Germanium facts for kids
Germanium is a special kind of chemical element. Its symbol is Ge, and its atomic number is 32. A scientist named Clemens Winkler found it. Germanium looks shiny, hard, and silver-white. It's called a metalloid, which means it has properties of both metals and non-metals. Germanium acts a lot like tin in how it forms compounds. It's also a key material for semiconductors, which are used to make things like transistors in electronics.
Contents
Where Germanium Comes From
In 2011, about 118 tonnes of germanium were made around the world. Most of it came from China, Russia, and the United States. Germanium is usually found and collected when people are mining for zinc. It's often a "by-product," meaning it's found alongside the main thing they are looking for.
You can find germanium in zinc ores, especially those from certain types of rock deposits. Scientists have found that there's a lot of germanium hidden in known zinc reserves. There's also a lot of germanium in coal reserves. Some germanium is even recycled from old products, which helps meet the demand for it.
Besides zinc ores, germanium can also be found in silver, lead, and copper ores. Another place to find germanium is in the fly ash from power plants that burn coal. Some coal has germanium in it. Countries like Russia and China get germanium this way. For example, Russia has deposits on Sakhalin Island. China's deposits are in places like Yunnan and Inner Mongolia.
How Germanium is Used
Germanium is used in many different ways. In 2007, the main uses were for fiber-optic cables, infrared optics, and as a helper in making plastics. It was also used in electronics and solar panels. A small amount went into things like special lights, metal mixtures, and some medicines.
Germanium in Optics
Germanium dioxide (GeO2) is special because it bends light a lot and doesn't scatter it much. This makes it great for wide-angle camera lenses and microscopes. It's also used in the center part of optical fibers, which carry internet and phone signals. It helps make these fibers strong and clear.
Germanium is also very useful for seeing in the infrared range. This means it can be used in thermal imaging cameras. These cameras can see heat, which is helpful for military uses, night vision, and for firefighters to find hot spots. Germanium is also used in special equipment that needs very sensitive infrared detectors. Because germanium bends light so much, it needs a special coating to prevent reflections.
Germanium in Electronics
Mixtures of Silicon-germanium are becoming very important for fast computer chips. Circuits made with silicon-germanium can work much faster than those made with only silicon. These chips are starting to replace other materials in wireless devices. The good thing is that silicon-germanium chips can be made using the same low-cost methods as regular silicon chips.
Solar panels are another big use for germanium. Germanium is used as the base for very efficient multijunction photovoltaic cells, especially for satellites in space. Bright LEDs (light-emitting diodes) used in car headlights and to light up LCD screens also use germanium.
Because germanium is similar to gallium arsenide, it can be used to make solar cells from gallium arsenide. The Mars Exploration Rovers and many satellites use these special solar cells.
Germanium is also being looked at as a possible replacement for silicon in tiny computer chips. Other electronic uses include special powders in fluorescent lamps and LEDs. Some musicians even use old germanium transistors in their guitar pedals to get a unique "fuzz" sound from early rock and roll music.
Other Uses of Germanium
Germanium dioxide is also used as a catalyst to help make polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This is the plastic used to make many bottles, especially shiny ones sold in Japan.
In recent years, germanium has been added to special metal mixtures, like those used for sterling silver. When germanium is added to silver, it helps prevent dark spots and makes the silver stronger. A special silver alloy called Argentium sterling silver contains 1.2% germanium.
Special detectors made from very pure germanium crystals can find and identify sources of radiation. This is useful in places like airports for security. Germanium is also used in equipment that helps scientists study materials using X-rays or neutrons.
Germanium is also becoming important in new technologies like spintronics and quantum computing. Scientists have shown that germanium can hold quantum information for a long time, which is key for future computers.
| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen & alkali metals |
Alkaline earth metals | Triels | Tetrels | Pnictogens | Chalcogens | Halogens | Noble gases |
||||||||||||
| Period |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | |||||||||||||||||||
Primordial From decay Synthetic Border shows natural occurrence of the element
- Ca: 40.078 — Abridged value (uncertainty omitted here)
- Po: [209] — mass number of the most stable isotope
Images for kids
-
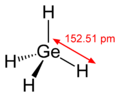
Germane is similar to methane.
-
Nucleophilic addition with an organogermanium compound.
See also
 In Spanish: Germanio para niños
In Spanish: Germanio para niños