Potassium facts for kids

Potassium pearls (in paraffin oil, ~5 mm each)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /pəˈtæsiəm/ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery gray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(K) | 39.0983(1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Potassium in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 1: hydrogen and alkali metals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 4s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 8, 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 336.53 K (63.38 °C, 146.08 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 1032 K (759 °C, 1398 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 0.862 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 0.828 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 336.35 K, kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.33 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 76.9 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 29.6 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −1, +1 (a strongly basic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 0.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 227 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 203±12 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 275 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of potassium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
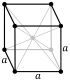
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 2000 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 83.3 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 102.5 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 72 n Ω⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 3.53 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 1.3 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 3.1 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 0.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 0.363 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-09-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Humphry Davy (1807) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Humphry Davy (1807) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symbol | "K": from New Latin kalium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of potassium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Potassium is a special chemical element you can find on the periodic table. Its symbol is K, which comes from the Latin word kalium. Potassium has an atomic number of 19. This means it has 19 protons and 19 electrons. You won't find pure potassium metal in nature because it reacts very easily with other things.
Potassium has different forms called isotopes. Two of its stable isotopes have 20 or 22 neutrons. Its atomic mass is about 39.098. There's also an unstable isotope with 21 neutrons. This one is a common radioactive material.
Contents
What is Potassium Like?
Physical Features
Potassium is a soft, silvery-gray metal. It's so soft you can easily cut it with a knife! It melts at a very low temperature, around 63 degrees Celsius (145.4 degrees Fahrenheit). This makes it one of the metals that melts easily. It belongs to a group of elements called alkali metals. After lithium, it's the second lightest metal.
How Potassium Reacts
Potassium reacts in many ways, similar to sodium and other alkali metals. When it touches air, it quickly gets a whitish layer on its surface. This is called oxidation or tarnishing. Because it reacts so fast with air and water, potassium is usually stored in oil.
If you put a large piece of potassium in water, it reacts very strongly. This reaction creates hydrogen gas, which can catch fire! It also forms a substance called potassium hydroxide. Potassium also burns easily in the air, forming other compounds like peroxides or superoxides.
Potassium Compounds
Potassium always forms compounds where it has a +1 oxidation state. This means it loses one electron when it forms a chemical bond. Potassium ions are clear and look a lot like sodium ions.
Many potassium compounds are safe to use. If a potassium compound is harmful, it's usually because of the other part of the compound, not the potassium itself. For example, potassium chromate is yellow and harmful because of the chromate part, not the potassium.
Here are some common potassium compounds:
- Potassium chloride: This can be used as a replacement for table salt.
- Potassium hydroxide: Also known as potash, it's a strong base and a white solid. It's used in alkaline cells.
- Potassium bromate: A colorless substance used in flour.
- Potassium bromide: A colorless compound once used as a sedative.
- Potassium carbonate: A colorless substance that reacts with acids.
- Potassium chlorate: Used in matches and explosives.
- Potassium dichromate: A red solid that is an oxidizing agent and toxic.
- Potassium fluoride: Used to make fluorine. It is corrosive.
- Potassium nitrate: A key ingredient in gunpowder.
- Potassium permanganate: A purple substance used as a disinfectant and an oxidizing agent.
- Potassium sulfate: A colorless compound often used in fertilizers.
Where Does the Name "Potassium" Come From?
The name "potassium" comes from the word "potash." Potash is a mix of potassium carbonate and potassium hydroxide. People have used potash for a very long time. In the past, it was made by burning ashes in pots. Today, potash is used to make fertilizer, soap, and glass.
Where is Potassium Found?
You won't find pure potassium metal in nature because it's too reactive. Instead, it's found in different minerals. We get potassium from these minerals using a process called electrolysis. This involves melting potassium hydroxide or potassium chloride at very high temperatures and then using electricity to separate the potassium.
How is Potassium Used?
Pure potassium metal is used in science to remove water from certain liquids called solvents. It's also used in some scientific tools.
Potassium compounds are used in many everyday items:
- They are found in soap.
- They are a key part of fertilizers, helping plants grow.
- Some potassium compounds are used in explosives and matches.
Potassium ions are super important for living things, including you! That's why fertilizers contain potassium compounds. These ions help send messages between cells in your body. They help biological membranes change their electric charge, which is needed for muscles to contract (get shorter and move things). This is also vital for your heart to beat and pump blood. If the amount of potassium in your blood is too high or too low, it can be very dangerous and even stop your heart. Foods like bananas, apricots, and raisins are good sources of potassium.
Is Potassium Safe?
Pure potassium metal is very dangerous. If it's left in the air, it can form a coating that might explode. It also reacts very strongly with water, creating a harmful liquid.
However, most potassium compounds are not dangerous on their own. They are only harmful if they contain a toxic anion, which is the other part of the compound, like chromate or chlorate.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The flame test of potassium.
-
Potassium in feldspar
-
Monte Kali, a potash mining and beneficiation waste heap in Hesse, Germany, consisting mostly of sodium chloride.
See also
 In Spanish: Potasio para niños
In Spanish: Potasio para niños