Quantum computer facts for kids
A quantum computer is a new kind of computer that uses special rules from quantum mechanics. These rules include ideas like superposition and entanglement. Imagine a regular computer uses bits that are either 0 (off) or 1 (on). A quantum computer uses qubits (short for quantum bit). A qubit can be 0, 1, or even both 0 and 1 at the same time! This "both at once" state is called superposition.
This idea of quantum computing is quite new. Scientists have done experiments with very small quantum computers, performing only a few operations on qubits. Many countries and military groups are interested in this research. They want to develop quantum computers for many uses, like breaking secret codes.
Today's regular computers, often called "classical" computers, store information as binary bits. Each bit is either fully on or fully off. But qubits in quantum computers can be in a mix of on and off states until we measure them. This means quantum computers work with probabilities, not certainties, for their data. Only very simple quantum computers have been built so far, but bigger designs are being imagined.
If we can build large quantum computers, they could solve some problems much faster than any computer we have today. For example, an algorithm called Shor's algorithm could quickly break many modern encryption codes. Quantum computers are different from other special computers, like those that use DNA or light. The amazing speed of quantum computers comes from using quantum mechanics, especially entanglement. While quantum computers can't solve problems that classical computers can't theoretically solve at all, they can solve many problems much, much faster.
Images for kids
-
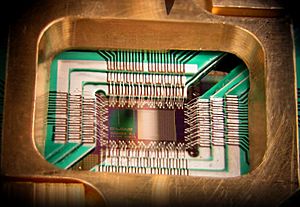
IBM Q System One (2019), the first commercial quantum computer that uses circuits.
See also
 In Spanish: Computación cuántica para niños
In Spanish: Computación cuántica para niños