Half-life (element) facts for kids
This article is about the property of radioactive elements. For the video game, see Half-Life (video game).
The half-life of a substance is the time it takes for half of it to change or "decay." This idea first came from studying radioactive elements. These are special elements whose atoms slowly break down over time. Half-life helps us understand how quickly these atoms decay. It's also used in other areas where things decrease steadily, like how long a medicine stays in your body.
| Number of half-lives that have happened |
Parts remaining |
As power of 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1/1 | 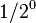 |
| 1 | 1/2 | 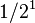 |
| 2 | 1/4 | 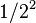 |
| 3 | 1/8 | 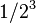 |
| 4 | 1/16 | 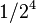 |
| 5 | 1/32 | 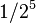 |
| 6 | 1/64 | 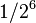 |
| 7 | 1/128 | 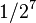 |
| ... | ... | |
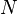 |
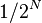 |
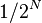 |
What is Half-Life?
Half-life is the time it takes for half of a substance to undergo radioactive decay. Imagine you have 100 radioactive atoms. After one half-life, you would have about 50 atoms left. After another half-life, you would have about 25 atoms left, and so on.
Scientists can measure half-life using special tools like a Geiger counter. This tool counts the tiny particles released during decay. When the number of particles counted drops to half of what it was at the start, that time is the half-life.
It's important to know that half-life is based on probability. This means we can't predict when a single atom will decay. However, when you have many atoms, the overall decay follows a very clear pattern. For example, Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years. This means that if you have a large group of Carbon-14 atoms, half of them will have decayed after 5,730 years.
Why Do Atoms Decay?
Radioactive atoms have unstable nuclei. The nucleus is the center of an atom, made of protons and neutrons. In unstable atoms, the way these protons and neutrons are arranged isn't steady.
Because they are unstable, these nuclei shake and eventually break apart. When they break, they change into different types of atoms. They also release energy and tiny particles. These particles can be alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. This process is called radioactive decay.
For example, a radioactive Carbon-14 atom releases a beta particle. When it does this, it changes into a Nitrogen-14 atom. Another example is Fermium-256. It can split into smaller atoms like Xenon-140 and Palladium-112, releasing neutrons in the process. This splitting is a type of decay called fission.
How Half-Life is Used
Half-life is a very useful concept in many fields. For instance, it helps scientists figure out the age of old things.
- Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years. This long half-life makes it perfect for dating ancient fossils and artifacts. By measuring how much Carbon-14 is left in a sample, scientists can estimate how old it is.
- Other elements have different half-lives. For example, Uranium-232 has a half-life of about 69 years.
- Plutonium-238 has a half-life of 88 years.
After about ten half-lives, more than 99.9% of the original radioactivity from a substance is gone. At this point, the material is only slightly radioactive. It is often considered safe for people because it no longer poses a significant risk.


