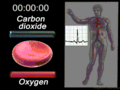Red blood cell facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Red blood cell |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
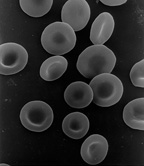
| Scanning electron micrograph of human red blood cells (about 6–8 μm in diameter) |
Red blood cells, also known as RBCs or erythrocytes, are tiny cells in your blood. Their most important job is to carry oxygen from your lungs to every part of your body. They also help carry carbon dioxide back to your lungs to be breathed out.
You have a lot of red blood cells! Women usually have about 4.8 million red blood cells in a tiny drop of blood (a microliter). Men have even more, around 5.4 million per microliter. Red blood cells look red because they contain a special protein called hemoglobin.
Contents
What are Red Blood Cells Like?
A human red blood cell looks like a tiny, flat disk, a bit like a doughnut without the hole. This shape is called a bi-concave disc. It's about 6 to 8 micrometers wide, which is super small! They are much smaller than most other cells in your body.
Adult humans have trillions of these cells, making up about 70% of all the cells in your body. Red blood cells are much more common than other blood cells, like white blood cells or platelets. It takes a red blood cell about 60 seconds to travel all the way through your body and back to where it started.
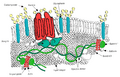
The red color of your blood comes from the iron inside the heme groups of hemoglobin. Each hemoglobin molecule can carry four oxygen molecules. Hemoglobin carries over 98% of the oxygen in your body.
The Life of a Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells are made in your bone marrow, which is found inside large bones. This process is called erythropoiesis and takes about 7 days.
Once they are ready, red blood cells live in your blood for about 100 to 120 days. After this time, they are removed from your blood. In some illnesses, their lifespan can be shorter.
How Red Blood Cells Work
The main job of red blood cells is to move oxygen (O2) to all your tissues and organs. Here's how it works:
- In your lungs, hemoglobin in the red blood cells picks up oxygen.
- The blood then travels through blood vessels to your heart.
- Your heart pumps this oxygen-rich blood to all the other cells in your body.
- Once the oxygen is delivered, the red blood cells pick up carbon dioxide (CO2), a waste product.
- They then travel back to your heart, which pumps the blood to your lungs to release the carbon dioxide and pick up more oxygen. This is why your blood travels in a "double circuit" through your body.
One interesting fact about human red blood cells is that they lose their nucleus when they become mature. This is different from red blood cells in most other animals, which keep their nucleus.
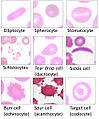
Sometimes, inherited diseases like sickle-cell disease can change the shape of red blood cells. Instead of being round, they can become sickle-shaped. This can cause problems by blocking blood flow in tiny blood vessels called capillaries.
Carrying Carbon Dioxide
Red blood cells also play a role in moving carbon dioxide (CO2) out of your body. Carbon dioxide is carried in your blood in a few ways:
- Most of it (about 68% to 83%) is changed into bicarbonate ions (HCO−
3) inside the red blood cells. This happens with the help of an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase. - A small amount (5% to 10%) is simply dissolved in the liquid part of your blood, called blood plasma.
- Another small amount (5% to 10%) attaches to hemoglobin.
Images for kids
-
Typical mammalian red blood cells: (a) seen from surface; (b) in profile, forming rouleaux; (c) rendered spherical by water; (d) rendered crenate (shrunken and spiky) by salt. (c) and (d) do not normally occur in the body. The last two shapes are due to water being transported into, and out of, the cells, by osmosis.
-
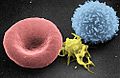
Scanning electron micrograph of blood cells. From left to right: human red blood cell, thrombocyte (platelet), leukocyte.
-
Animation of a typical human red blood cell cycle in the circulatory system. This animation occurs at a faster rate (~20 seconds of the average 60-second cycle) and shows the red blood cell deforming as it enters capillaries, as well as the bars changing color as the cell alternates in states of oxygenation along the circulatory system.
-
Affected by Sickle-cell disease, red blood cells alter shape and threaten to damage internal organs.
See also
 In Spanish: Eritrocito para niños
In Spanish: Eritrocito para niños
 | Jackie Robinson |
 | Jack Johnson |
 | Althea Gibson |
 | Arthur Ashe |
 | Muhammad Ali |