Semimetal facts for kids

A semimetal is a special type of material that acts a bit like a metal and a bit like a semiconductor. In these materials, the energy levels where electrons can move freely (called the conduction band) and the energy levels where electrons are usually found (called the valence band) are very close. They even overlap a tiny bit!
Think of it like this: in some materials, electrons need a big push to jump from their usual spots to where they can conduct electricity. This "push" is called a band gap.
- Insulators (like rubber) have a very big gap, so electrons almost never move.
- Semiconductors (like silicon) have a smaller gap, so electrons can sometimes jump and conduct.
- Metals (like copper) have no gap at all; electrons move freely.
Semimetals are unique because they have a tiny overlap between these bands, meaning some electrons are always ready to move, but not as many as in a true metal.
Contents
How Semimetals Conduct Electricity
Semimetals are interesting because they conduct electricity using two types of tiny particles: electrons and "holes." Think of a hole as an empty space where an electron should be. When an electron moves, it leaves a hole behind, and another electron can jump into that hole. Both moving electrons and moving holes help carry the electric current.
Temperature's Role
How well a material conducts electricity often changes with temperature.
- In a typical metal, as it gets hotter, its ability to conduct electricity usually goes down. This is because the atoms vibrate more, making it harder for electrons to move smoothly.
- For semiconductors and insulators, it's different. When they get a little warmer, more electrons can jump into the conduction band, so their conductivity actually increases at first.
- Semimetals are a bit like metals in that their conductivity doesn't always change much with temperature at lower levels. However, some semimetals, like bismuth, can start to act more like semiconductors if they get hot enough. A key difference is that semimetals always conduct some electricity, even at very cold temperatures, unlike semiconductors which might stop conducting completely.
How We Classify Semimetals
Scientists classify materials by looking at their electron energy bands. For semimetals, the lowest part of the conduction band and the highest part of the valence band overlap in energy. However, this overlap happens in a special way: the highest point of the valence band and the lowest point of the conduction band are not in the same "location" when we map out the electron energies.
Sometimes, it can be quite hard to tell if a material is a true semimetal or a semiconductor with a very, very tiny energy gap. This is because their electrical behaviors can be very similar.
Understanding the Energy Bands
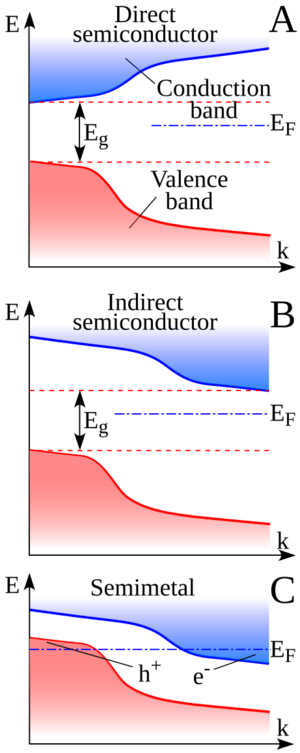
The image helps us visualize how electron energy bands look in different materials:
- A shows a semiconductor where electrons can jump directly from the valence band to the conduction band. An example is copper indium selenide.
- B shows another type of semiconductor, like silicon. Here, electrons need to change their "location" slightly to jump from the valence band to the conduction band.
- C shows a semimetal. Notice how the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band slightly overlap. Examples include tin and graphite.
Because of this overlap, semimetals always have some free electrons and holes ready to conduct electricity. However, they don't have as many free carriers as a true metal. This is why their electrical properties are somewhere between those of metals and semiconductors.
What Makes Semimetals Special?
Since semimetals have fewer free electrons and holes compared to metals, they usually don't conduct electricity or heat as well as metals do. Imagine a busy highway: metals are like a highway with many cars (electrons) moving freely. Semimetals are like a highway with fewer cars, so traffic (electricity) doesn't flow quite as easily.
Common Semimetals We Know
Some well-known elements that are semimetals include:
It's important to know that "semimetal" is not the same as "metalloid." Metalloids are elements that have properties between metals and nonmetals. While arsenic and antimony are both semimetals and metalloids, other semimetals like bismuth and graphite are not usually called metalloids. Also, semimetals can be chemical compounds, like mercury telluride (HgTe), not just single elements.
Scientists have also found that some materials can become semimetals under very special conditions, like extreme pressure. Even some conductive polymers (plastics that can conduct electricity) have been shown to act like semimetals!
See Also
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |