Bismuth facts for kids
Bismuth is a special chemical element. It is number 83 on the periodic table and its symbol is Bi. Its atomic mass is 209. Bismuth is only slightly radioactive, so it is usually thought of as non-radioactive. It is found naturally as just one isotope, which is the almost non-radioactive kind. Scientists predicted its radioactivity, and then proved it by studying the metal. Bismuth belongs to Group 15 on the periodic table.
Contents
What is Bismuth Like?
Physical Features
Bismuth is a silver-colored metal with a hint of pink. This pink color comes from a thin layer of oxide on its surface. It is a post-transition metal, which means it has properties similar to both metals and nonmetals. Bismuth is one of the strongest diamagnetic metals, meaning it is slightly pushed away by a magnetic field. It is almost as heavy as lead.
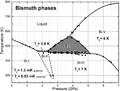
Bismuth has a fairly low melting point of 271.5 °C (520.7 °F). This is common for post-transition metals. It is quite brittle, meaning it can break easily. Bismuth can form beautiful crystals with a shiny surface. Interestingly, when bismuth is a liquid, it is heavier than when it turns into a solid. Water also does this! Bismuth does not conduct electricity or heat very well.
Chemical Features
Bismuth is somewhat like the element antimony. When bismuth is in the air, it forms a thin coating of bismuth(III) oxide. This is what creates the colorful look on bismuth crystals. This oxide layer also stops the metal from oxidizing any further. If bismuth powder is burned, it creates a bright blue flame and yellow bismuth(III) oxide fumes.
Bismuth also reacts with sulfur when it is melted. It reacts with nitric acid to make bismuth(III) nitrate. With strong sulfuric acid, it forms bismuth(III) sulfate and sulfur dioxide. Bismuth also reacts with halogens to create bismuth(III) halides. However, with fluorine, it makes bismuth(V) fluoride unless the fluorine is made weaker.
Bismuth Compounds
Bismuth forms chemical compounds in two main oxidation states: +3 and +5. The +3 state is much more common. Compounds in the +3 state are weak oxidizing agents and are usually light yellow. Compounds in the +5 state are strong oxidizing agents. Bismuthates are the most common +5 compounds. Bismuth(V) fluoride is another +5 compound. Bismuth(V) oxide is a red solid that is not very stable.
Bismuth(III) sulfide is a common ore where bismuth is found. Bismuthine, which is a bismuth hydride, is very unstable and can only be made at very cold temperatures. Bismuth also creates many oxy-compounds, like bismuth oxychloride. These compounds are formed when bismuth halides dissolve in water.
Trioxides (Common Compounds)
These +3 compounds are usually pale yellow and are weak oxidizing agents, except for bismuthine.
- Bismuthine: An unstable gas.
- Bismuth(III) bromide: A pale yellow solid.
- Bismuth(III) chloride: A pale yellow solid.
- Bismuth(III) fluoride: A gray-white solid.
- Bismuth(III) iodide: A dark gray solid.
- Bismuth(III) oxide: A pale yellow solid.
- Bismuth(III) oxychloride: A whitish solid.
- Bismuth(III) sulfide: A brown solid.
Pentoxides (Strong Oxidizers)
Bismuth(V) oxides (+5 compounds) are very strong oxidizing agents. Its chemical formula is Bi2O5. It is a scarlet red solid. It easily breaks down into bismuth(III) oxide and oxygen. It is made by using electricity to break down bismuth(III) oxide in a hot, strong alkali like sodium hydroxide.
- Bismuth(V) fluoride: A colorless solid.
- Bismuth(V) oxide: An unstable red solid.
- Bismuthate: The ion (a charged atom or molecule).
- Sodium bismuthate: A light brown solid that does not dissolve in water.
Bismuth's History
People have known about bismuth since ancient times. However, it was often confused with other metals like tin and lead. No single person is given credit for discovering bismuth. It was in the 1500s that people began to realize bismuth was a different element from tin or lead.
Where is Bismuth Found?
Bismuth is not very common in the Earth's crust. It is only about twice as common as gold. Bismite, which is a bismuth oxide mineral, and bismuthinite, a bismuth sulfide, are two common ores. Sometimes, bismuth is also found as a pure metal.
How is Bismuth Made?
Bismuth and its minerals are too rare to be mined directly. Instead, they are usually obtained through "secondary extraction." This means it is often found mixed with lead metal. The lead metal is cleaned using electrolysis, which leaves the bismuth behind as a thick sludge at the bottom of the container. Then, any copper is removed from the sludge. Finally, the bismuth is purified by being reduced in a furnace, and all the unwanted materials are filtered out.
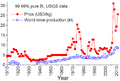
China produces the most bismuth in the world. Peru, Mexico, and Japan also produce bismuth.
Bismuth can also be recycled. However, this can be difficult in many places. Bismuth is used in things like bullets, solder, and stomach medicine, which get spread out and are hard to collect again.
What is Bismuth Used For?
As an Element
Bismuth is used in alloys that have very low melting points. Some of these alloys can even melt in hot water! It is also found in solder that does not contain lead. Bismuth can be mixed with other metals to make them more malleable, meaning they can be shaped more easily.
It is also used in bullets to replace lead. In some places, lead bullets are not allowed because birds might eat them and get lead poisoning. Bismuth is also used in alloys for plumbing pipes. You can also find it in fishing sinkers.
As Chemical Compounds
Bismuth is used in some medicines, such as Pepto-Bismol. This medicine contains bismuth subsalicylate. It is also used as an internal deodorant and to treat eye infections and peptic ulcers.
Bismuth oxychloride is used in cosmetics to give them a pearly shine. Bismuth telluride is used in electronic thermometers. Another bismuth compound is used in superconductors, which can conduct electricity with no resistance at a high temperature. Bismuth compounds can also be used as a pigment (color) and in fireworks to make crackling sounds. It is even used in the nuclear fuel of a nuclear reactor.
Is Bismuth Safe?
Bismuth is much less toxic than other heavy metals like lead. This is why it is replacing lead in many products. It does not build up in the body like other heavy metals do. However, a very large amount of bismuth can still harm the kidneys and liver. Because its oxide does not dissolve in water, it is considered safe for the environment.
| Periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bismuto para niños
In Spanish: Bismuto para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |