Blood facts for kids
Blood is a special liquid found in humans and most animals (but not insects!). Your heart pumps blood all around your body. Blood carries important things like nutrients and oxygen to your tissues and organs. It also helps remove waste products and carbon dioxide. Think of it like a tiny delivery truck system that brings all the good stuff your body needs to every single cell, and then takes away all the waste products. It's always on the move, making sure everything in your body works just right.
Contents
Quick Facts
- Main Job: Delivers oxygen and nutrients, removes waste.
- Color: Bright red when it has lots of oxygen, darker red when it doesn't.
- Main Parts: Plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The Amazing Jobs Blood Does
Blood is a real multi-tasker! It performs many vital functions to keep you healthy and strong:
- Oxygen Delivery: Your blood carries oxygen from the air you breathe in your lungs to every part of your body. Your brain, muscles, and all your organs need oxygen to work!
- Nutrient Supply: After you eat, your food is broken down into tiny nutrients like sugars and proteins. Blood picks these up and delivers them to your cells, giving you energy to play and learn.
- Waste Removal: Just like a garbage truck, blood collects waste products from your cells, such as carbon dioxide (which you breathe out) and other waste that your kidneys filter out.
- Fighting Germs: Blood has special cells that are like tiny superheroes! They find and fight off germs, viruses, and other invaders that can make you sick, helping your immune system keep you healthy.
- Stopping Bleeding: If you get a cut, blood has special little helpers called platelets that rush to the rescue. They work with other parts of your blood to form a clot, which is like a natural bandage, to stop the bleeding.
- Carrying Messages: Blood transports important chemical messengers called hormones. These hormones tell different parts of your body what to do, like helping you grow or telling you when you're hungry.
- Temperature Control: Blood helps keep your body at the right temperature. When you're hot, blood flows closer to your skin to release heat. When you're cold, it moves deeper inside to keep your important organs warm.
- Hydraulic Functions: In some animals, like the jumping spider, blood can be quickly pushed into their legs to help them make powerful jumps!
What is Blood Made Of?
Your blood might look like just one red liquid, but it's actually made up of several different parts, each with its own special job! Let's break down what's inside:
Plasma (The Liquid Part)
About 55% of your blood is a yellowish liquid called plasma. Think of it as the river that carries everything else. Plasma is about 92% water! This is why staying hydrated by drinking water is so important for your blood. It also contains important proteins, sugars (glucose), mineral salts, hormones, and all those nutrients and waste products we talked about.
Blood Cells (The Solid Parts)
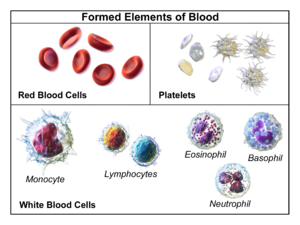
Suspended in the plasma are three main types of "formed elements" or blood cells:
- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
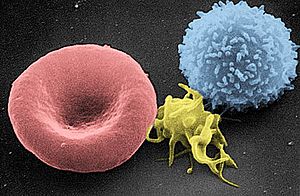
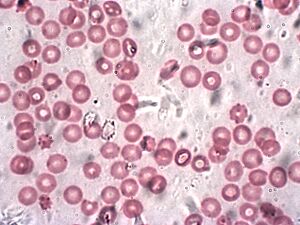
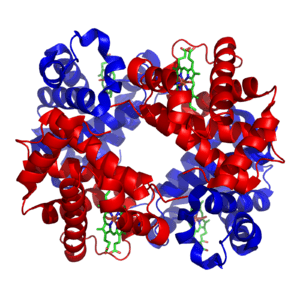
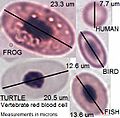
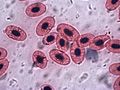
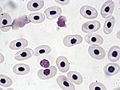
These are the most abundant cells in your blood, and their main job is to carry oxygen. They contain a special protein called hemoglobin, which is what makes your blood red! Hemoglobin grabs onto oxygen in your lungs and releases it where your body needs it. In just one tiny drop of blood (a microliter), there are millions of red blood cells! Red blood cells also have special markers on their surface that determine your blood type (like A, B, AB, or O).
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes):
These are your body's defenders! White blood cells are part of your immune system and work to find and destroy germs, viruses, and other things that don't belong in your body. They also help clean up old or damaged cells. There are far fewer white blood cells than red blood cells, but they are mighty! There are different kinds of white blood cells, each with a specific way of fighting off invaders.
- Platelets (Thrombocytes):
These are tiny cell fragments that are super important for stopping bleeding. When you get a cut, platelets rush to the site and stick together to form a plug, helping your blood clot. A tiny drop of blood contains hundreds of thousands of platelets!
Acidity (pH Balance)
Your blood needs to stay at a very specific level of acidity, which we measure with something called pH. It's usually slightly basic, between 7.35 and 7.45. Your body has amazing ways to keep this balance just right, mainly through your breathing and your kidneys.
How Blood Works in Your Body
Let's take a journey through your circulatory system to see how blood moves and does its work!
The Circulatory System
Your heart is like a powerful pump that keeps your blood moving through a network of tubes called blood vessels.
- Arteries: These vessels carry bright red, oxygen-rich blood away from your heart to all your body's tissues.
- Veins: These vessels carry darker red, oxygen-poor blood back to your heart.
- Lungs: From your heart, blood goes to your lungs to pick up fresh oxygen and drop off carbon dioxide. Then it returns to your heart to be pumped out to the rest of your body again. It's a continuous loop!
Making and Breaking Down Blood Cells
Your body is constantly making new blood cells!
Most blood cells are made in your bone marrow, which is the spongy material inside your bones. This process is called hematopoiesis.
Red blood cells live for about 120 days. After that, they get old and are broken down by organs like your spleen and liver, which also help clean your blood. Your liver also makes many of the proteins in your blood, and your kidneys help filter out waste products to make urine.
Oxygen Transport
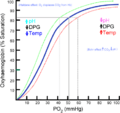
As we learned, hemoglobin in your red blood cells is the star of oxygen transport. It's so good at its job that it increases the amount of oxygen your blood can carry by about 70 times! When blood leaves your lungs, almost all of its hemoglobin is full of oxygen, ready to deliver it where it's needed. Even after delivering oxygen, your blood still has some oxygen left when it returns to your lungs, ready for another refill.
Carbon Dioxide Transport
Blood also has clever ways to carry carbon dioxide, the waste gas from your cells, back to your lungs to be exhaled. Most of it is changed into a different form called bicarbonate ions, some dissolves in the plasma, and some attaches to hemoglobin.
Controlling Body Temperature
Blood plays a big role in keeping your body at a comfortable temperature.
When you get hot, like after running around, your blood vessels near your skin get wider. This allows more blood to flow to the surface, releasing heat and helping you cool down.
When you're cold, these vessels get narrower, keeping blood closer to your core organs to conserve heat.
Color
You might think blood is just red, but its exact shade can tell us a lot!
- Bright Red: This is the color of arterial blood, which is full of oxygen. The oxygen makes the hemoglobin a vibrant red.
- Dark Red: This is the color of venous blood, which has delivered its oxygen and is on its way back to the lungs. It's still red, just a darker shade.
- Other Colors: In very rare cases, certain conditions can change blood color. For example, carbon monoxide poisoning makes blood bright red, which can be very dangerous because the hemoglobin is holding onto carbon monoxide instead of oxygen.
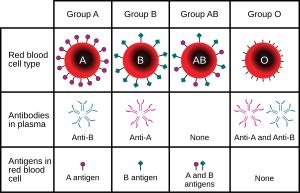
Blood types
Sometimes, people need extra blood because of an accident, surgery, or an illness. This is called a blood transfusion. It's like getting a refill for your body's vital fluid! But it's not as simple as just giving anyone's blood to anyone else. The blood types must match!
Imagine your blood is like a secret club, and each club member (your red blood cells) has a special badge. These badges are called antigens. Your body also has "security guards" called antibodies that float in your blood plasma. These antibodies are always on the lookout for badges that don't belong. If they see a badge they don't recognize, they'll try to clump it up, which can cause big problems!
Before a transfusion, doctors always do careful tests to make sure the donor's blood is a perfect match for the recipient's blood. This is called cross-matching. If the blood isn't compatible, it can cause very serious problems for the patient.
The ABO Blood Group System: A, B, AB, and O
In 1901, an Austrian doctor named Karl Landsteiner classified human blood into three groups: A, B, and C (which was later renamed O). A year later, his students discovered the fourth group, AB. For this incredible work, Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930.
It took a while for everyone to agree on the names for blood types. There were different systems used in different countries, which caused a lot of confusion! But eventually, in 1928, Landsteiner's system of O, A, B, and AB became the standard that we use all around the world today.
The ABO system is all about two main antigens: Antigen A and Antigen B. Depending on which of these antigens you have on your red blood cells, you'll have one of four main blood types:
- Type A: If your red blood cells have only Antigen A badges. Your plasma will have "security guards" (antibodies) against Antigen B.
- Type B: If your red blood cells have only Antigen B badges. Your plasma will have "security guards" against Antigen A.
- Type AB: If your red blood cells have both Antigen A and Antigen B badges. Your plasma won't have any "security guards" against A or B, because both are recognized as friendly!
- Type O: If your red blood cells have neither Antigen A nor Antigen B badges. Your plasma will have "security guards" against both A and B.
This system is super important for blood transfusions because if you get blood with antigens your body doesn't recognize, your antibodies will attack it, causing a serious reaction.
The Rh Blood Group System: Positive (+) or Negative (-)
The second big system is the Rh system, and it's mostly about one special antigen called the D antigen.
If you have the D antigen on your red blood cells, you are Rh positive (+). If you don't have the D antigen, you are Rh negative (-). So, when you hear someone say their blood type is "A positive," it means they have Antigen A and the D antigen. If they say "O negative," it means they have neither Antigen A, Antigen B, nor the D antigen.
Rh negative blood types are more common in people from European backgrounds (about 15%) and less common in Asian populations (about 0.3%).
People with O negative blood are often called "universal donors" for red blood cells. This is because their red blood cells have no A, B, or D antigens, so they're like "blank" badges that most other blood types won't attack. However, O negative blood is very precious and often in short supply, so doctors try to save it for emergencies or for O negative patients.
People with AB positive blood are often called "universal recipients" for red blood cells. This is because their red blood cells have A, B, and D antigens, and their plasma doesn't have antibodies against any of them. So, they can usually receive blood from any ABO and Rh type.
How Do We Find Out Our Blood Type?
Finding out your blood type is usually a quick and simple test! A doctor or nurse takes a small sample of your blood. Then, in a lab, they mix tiny drops of your blood with special liquids that contain different antibodies. If your blood clumps up when mixed with a certain antibody, it tells them which antigens you have. For example, if your blood clumps with anti-A antibodies, it means you have A antigens!
When Blood Needs Help
Sometimes, blood can have problems, which are called disorders. Doctors who specialize in blood are called hematologists.
- Blood Loss: If you get a big cut or injury, you can lose a lot of blood. Your body can handle losing a little bit, but too much can be serious. That's why platelets and clotting are so important!
- Anemia: This happens when you don't have enough healthy red blood cells or enough hemoglobin. It can make you feel tired and weak because your body isn't getting enough oxygen. Anemia can be caused by not getting enough iron, or by certain genetic conditions like sickle-cell anemia, where red blood cells are shaped differently and don't carry oxygen as well.
- Clotting Problems:
- Hemophilia: This is a genetic condition where blood doesn't clot properly, so even a small cut can bleed for a long time.
- Thrombosis: Sometimes, blood can clot too easily inside blood vessels when it shouldn't, which can block blood flow.
- Cell Production Problems:
- Leukemia': This is a type of cancer where the body makes too many abnormal white blood cells.
- Polycythemia Vera: This is when the body makes too many red blood cells.
- Germs in Blood: Tiny germs like bacteria or viruses can sometimes get into the blood and make a person very sick. This is why doctors and nurses are always super careful when dealing with blood, treating it as a "biohazard" to prevent the spread of germs.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: As we mentioned, carbon monoxide is a dangerous gas that can attach to hemoglobin instead of oxygen, preventing your body from getting the oxygen it needs. This is why it's important to have good ventilation when burning things, like in a fireplace.
Dates & Discoveries
- 1900: Karl Landsteiner discovered the ABO blood group system.
- 1907: Jan Janský classified blood into the four main types (A, B, AB, O) that we still use today.
- 1907: The first successful blood transfusion using the ABO system was performed.
- 1937: The Rhesus factor, another important blood type system, was discovered.
Cultural Meanings
We often use blood to talk about family. Being "related by blood" means you share ancestors, and sayings like "blood is thicker than water" show how important family connections are.
In Christianity, the blood of Jesus is seen as a symbol of forgiveness and new life. Many Christians also believe that during a special service called the Eucharist, the wine they drink becomes the blood of Jesus.
In stories and folklore from around the world, there are mythical creatures called vampires who are said to drink blood to live forever. Of course, these are just stories and not real!
Cool Facts about Blood
- Blood makes up about 7% of your body weight.
- An average adult has about 5 liters (that's about 1.3 gallons) of blood.
- Not all organs get the same amount of blood. Your liver, kidneys, and brain are some of the organs that receive a very generous blood supply because they are constantly working hard!
- Ancient Greek thinkers, like Plato and Aristotle, believed that blood was made from the food we eat. They also had a theory called "humorism," which suggested that the body contained four main fluids, or "humors," including blood, which influenced a person's health and personality. This idea came from observing how blood separates into layers when left in a container.
- The amazing discovery of how blood circulates was described by a scientist named William Harvey way back in 1628!
- Forensic scientists can use tiny traces of blood found at a scene to help solve mysteries. They can learn about what happened, and sometimes even identify people involved, by studying bloodstains.
- Archaeologists can analyze ancient blood residues to learn about how people lived long ago, what they ate, or what tools they used.
- If someone loses a lot of blood or has severe anemia, they might need a blood transfusion. This is when healthy blood from a donor is given to them. It's super important that the donor's blood type matches the recipient's blood type to avoid problems. This is why we have blood banks where people can donate their blood to help others!
- Many medicines, like antibiotics, are given directly into a vein through a small tube. This is called an IV, and it helps the medicine get into the bloodstream quickly to travel throughout the body. If someone is very dehydrated or has lost a lot of fluid, doctors can also give them special liquid solutions through an IV to help their blood volume.
- This might sound strange, but in the past, people sometimes thought that taking blood out of a sick person would help them. We now know that this is rarely helpful, but in a few very specific and rare conditions today, doctors might carefully remove a small amount of blood to help a patient.
- Not all animals have blood exactly like ours! In many invertebrates (animals without a backbone, like insects, spiders, and snails), they have a fluid called hemolymph. This fluid is similar to blood but isn't always contained in a closed system of vessels like ours.
- Medical words about blood often start with "hemo-" or "hemato-", which comes from an ancient Greek word for blood!
- Some invertebrates, like crabs and snails, use a different molecule called hemocyanin to carry oxygen, which can make their "blood" look blue or green!
- Even though the blood inside your veins is dark red, your veins might look blue through your skin. This is because of how light scatters and is absorbed by your skin and the blood vessels, not because your blood is actually blue.
- Most insects don't even need oxygen-carrying molecules in their hemolymph because they have a special breathing system that delivers oxygen directly to their tissues.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sangre para niños
In Spanish: Sangre para niños