Speed of sound facts for kids

The speed of sound is how fast sound waves travel through something. In dry air at room temperature, sound travels about 1,235 kilometres (767 mi) per hour. That's also about 330 metres (1,083 ft) every second!
Sound moves much faster through liquids and solids than it does through air. This is because the particles in liquids and solids are closer together. They can pass on the sound vibrations more easily. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum, which is an empty space with no air or matter at all.
The speed of sound also changes with temperature. Sound travels slower when it's colder. For example, in very cold places like the stratosphere (a layer of Earth's atmosphere), sound moves more slowly.
Understanding Mach 1
The speed of sound is also known as Mach 1. When something travels faster than Mach 1, it is called supersonic. This means it is moving faster than the sound it creates. You might hear a loud "boom" when a supersonic jet flies overhead. This is called a sonic boom.
Images for kids
-
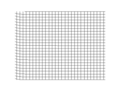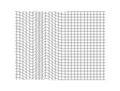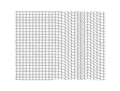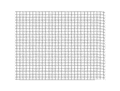
Pressure-pulse or compression-type wave (longitudinal wave) confined to a plane. This is the only type of sound wave that travels in fluids (gases and liquids). A pressure-type wave may also travel in solids, along with other types of waves (transverse waves, see below)
-
Transverse wave affecting atoms initially confined to a plane. This additional type of sound wave (additional type of elastic wave) travels only in solids, for it requires a sideways shearing motion which is supported by the presence of elasticity in the solid. The sideways shearing motion may take place in any direction which is at right-angle to the direction of wave-travel (only one shear direction is shown here, at right angles to the plane). Furthermore, the right-angle shear direction may change over time and distance, resulting in different types of polarization of shear-waves
See also
 In Spanish: Velocidad del sonido para niños
In Spanish: Velocidad del sonido para niños