Beta decay facts for kids
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay. It's when an atom's nucleus changes by sending out a tiny particle called a beta particle. This particle can be an electron or a positron. This process helps unstable atoms become more stable.
Contents
What is Beta Decay?
Beta decay is a special way that unstable atoms change. It's a type of radioactive decay. During this change, an atom's nucleus sends out a tiny particle. This particle is called a beta particle.
Two Kinds of Beta Decay
There are two main types of beta decay:
Beta Minus Decay (β⁻ decay)
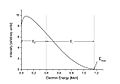
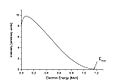
In beta minus decay, a neutron inside the atom's nucleus changes into a proton. When this happens, the atom sends out an electron. It also sends out a tiny, invisible particle called an antineutrino. This type of decay makes the atom's atomic number go up by one. The mass number stays the same.
Beta Plus Decay (β⁺ decay)
In beta plus decay, a proton inside the atom's nucleus changes into a neutron. When this happens, the atom sends out a particle called a positron. A positron is like an electron but has a positive electric charge. This type of decay also sends out a neutrino. This process makes the atom's atomic number go down by one. The mass number stays the same.
Why Does Beta Decay Happen?
Beta decay happens because of something called the weak force. This is one of the four basic forces in nature. The weak force is responsible for changing one type of subatomic particle into another. It allows neutrons to turn into protons, and protons to turn into neutrons. This helps unstable atoms find a more stable form.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Desintegración beta para niños
In Spanish: Desintegración beta para niños