Barium facts for kids
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Barium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈbɛəriəm/ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery gray; with a pale yellow tint | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Ba) | 137.327(7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Barium in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 2 (alkaline earth metals) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 6s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 1000 K (727 °C, 1341 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 2118 K (1845 °C, 3353 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 3.51 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 3.338 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 7.12 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 142 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 28.07 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | +1, +2 (a strongly basic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 0.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 222 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 215±11 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 268 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of barium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
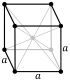
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 1620 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 20.6 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 18.4 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 332 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | +20.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 13 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 4.9 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 9.6 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 1.25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-39-3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Carl Wilhelm Scheele (1772) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Humphry Davy (1808) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of barium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barium is a chemical element with the number 56 on the periodic table. Its special symbol is Ba. It has 56 protons and 56 electrons. Its weight is about 137.3. Barium is a type of metal.
Contents
What is Barium?
Physical Features
Barium belongs to a group of elements called alkaline earth metals. It is a shiny, silver-colored metal. However, it quickly turns black when exposed to air. Barium is soft and can be easily shaped, which means it is ductile. It can mix with other metals to form special mixtures called alloys.
How Barium Reacts
Barium is a very reactive metal. If you leave pure barium metal in the air, it will react with oxygen. First, it turns black, then it becomes white as a new substance called barium oxide forms. Barium also reacts with water, creating barium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. It reacts very quickly with acids, making a barium salt and hydrogen. If you burn barium in air, it can form barium peroxide.
Barium can also react with many other metal oxides and sulfides. This creates barium oxide or sulfide and the original metal. At high temperatures, it even reacts with carbon and nitrogen to form barium cyanide.
Barium Compounds
Because barium metal is so reactive, you won't find it as a pure metal in the Earth. Instead, it is always found as part of chemical compounds. Barium always has a charge of +2 when it forms compounds. Most barium compounds are clear or colorless.
Be careful! Many barium compounds that dissolve in water or stomach acid are very poisonous. However, Barium sulfate is different. It does not dissolve in water or acids, which makes it special. Barium compounds are quite heavy. When heated until they are red-hot, barium compounds produce a bright greenish flame.
Where is Barium Found?
Barium is found in the ground as two main minerals: barium sulfate (also known as barite) and barium carbonate (called witherite). Both of these minerals do not dissolve in water. Barium sulfate is especially hard to dissolve in anything. You can find a lot of barium in countries like China, Germany, India, Morocco, and the US.
How is Barium Made?
It is quite difficult to get pure barium metal from barium sulfate. So, barium sulfate is first changed using carbon to create barium sulfide and carbon dioxide. This barium sulfide is then dissolved in hydrochloric acid. This process makes hydrogen sulfide and barium chloride.
Next, the barium chloride is melted. Then, a process called electrolysis is used. This means electricity is passed through the melted barium chloride to separate it, giving us liquid barium metal. The liquid barium metal then cools down and becomes solid. It is stored in oil to keep it from reacting with air.
Barium carbonate, the other mineral, is easier to work with. It is dissolved in hydrochloric acid to make barium chloride and carbon dioxide. Then, just like before, the barium chloride is melted and electrolyzed to get pure barium metal.
What is Barium Used For?
As a Metal
Barium metal is used to remove oxygen from things like old cathode ray tubes (found in older TVs) and vacuum tubes. It is placed inside these tubes and reacts with any oxygen, using it all up. Barium is also used in spark plug wires in cars.
As Chemical Compounds
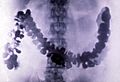
Some compounds of barium, like barium sulfate, are not poisonous. This means they can be safely put into the human body. Doctors use barium sulfate to help them see inside the body using X-rays. When someone swallows a special liquid containing barium sulfate, it shows up clearly on X-rays. This helps doctors find problems like blockages in the stomach or intestines. Barium sulfate absorbs the X-rays, creating a clear image of the inside of the body. This method gives a good picture with less radiation than some other scans. Barium sulfate can also be used as a pigment to add color to things.
Other barium compounds have many different uses in various industries.
Is Barium Safe?
Barium is a very toxic element, meaning it can be dangerous. There is a tiny amount of barium in our food, but this small amount does not cause problems. However, if we get barium from other places, it can cause serious health issues. Even a small amount, like 1 gram of barium, can be deadly.
Barium is dangerous because it acts like other very important elements in our body, such as calcium and magnesium. If barium replaces these important elements, it can mess up how our body works.
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen & alkali metals |
Alkaline earth metals | Triels | Tetrels | Pnictogens | Chalcogens | Halogens | Noble gases |
||||||||||||
| Period |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | |||||||||||||||||||
Primordial From decay Synthetic Border shows natural occurrence of the element
- Ca: 40.078 — Abridged value (uncertainty omitted here)
- Po: [209] — mass number of the most stable isotope
Images for kids
-
Sir Humphry Davy, who first isolated barium metal
-
Benitoite crystals on natrolite. The mineral is named for the San Benito River in San Benito County where it was first found.
-
Amoebiasis as seen in a radiograph of a barium-filled colon
See also
 In Spanish: Bario para niños
In Spanish: Bario para niños