Tantalum facts for kids
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tantalum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈtæntələm/ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | gray blue | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Ta) | 180.94788(2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tantalum in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | d | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d3 6s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 11, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 3290 K (3017 °C, 5463 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 5731 K (5458 °C, 9856 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 16.69 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 15 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 36.57 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 753 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.36 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −3, −1, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5 (a mildly acidic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 146 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 170±8 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of tantalum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
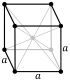
| Crystal structure | body-centered cubic (bcc)
α-Ta |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
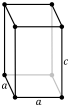
| Crystal structure | tetragonal
β-Ta |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 3400 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 6.3 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 57.5 W/(m⋅K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 131 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | +154.0·10−6 cm3/mol (293 K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 186 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 69 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 200 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vickers hardness | 870–1200 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 440–3430 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-25-7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Anders Gustaf Ekeberg (1802) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized as a distinct element by | Heinrich Rose (1844) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of tantalum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tantalum is a fascinating chemical element that you might not have heard much about! It has the chemical symbol Ta and its atomic number is 73. This means each atom of Tantalum has 73 protons in its center. Tantalum is a rare and very hard metal with a cool blue-gray color. Scientists group it with other metals called transition metals.
One of the best things about Tantalum is that it doesn't easily rust or wear away. You can find this special metal in a mineral called tantalite.
Contents
What is Tantalum?
Tantalum is a very strong and shiny metal. It's known for being super resistant to heat and chemicals. This means it doesn't react much with other substances, which makes it very useful for many things. It can also conduct electricity very well.
Where is Tantalum Found?
Tantalum is not found everywhere on Earth. It is a rare element, mostly found in a mineral called tantalite. Large amounts of tantalite are mined in places like Australia, Brazil, Canada, and some parts of Africa. Extracting Tantalum from this mineral is a complex process.
What is Tantalum Used For?
Because Tantalum is so strong and doesn't corrode, it's used in many important technologies.
Electronics and Gadgets
Tantalum is a key material in making tiny, powerful electronic parts called capacitors. These capacitors store electrical energy and are found in almost all modern electronics. Think about your smartphones, laptops, and video game consoles – they all likely have Tantalum inside!
Medical Uses
Since Tantalum is not harmful to the human body and doesn't react with body fluids, it's used in medicine. Doctors use it for things like surgical tools, implants, and even in some artificial joints.
Other Cool Uses
Tantalum is also used to make special alloys (mixtures of metals) that are very strong and resistant to heat. These alloys are used in jet engines, chemical processing equipment, and even in some types of jewelry.
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen & alkali metals |
Alkaline earth metals | Triels | Tetrels | Pnictogens | Chalcogens | Halogens | Noble gases |
||||||||||||
| Period |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | |||||||||||||||||||
Primordial From decay Synthetic Border shows natural occurrence of the element
- Ca: 40.078 — Abridged value (uncertainty omitted here)
- Po: [209] — mass number of the most stable isotope
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tántalo (elemento) para niños
In Spanish: Tántalo (elemento) para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |