Cobalt facts for kids
Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. It's a hard, shiny, silver-gray metal. You can find cobalt in the Earth's crust, usually mixed with other chemicals. It's only found as a pure metal in tiny amounts, often in meteoric iron from space!
People have used cobalt for a very long time. Blue colors made from cobalt, like cobalt blue, were used in ancient times for jewelry and paints. They also gave a special blue tint to glass.
Most of the cobalt we use today comes from copper and nickel mining. The "copper belt" in places like the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia produces most of the world's cobalt.
Cobalt is super useful! It's mainly used to make strong, wear-resistant, and magnetic alloys. Cobalt compounds also give a deep blue color to things like glass, ceramics, inks, and paints.
Did you know cobalt is also important for living things? It's a key part of vitamin B12, which is a vitamin all animals need to stay healthy. It's also a tiny but important nutrient for bacteria, algae, and fungi.
Contents
History of Cobalt
People have used cobalt compounds for hundreds of years to make beautiful blue colors. These colors appeared in glass, glazes, and ceramics. We've found cobalt in old Egyptian sculptures and Persian jewelry from thousands of years ago. It was also found in the ruins of Pompeii and in ancient Chinese art from the Tang Dynasty and Ming dynasty.
Cobalt has been used to color glass since the Bronze Age. An ancient shipwreck from the 14th century BC, called the Uluburun shipwreck, had a block of blue glass colored with cobalt. The oldest cobalt-colored glass comes from the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (around 1550–1292 BC).
The word cobalt comes from an old German word, kobalt. This word meant "goblin" or "evil spirit." Miners used this term for cobalt ore because it was tricky to work with. When they tried to melt these ores to get copper or nickel, they often failed. Instead, they got a powder (cobalt(II) oxide). Also, cobalt ores often contain arsenic. When melted, the arsenic turned into a very poisonous gas, making the ore seem even more "goblin-like."
A Swedish chemist named Georg Brandt discovered cobalt around 1735. He showed that it was a brand new element, different from other known metals. Cobalt was the first metal discovered since ancient times! Before Brandt, all known metals like iron, copper, silver, and gold had no recorded discoverers.
Where is Cobalt Found?
Cobalt is too reactive to be found as a pure metal in nature. Instead, it's always mixed with other elements in different minerals. You'll often find it alongside copper and nickel deposits. These three metals are usually bonded with arsenic and sulfur.
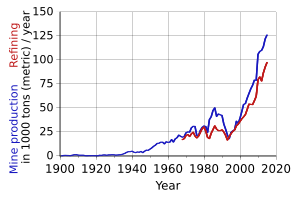
Most of the cobalt we use is a "by-product." This means it's a leftover substance when copper and nickel are mined and processed. It's made by reacting with the sludge that comes from copper and nickel production.
How is Cobalt Made?
The main minerals that contain cobalt are cobaltite, erythrite, glaucodot, and skutterudite. However, most cobalt is actually obtained by processing the leftover materials from nickel and copper mining and melting.
What is Cobalt Used For?
The main use for cobalt is in making high-performance alloys.
Strong Alloys
Most of the cobalt produced goes into making special alloys called "superalloys." These alloys can handle very high temperatures. This makes them perfect for parts in turbines, like the blades in gas turbines and jet aircraft engines. Cobalt alloys also resist corrosion (rusting) and wear. This makes them useful for medical implants, like hip and knee replacements, because they don't wear out easily. They are also used in dental parts.
Batteries
A compound called Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) is widely used in the parts of lithium-ion batteries that store energy. These are the batteries found in many of our phones and laptops!
Catalysts
Cobalt compounds, often called "cobalt soaps," are used as catalysts. Catalysts help chemical reactions happen faster. They are also used in paints, varnishes, and inks to help them dry. The same compounds help rubber stick to steel in things like steel-belted car tires.
Colors and Pigments
Before the 1800s, cobalt was mostly used as a pigment, which is a material that gives color. Since the Middle Ages, it has been used to make "smalt," which is a blue-colored glass.
Radioactive Cobalt
Some types of cobalt are radioactive, meaning they give off radiation. These are called radioisotopes. They are used in external beam radiotherapy to treat certain illnesses. They also sterilize medical supplies and waste. Radioactive cobalt can even be used to treat foods to make them safer (like a "cold pasteurization"). It's also used in industrial radiography to check materials. However, radioactive cobalt can create a fine dust, which makes radiation protection important. If not handled correctly, cobalt from these machines can be dangerous.
Other Uses
Cobalt is used in electroplating because it looks nice, is hard, and resists oxidation (like rusting). It's also used as a base layer for porcelain enamels.
Why is Cobalt Important for Living Things?
Cobalt is essential for all animals to live and grow. It's a key part of a very important vitamin called cobalamin, or vitamin B12. Because of this, having enough cobalt in the soil helps the health of grazing animals like cows and sheep. Animals need to get a small amount of cobalt every day because they can't make vitamin B12 themselves.
Is Cobalt Safe?
Your body needs tiny amounts of cobalt for certain vitamins to work. Cobalt compounds can even be used to help stop cyanide poisoning. However, in large amounts, cobalt can be toxic. In the past, cobalt compounds were sometimes added to beer, and people who drank it got sick. Touching cobalt can also cause skin irritation for some people.
What are Cobalt's Properties?
Cobalt is a transition metal. It's shiny and can conduct electricity. It is also magnetic. Cobalt is a hard metal and is moderately reactive. It dissolves slowly in acids. Most cobalt compounds that dissolve in water are red. However, they can also be green, blue, brown, or black.
- Cobalt(II) compounds
- Cobalt(II) chloride: A red solid, and the most common cobalt compound.
- Cobalt(II) fluoride: A red solid used in dentistry.
- Cobalt(II) hydroxide: Can be a red or green-blue solid.
- Cobalt(II) oxide: A black solid.
- Cobalt(II) sulfate: A reddish solid used in pigments.
- Mixed oxidation state
- Cobalt(II,III) oxide: A black solid that can help other chemicals react.
- Cobalt(III) compounds
- Cobalt(III) fluoride: A brown solid that is a strong chemical agent.
- Cobalt(III) oxide: A black solid.
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cobalto para niños
In Spanish: Cobalto para niños
 | Aurelia Browder |
 | Nannie Helen Burroughs |
 | Michelle Alexander |