduced at 3% in 1965.
Energy in Idaho
Idaho has a regulated electricity market. The Idaho Public Utilities Commission oversees three main power companies.
Idaho uses almost four times more energy than it produces. In 2022, 75% of the electricity generated in Idaho came from renewable sources. This is the fourth-highest share of renewable electricity for any state. Half of Idaho's large-scale electricity comes from hydroelectric power plants. About 25% comes from natural gas. Wind facilities provide 17% of the state's electricity. Solar power provides 4%, and geothermal provides 1%. Most of the natural gas used in Idaho comes from Washington State.
Idaho has a lot of potential for renewable energy. It could generate a lot of power from wind and solar. As of 2020, Idaho had 973 megawatts of installed wind power.
Transportation in Idaho
The Idaho Transportation Department manages Idaho's transportation system. This includes roads, airports, and planning for future needs. They also handle federal and state money for transportation projects.
Highways in Idaho
Here are some of the major highways in Idaho:
- North/South Highways
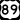 US 89
US 89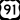 US 91
US 91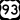 US 93
US 93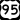 US 95
US 95
- West/East Highways
 US 2
US 2 US 12
US 12 US 20
US 20 US 26
US 26 US 30
US 30
- Interstates
Airports in Idaho
The main airports include the Boise Airport, which serves southwest Idaho. The Spokane International Airport in Washington serves northern Idaho. Other airports with regular flights are the Pullman-Moscow Regional Airport, Lewiston-Nez Perce County Airport, Magic Valley Regional Airport in Twin Falls, Friedman Memorial Airport in Hailey, Idaho Falls Regional Airport, and Pocatello Regional Airport.
Railroads in Idaho
Idaho has three major railroads that cross the country. The Burlington Northern Santa Fe (BNSF) connects the Idaho Panhandle to cities like Seattle and Portland in the west, and Minneapolis and Chicago in the east. The Union Pacific Railroad also crosses northern Idaho. It comes from Canada and goes to Spokane. The Canadian Pacific Railway uses Union Pacific tracks in North Idaho.
Amtrak's Empire Builder train crosses northern Idaho. Its only stop in the state is in Sandpoint. The Union Pacific Railroad also crosses southern Idaho. It connects Portland, Oregon, Green River, Wyoming, and Ogden, Utah. It serves cities like Boise, Nampa, Twin Falls, and Pocatello.
Ports in Idaho
The Port of Lewiston is the farthest inland Pacific port on the west coast. A series of dams and locks on the Snake and Columbia Rivers allow barges to travel from Lewiston to Portland. From Portland, goods can be loaded onto ocean-going ships.
Education in Idaho
K–12 Schools
As of January 2020, Idaho has 105 school districts and 62 charter schools. School districts can be very small, with only two students, or very large, with over 39,000 students.
Idaho school districts are managed by elected school boards. These boards are chosen in November of odd-numbered years. The only exception is the Boise School District, which holds its elections in September.
Colleges and Universities in Idaho

The Idaho State Board of Education oversees three main universities. The University of Idaho in Moscow was the first university in the state. It was founded in 1889 and opened in 1892. It is the state's main research university. Idaho State University in Pocatello opened in 1901. It became a four-year university in 1947. Boise State University is the newest to become a university in Idaho. It started as a junior college in 1932 and became Boise State University in 1974. Lewis-Clark State College in Lewiston is the only public four-year college in Idaho that is not a university. It opened in 1893.
Idaho also has four regional community colleges:
- North Idaho College in Coeur d'Alene
- College of Southern Idaho in Twin Falls
- College of Western Idaho in Nampa, which opened in 2009
- College of Eastern Idaho in Idaho Falls, which changed from a technical college in 2017
Private colleges in Idaho include:
- Boise Bible College
- Brigham Young University-Idaho in Rexburg
- College of Idaho in Caldwell
- Northwest Nazarene University in Nampa
- New Saint Andrews College in Moscow
- McCall College in McCall (a two-year private college)
Sports and Recreation in Idaho
Central Idaho is home to one of North America's oldest ski resorts, Sun Valley. The world's first chairlift was installed there in 1936. Other popular outdoor spots include Hells Canyon, the Salmon River, and Riggins.
| Club | Sport | League |
|---|---|---|
| Boise Hawks | Baseball | Pioneer League |
| Boise State Broncos | NCAA | Div I FBS, MWC |
| Idaho Vandals | NCAA | Div I FCS, Big Sky |
| Idaho State Bengals | NCAA | Div I FCS, Big Sky |
| Idaho Falls Chukars | Baseball | Pioneer League |
| Idaho Steelheads | Ice hockey | ECHL |
| Idaho Falls Spud Kings | Ice hockey | USPHL |
The Boise Open is a professional golf tournament. It has been played at Hillcrest Country Club since 1990. High school sports in Idaho are managed by the Idaho High School Activities Association (IHSAA).
In 2016, Michael Slagowski from Meridian ran 800 meters in 1 minute, 48.70 seconds. This is one of the fastest 800-meter times ever run by a high school boy in the United States.
Idaho in Movies and Pop Culture
Idaho has been featured in several movies. The 1980 film Bronco Billy was filmed in Boise, Idaho for two months. The 1985 movie Pale Rider was mostly filmed in the Boulder Mountains and the Sawtooth National Recreation Area. This area is in central Idaho, north of Sun Valley.
River Phoenix and Keanu Reeves starred in the 1991 movie My Own Private Idaho. Parts of this film take place in Idaho. The popular 2004 film Napoleon Dynamite is set in Preston, Idaho. The movie's director, Jared Hess, went to Preston High School.
Images for kids
-
Köppen climate types of Idaho, using 1991–2020 climate normals
See also
 In Spanish: Idaho para niños
In Spanish: Idaho para niños