Redox facts for kids
Redox is a short way of saying reduction-oxidation. It describes a special type of chemical reaction. In these reactions, atoms either gain or lose electrons.
Think of electrons as tiny particles that orbit the center of an atom. When atoms react, they can swap or share these electrons. Redox reactions are all about this electron transfer.
The word redox comes from two main ideas:
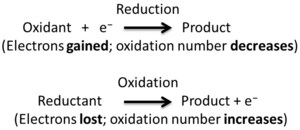
- Oxidation means an atom, molecule, or ion loses electrons.
- Reduction means an atom, molecule, or ion gains electrons.
A simple way to remember this is the saying "OIL RIG":
- Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons)
- Reduction Is Gain (of electrons)
These two processes always happen together. If one atom loses electrons (oxidizes), another atom must gain them (reduces).
How Redox Reactions Work
Redox reactions are very common in everyday life and in nature. For example, when iron rusts, it's a redox reaction. The iron atoms lose electrons (oxidize) to oxygen atoms, which gain electrons (reduce).
Another example is when you burn wood in a bonfire. This is called combustion. The carbon in the wood reacts with oxygen in the air. The carbon atoms lose electrons, and the oxygen atoms gain them.
In these reactions, one substance helps the other to oxidize or reduce:
- The substance that causes another to oxidize (by gaining electrons itself) is called the oxidizing agent. It gets reduced.
- The substance that causes another to reduce (by losing electrons itself) is called the reducing agent. It gets oxidized.
Everyday Examples of Redox
You can see redox reactions happening all around you:
- Rusting: As mentioned, iron turning into rust is a classic redox reaction.
- Batteries: The chemical reactions inside batteries that produce electricity are redox reactions.
- Breathing: When your body uses oxygen to get energy from food, it's a complex series of redox reactions.
- Food Browning: When a cut apple turns brown, it's due to enzymes causing oxidation reactions.
These reactions are very important for life and for many industrial processes.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
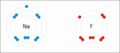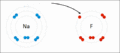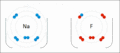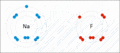
Sodium and fluorine bonding to form sodium fluoride. Sodium loses an electron (oxidized), and fluorine gains it (reduced).
-
Oxides, like rust, form when oxygen combines with other elements.
-
Iron rusting inside pyrite cubes.
See also
 In Spanish: Reducción-oxidación para niños
In Spanish: Reducción-oxidación para niños
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |