Tang Dynasty facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Tang
唐
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
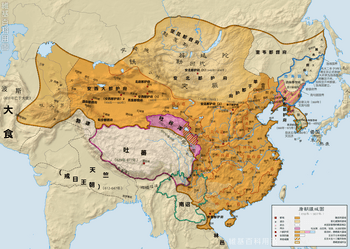
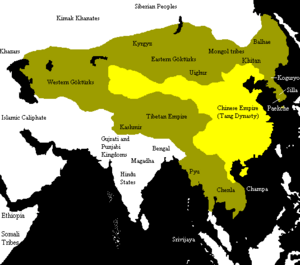
Tang dynasty c. 669
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Middle Chinese | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 618–626 (first)
|
Emperor Gaozu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 626–649
|
Emperor Taizong | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 712–756
|
Emperor Xuanzong | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
June 18, 618 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Usurped
by Wu Zetian |
690–705a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 755–763b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Abdication in favour of the Later Liang
|
June 1, 907 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 715 | 5,400,000 km2 (2,100,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 7th century
|
50 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• 9th century
|
80 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a October 8, 690 – March 3, 705.
b December 16, 755 – February 17, 763. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tang Dynasty | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
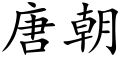
"Tang dynasty" in Han characters
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 唐朝 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Tang Dynasty (Chinese: 唐朝; Pinyin: Táng Cháo) was a very important time in Chinese history. It lasted from June 18, 618, to June 4, 907. This dynasty came after the Sui dynasty and was followed by a period called the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
The Tang Dynasty was started by the Li (李) family. They rose to power when the Sui Empire was falling apart. For a short time, the Tang Dynasty was paused by the Zhou Dynasty. This happened from October 16, 690, to March 3, 705. The Zhou Dynasty was founded by Empress Wu Zetian, who became the first and only female emperor of China.
Historians often see the Tang Dynasty as a high point in Chinese civilization. Some even think it was greater than the earlier Han Dynasty. It was a "golden age" for culture, known for being very open and welcoming to people from all over the world.
Contents
The Tang Dynasty: A Golden Age
The Tang Dynasty is famous for its strong government and amazing culture. It was a time when China was very powerful and respected by other countries. Many new ideas and inventions came from this period.
The Amazing Capital City: Chang'an
The capital city of the Tang Dynasty was Chang'an. Today, this city is known as Xi'an. During the Tang era, Chang'an was the largest city in the entire world. It was a bustling center of trade, culture, and learning. People from many different countries lived and worked there. This made Chang'an a truly global city.
Empress Wu Zetian: China's Only Female Ruler
One of the most interesting figures of the Tang Dynasty was Empress Wu Zetian. She was the only woman in China's long history to rule as an emperor. She was very smart and talented. Empress Wu took control of the empire from 690 to 705. She was a strong leader who made many changes. Her rule showed that a woman could lead a powerful empire.
A Time of Great Culture and Art
The Tang Dynasty was a golden age for Chinese culture. Poetry, art, and music all flourished. Many famous poets lived during this time, like Li Bai and Du Fu. Their poems are still loved today.
Buddhism became very popular during the Tang Dynasty. Many temples and statues were built. New technologies also appeared, like woodblock printing. This made it easier to share books and ideas. The Tang Dynasty was also known for its beautiful pottery, especially the colorful sancai glazed ceramics.
How the Tang Dynasty Ended
The Tang Dynasty began to weaken over time. There were many rebellions and conflicts. One major event was the An Lushan Rebellion, which lasted from 755 to 763. This rebellion caused a lot of damage and made the empire less stable.
Finally, in 907, the Tang Dynasty came to an end. A military leader named Zhu Wen took control. He removed Emperor Ai of Tang from the throne. Zhu Wen then started his own dynasty, called the Later Liang. This marked the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, a time when China was divided into many smaller states. Emperor Ai later died.
Images for kids
-
Portrait painting of Emperor Yang of Sui, commissioned in 643 by Taizong, painted by Yan Liben (600–673)
-
The Fengxian cave (circa 675 AD) of the Longmen Grottoes, commissioned by Wu Zetian.
-
Xumi Pagoda, built in 636
-
A late Tang mural commemorating the victory of General Zhang Yichao over the Tibetans in 848 AD, from Mogao cave 156
-
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang wearing the robes and hat of a scholar
-
Civil service exam candidates gather around the wall where results had been posted. Artwork by Qiu Ying.
-
Emperor Taizong (r. 626–649) receives Gar Tongtsen Yülsung, ambassador of the Tibetan Empire, at his court; later copy of an original painted in 641 by Yan Liben (600–673)
-
Pottery tomb figure of a warrior from Duan's Tomb, Shaanxi.
-
A 10th-century mural painting in the Mogao Caves at Dunhuang showing monastic architecture from Mount Wutai, Tang dynasty; Japanese architecture of this period was influenced by Tang Chinese architecture
-
Illustration of Byzantine embassy to Tang Taizong 643 CE
-
A mural depicting a corner tower, most likely one of Chang'an, from the tomb of Prince Yide (d. 701) at the Qianling Mausoleum, dated 706
-
A Tang dynasty era copy of the preface to the Lantingji Xu poems composed at the Orchid Pavilion Gathering, originally attributed to Wang Xizhi (303–361 AD) of the Jin dynasty
-
Calligraphy of Emperor Taizong on a Tang stele
-
A Tang dynasty sculpture of a Bodhisattva
-
A Tang sancai-glazed carved relief showing horseback riders playing polo
-
Palace ladies in a garden from a mural of Prince Li Xian's tomb in the Qianling Mausoleum, where Wu Zetian was also buried in 706
-
A page of Lu Yu's The Classic of Tea
-
The Diamond Sutra, printed in 868, is the world's first widely printed book to include a specific date of printing.
-
The Dunhuang map, a star map showing the North Polar region. c. 700. The whole set of star maps contains over 1,300 stars.
-
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang giving audience to Zhang Guo, by Ren Renfa (1254–1327)
See also
 In Spanish: Dinastía Tang para niños
In Spanish: Dinastía Tang para niños