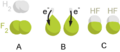Oxidation facts for kids
Oxidation is a type of chemical reaction where a substance loses electrons. It's a very common process that happens all the time, from when you breathe to when metal rusts.
When something is oxidized, it means it has given away some of its electrons. The substance that gains these electrons is said to be "reduced." Oxidation and reduction always happen together. This pair of reactions is called a redox reaction (short for reduction-oxidation).
Contents
What is Oxidation?
Oxidation is a chemical process where atoms, molecules, or ions lose electrons. Think of electrons as tiny particles that orbit the center of an atom. When an atom loses one or more of these electrons, it becomes oxidized.
For example, when iron (like in a nail or a bike) is exposed to oxygen and water, it rusts. In this process, the iron atoms lose electrons to the oxygen atoms. The iron is oxidized, and the oxygen is reduced. The rust you see is a new chemical compound formed from this reaction.
Oxidation and Reduction Go Together
You can't have oxidation without reduction, and you can't have reduction without oxidation. They are like two sides of the same coin.
- When one substance loses electrons (oxidation), another substance must gain those electrons (reduction).
- The substance that causes another to be oxidized is called an oxidizing agent.
- The substance that causes another to be reduced is called a reducing agent.
Oxidation with Oxygen and Hydrogen
Originally, oxidation was just about reactions involving oxygen.
- When a substance gains oxygen, it is oxidized. For example, when wood burns, it combines with oxygen and is oxidized.
- When a substance loses oxygen, it is reduced.
Later, scientists realized that oxidation also involves the loss of hydrogen atoms. So, oxidation can be:
- The gain of oxygen atoms.
- The loss of hydrogen atoms.
- The loss of electrons.
All these definitions describe the same basic chemical process.
Examples of Oxidation in Everyday Life
Oxidation reactions are happening all around us and inside us!
Rusting
One of the most common examples is rust. Rust forms when iron or steel (which is mostly iron) reacts with oxygen in the air, especially when water is present. This is why cars, bikes, and metal fences can get rusty over time.
Food Browning
Have you ever seen a sliced apple turn brown? This is another example of oxidation! When you cut an apple, the inside of the apple is exposed to oxygen in the air. Enzymes in the apple react with the oxygen, causing the browning. This is called enzymatic browning. Bananas, avocados, and potatoes can also turn brown due to oxidation.
Breathing
Even breathing is a type of oxidation! When you breathe in oxygen, your body uses it to "burn" the food you eat (like sugars and fats) to create energy. This process is called cellular respiration, and it's a complex series of redox reactions. Your body oxidizes the food molecules to get the energy it needs to live.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
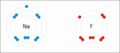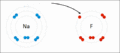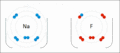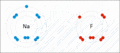
Sodium and fluorine bonding ionically to form sodium fluoride. Sodium loses its outer electron to give it a stable electron configuration, and this electron enters the fluorine atom exothermically. The oppositely charged ions are then attracted to each other. The sodium is oxidized; and the fluorine is reduced.
-
Oxides, such as iron(III) oxide or rust, which consists of hydrated iron(III) oxides Fe2O3·nH2O and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3), form when oxygen combines with other elements
-
Iron rusting in pyrite cubes
See also
 In Spanish: Reducción-oxidación para niños
In Spanish: Reducción-oxidación para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |