Bicarbonate facts for kids
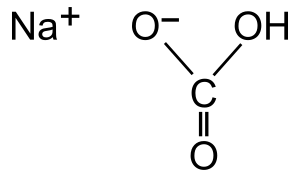
Bicarbonate is a special type of tiny particle called an ion. It has a negative electrical charge. Its chemical formula is HCO3−. Bicarbonate is very important because it can react with acids to create carbon dioxide gas. You might know it best as a part of sodium bicarbonate, which is also called baking soda! When bicarbonate is heated, it can change into another particle called carbonate.
Contents
What is Bicarbonate?
Bicarbonate is a negatively charged ion. Think of an ion as an atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost electrons, giving it an electrical charge. Bicarbonate has one extra electron, so it has a negative charge.
How Bicarbonate Works
Bicarbonate plays a big role in many natural processes. For example, it helps keep the pH balance in your blood just right. This is super important for your body to work properly.
Bicarbonate and Acids
When bicarbonate meets an acid, they react together. This reaction produces carbon dioxide gas. You can see this happen if you mix baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) with vinegar (an acid). It fizzes a lot!
Bicarbonate and Heat
If you heat bicarbonate, it breaks down. It turns into carbonate, water, and carbon dioxide gas. This is why baking soda helps cakes rise – the heat in the oven makes it release carbon dioxide bubbles.
Where Do We Find Bicarbonate?
Bicarbonate is all around us and inside us!
In Nature
- In water: Bicarbonate is found in natural waters like rivers, lakes, and oceans. It helps control the water's pH.
- In rocks: It's also part of many minerals and rocks.
In Our Bodies
- In blood: Your blood contains bicarbonate. It acts as a "buffer" to keep your blood from becoming too acidic or too basic. This is vital for your health.
- In digestion: Your stomach and pancreas use bicarbonate to help with digestion. It neutralizes strong stomach acids.
Common Bicarbonate Compounds
Many useful substances contain bicarbonate. Here are a few:
- Sodium bicarbonate: This is baking soda, used in cooking, cleaning, and even some medicines.
- Potassium bicarbonate: Similar to baking soda, sometimes used as a leavening agent or in antacids.
- Calcium bicarbonate: Often found dissolved in hard water, which can cause limescale.
- Ammonium bicarbonate: Used in some food products and as a fertilizer.
- Carbonic acid: This forms when carbon dioxide dissolves in water. It's a weak acid that can turn into bicarbonate.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bicarbonato para niños
In Spanish: Bicarbonato para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |