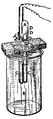Argon facts for kids
Argon is a chemical element. Its symbol is Ar, and its atomic number (which is the number of protons) is 18. Argon is a special type of gas called a noble gas. This means its atoms are very stable and usually don't react with other elements. They don't easily lose or gain electrons or protons.
Argon atoms are found all around us in the air. About 1% of the Earth's atmosphere (the air we breathe) is made up of argon.
Argon is very useful in many ways. For example, it's often used when people are welding steel. It helps by pushing away the air around the weld. This stops the oxygen in the air from mixing with the hot metal, which could cause problems.
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Argon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈɑːrɡɒn/ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | colorless gas exhibiting a lilac/violet glow when placed in a high voltage electric field | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Ar) | [39.792, 39.963] conventional: 39.948 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Argon in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 18 (noble gases) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | gas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 83.80 K (−189.35 °C, −308.83 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 87.30 K (−185.85 °C, −302.53 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at STP) | 1.784 g/L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at b.p.) | 1.40 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 83.8058 K, 69 kPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 150.87 K, 4.898 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 1.18 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 6.43 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 5R/2 = 20.786 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: no data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 106±10 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 188 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of argon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound | (gas, 27 °C) 323 m/s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 17.72x10-3 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440–37–1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay (1894) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay (1894) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of argon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Contents
What is Argon?
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar. It has an atomic number of 18, meaning each argon atom has 18 protons in its center. It belongs to a special group of elements called noble gases.
Why is it called a Noble Gas?
Noble gases are known for being very unreactive. This means they don't easily combine with other elements to form new substances. Argon's atoms have a full outer shell of electrons, which makes them very stable. Because of this, they don't usually lose or gain electrons.
Where is Argon Found?
Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere. It makes up about 1% of the air we breathe. It's a colorless, odorless gas, so you can't see or smell it.
How is Argon Used?
Argon has many important uses because of its unreactive nature.
- Welding: One of its main uses is in welding. When metals are heated to very high temperatures during welding, they can react with oxygen in the air. Argon is used to create a protective shield around the weld, pushing away the air. This stops the metal from reacting with oxygen and keeps the weld strong.
- Light Bulbs: Argon is also used in incandescent light bulbs. Filling the bulb with argon helps to stop the hot wire (filament) from burning out quickly.
- Protecting Materials: Because it doesn't react, argon is used to protect sensitive materials from air and moisture. For example, some old documents or valuable artworks are stored in an argon atmosphere to preserve them.
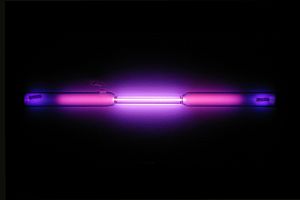
- Glow in the Dark: When electricity passes through argon gas, it glows with a beautiful lilac or violet color. This is why it's used in some types of neon lamps and plasma balls.
Who Discovered Argon?
Argon was discovered in 1894 by two scientists: Lord Rayleigh and William Ramsay. They found it while studying air and noticed there was a small amount of gas that didn't react with anything. They named it "argon," which comes from a Greek word meaning "lazy" or "inactive," because of its unreactive nature.
Related pages
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen & alkali metals |
Alkaline earth metals | Triels | Tetrels | Pnictogens | Chalcogens | Halogens | Noble gases |
||||||||||||
| Period |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | |||||||||||||||||||
Primordial From decay Synthetic Border shows natural occurrence of the element
- Ca: 40.078 — Abridged value (uncertainty omitted here)
- Po: [209] — mass number of the most stable isotope
Images for kids
-
Captioned "Argon", caricature of Lord Rayleigh in Vanity Fair, 1899
-
A sample of caesium is packed under argon to avoid reactions with air
-
Argon gas-discharge lamp forming the symbol for argon "Ar"
See also
 In Spanish: Argón para niños
In Spanish: Argón para niños