Later Liang (Five Dynasties) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Liang
梁
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 907–923 | |||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||
| Capital | Luoyang (907–913) Kaifeng (913–923) |
||||||||||||
| Common languages | Middle Chinese | ||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||||
|
• 907–912
|
Emperor Taizu | ||||||||||||
|
• 912–913
|
Zhu Yougui | ||||||||||||
|
• 913–923
|
Emperor Modi | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties | ||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1 June 907 | ||||||||||||
|
• Surrender of Kaifeng
|
19 November 923 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||||||
The Later Liang (simplified Chinese: 后梁; traditional Chinese: 後梁; pinyin: Hòu Liáng) was an important Chinese dynasty. It existed from June 1, 907, to November 19, 923. This dynasty was the first of the Five Dynasties in a time of big changes in China.
It was started by a powerful leader named Zhu Wen, also known as Emperor Taizu. He took control after the Tang dynasty ended. The Later Liang dynasty ruled for 16 years until it was defeated by the Later Tang dynasty.
Contents
How the Later Liang Dynasty Began
The Later Liang dynasty started with a man named Zhu Wen. He was once a soldier for another leader, Huang Chao. But Zhu Wen was very ambitious. He took some of Huang Chao's best soldiers. Then, he built his own power base in a city called Kaifeng.
By the year 904, Zhu Wen had become very strong. He controlled the two main capital cities of the Tang dynasty: Chang'an and Luoyang. He made sure the Tang emperors lost their power. The Tang emperor Zhaozong died in 904. Three years later, the last Tang emperor, Ai Di, was forced to step down. Emperor Ai of Tang also died in 908, after Zhu Wen had taken control.
In 907, Zhu Wen declared himself the new emperor. He named his dynasty the Later Liang. This name came from the Henan region, which was the heart of his new empire.
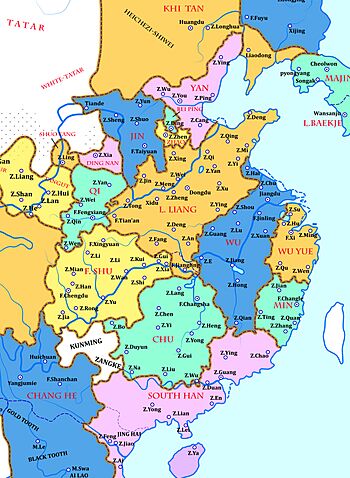
Where the Later Liang Ruled
The Later Liang dynasty controlled most of northern China. However, some areas were not under their full control. These included parts of Shaanxi, which was ruled by the Qi state. Also, Hebei was controlled by the Yan state. And Shanxi was ruled by the Shatuo Turks state called Jin.
The End of the Later Liang Dynasty
The Later Liang dynasty had a difficult relationship with the Shatuo Turks. This was because of a long-standing rivalry. It began between Zhu Wen and a leader named Li Keyong during the Tang dynasty.
After Li Keyong passed away, his son, Li Cunxu, took over. Li Cunxu continued to make his State of Jin stronger. He was a very skilled military leader. In 923, Li Cunxu's forces defeated the Later Liang dynasty. After this victory, Li Cunxu established his own dynasty, which he called the Later Tang.
Understanding the Mandate of Heaven
In Chinese history, the idea of the Mandate of Heaven was very important. It meant that a ruler had the blessing of the gods to govern. Historians often wrote about this to show why new dynasties were legitimate.
For example, a historian from the later Song dynasty, Xue Juzheng, wrote about the Five Dynasties. He said that the Later Liang and the other Five Dynasties had the Mandate of Heaven. This helped connect the Song dynasty to these earlier rulers. It made the Song dynasty seem more powerful and rightful.
One reason given was that these dynasties controlled the main parts of China. However, the Later Liang was known for being very harsh. Some people didn't want to say they had the Mandate of Heaven. But if they didn't, it would break the historical chain. This chain connected the Later Liang to the other Five Dynasties, and eventually to the Song dynasty itself.
Later Liang Rulers
| Temple names | Posthumous names | Family names and given name | Chinese naming conventions | Durations of reigns | Era names and their according durations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taìzǔ (太祖) | (Not commonly used) | Zhū Wēn (朱溫) | Family name and given name | 907–912 | Kaīpíng (開平) 907–911 Qiánhuà (乾化) 911–912 |
| Did not exist | none | Zhu Yougui (朱友珪) | Family name and given name | 912–913 | Qiánhuà (乾化) 912–913 Fènglì (鳳曆) 913 |
| Did not exist | Mò (末) | Zhū Zhèn (朱瑱) | Family name and given name | 913–923 | Qiánhuà (乾化) 913–915 Zhēnmíng (貞明) 915–921 Lóngdé (龍德) 921–923 |
Rulers' Family Tree
| Later Liang | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Huang Chao
- Jiedushi
- Tang dynasty
Images for kids
-
Two Emperors of the Qi and Liang Dynasties, from Jami al-Tawarikh (Compendium of Chronicles), by Rashid al-Din, Iran, 1306 CE
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |




