Chemical reaction facts for kids
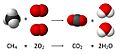
A chemical reaction is a process where one or more substances change into new and different substances. It's like mixing ingredients to bake a cake – you start with flour, sugar, and eggs, and you end up with something completely new!
Here are some everyday examples of chemical reactions:
- When iron and oxygen mix, they create rust.
- Mixing vinegar and baking soda makes carbon dioxide gas, which causes fizzing.
- Things burning, like wood in a campfire, are chemical reactions.
- Many reactions happen inside your body to help you live and grow.
- When you use or charge batteries, chemical reactions are taking place.
Some chemical reactions happen very quickly, like an explosion. Others are very slow, like iron rusting over time. How fast a reaction happens can depend on things like temperature. For example, wood won't burn in cold air, but if you heat it up enough, it will catch fire.
Chemical reactions can also involve energy.
- Some reactions release energy, often as heat or light. These are called exothermic reactions. A burning fire is an exothermic reaction.
- Other reactions take in energy from their surroundings. These are called endothermic reactions.
It's important to know that Nuclear reactions are not chemical reactions. Chemical reactions only involve the outer parts of atoms called electrons. Nuclear reactions, however, involve the center of atoms, called the nucleus, where protons and neutrons are found.
Contents
Four Main Types of Chemical Reactions
Scientists group chemical reactions into different types based on how the atoms rearrange. Here are four basic kinds:
Synthesis Reactions
A synthesis reaction is when two or more simple substances combine to form one more complex substance. Think of it as building something bigger from smaller pieces.
You can spot a synthesis reaction because it starts with two or more ingredients and ends with just one new product. For example, when iron and sulfur combine, they form iron(II) sulfide. Another simple example is when hydrogen gas and oxygen gas combine to make water.
Decomposition Reactions
A decomposition reaction is the opposite of a synthesis reaction. In this type, a complex substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances. It's like taking a toy apart into its individual pieces.
For instance, if you use electrolysis to pass electricity through water, the water will break down into oxygen gas and hydrogen gas.
Single Replacement Reactions
In a single replacement reaction, one element takes the place of another element in a compound. It's like one person swapping places with another in a pair.
An example is when magnesium metal reacts with water. The magnesium replaces the hydrogen in the water, creating magnesium hydroxide and releasing hydrogen gas.
Double Replacement Reactions
A double replacement reaction is when the parts of two different compounds switch places to form two completely new compounds. Imagine two dancing couples, and then the partners switch to form two new couples.
For example, when barium chloride and magnesium sulfate react, the parts of each compound swap. This creates barium sulfate and magnesium chloride. Another example is when lead(II) nitrate reacts with potassium iodide to form lead(II) iodide and potassium nitrate.
Related Topics
Images for kids
-
A thermite reaction using iron(III) oxide. This reaction creates very hot, molten iron.
-
Antoine Lavoisier was a scientist who helped explain how burning is a chemical reaction with oxygen.
-
Sodium chloride is formed when sodium metal and chlorine gas react.
-
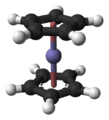
Ferrocene – an iron atom sandwiched between two C5H5 ligands.
-
Solid catalysts are often placed on meshes inside catalytic converters to increase their surface area. This helps reactions happen faster.
See also
 In Spanish: Reacción química para niños
In Spanish: Reacción química para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |