Transistor facts for kids
 |
|
| Type | Active |
|---|---|
| First production | 1950s |
| Pin configuration | Base, collector, and emitter |
| Electronic symbol | |
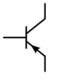 NPN and PNP symbols |
|
A transistor is a tiny electronic switch or amplifier. Think of it as a super-fast mini-gate that can turn electrical signals on or off, or make them stronger. It's one of the most important inventions ever, forming the basic building blocks of almost all modern electronics, from your smartphone to giant computers!
Transistors are made from special materials called semiconductors, like silicon. They usually have at least three connection points, called terminals. By sending a small electrical signal to one part of the transistor, you can control a much larger signal flowing through another part. This ability to control a big signal with a small one is what allows transistors to amplify signals or act like a quick switch.
Even though the idea for a transistor was first thought of in 1925 by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld, the first working transistor was invented in 1947 by scientists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley at Bell Labs. They even won a Nobel Prize in Physics for it in 1956! This invention changed everything, making electronics much smaller, cheaper, and more powerful. Today, the most common type is called the MOSFET, invented a few years later.
Transistors are much smaller and use less power than older electronic parts called vacuum tubes. This is why they helped create the amazing electronic world we live in today.
Contents
The History of Transistors
Before transistors, electronic devices used large, fragile vacuum tubes. These tubes used a lot of power and broke easily. In 1925, a physicist named Julius Edgar Lilienfeld imagined a "solid-state" device that could replace vacuum tubes. He even filed patents for his idea. However, the materials needed to build it weren't available yet.
The First Working Transistor

In 1947, at Bell Labs in New Jersey, scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain made a breakthrough. They discovered that by touching two gold wires to a piece of germanium, they could make a small electrical signal control a larger one. This was the first working transistor!
Their team leader, William Shockley, quickly saw how important this discovery was. He worked to understand and improve the new device. In 1956, Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley shared the Nobel Prize in Physics for their amazing invention.
Transistors Change the World
The invention of the transistor quickly led to many new technologies. In 1954, the first pocket-sized transistor radio was released. This was a huge deal because radios used to be big and needed lots of power. Soon, companies like Sony started mass-producing these radios, making them popular worldwide.
Transistors also made computers much smaller and more powerful. They replaced bulky vacuum tubes, paving the way for the tiny, fast electronic devices we use every day.
The MOSFET Revolution
While the first transistors were important, an even more powerful type was invented later. In 1959, Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs created the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET).
The MOSFET was special because it used less power and could be made much smaller. This allowed engineers to pack millions, and later billions, of transistors onto a single tiny chip. The MOSFET became the most important transistor, making modern integrated circuits and the digital age possible.
Why Transistors Are So Important
Transistors are truly one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century. They are the tiny "brains" behind almost all modern electronics.
- Everywhere You Look: From your smartphone and laptop to your TV and car, transistors are inside. They make these devices work by processing information and controlling electricity.
- Making Things Smaller: Transistors allowed electronics to shrink dramatically. Imagine if your phone was as big as a refrigerator!
- Saving Power: They use very little electricity, which means your devices can run on batteries for longer.
- Incredibly Cheap: Because they can be made in huge numbers, each transistor costs almost nothing. This makes advanced electronics affordable for everyone.
By 2018, more than 13 quintillion (that's 13 followed by 18 zeros!) MOSFETs had been made. This makes them the most produced artificial objects in history!
How a Transistor Works Simply
A transistor is like a tiny electronic gate with three main connections. A small signal at one connection can control a much larger signal flowing through the other two. This gives transistors two main jobs:
- As a Switch: They can quickly turn an electrical current completely on or off. This is how digital devices like computers work, using "on" (1) and "off" (0) signals.
- As an Amplifier: They can take a weak electrical signal and make it much stronger. This is useful in things like radios and audio systems.
There are two main families of transistors:
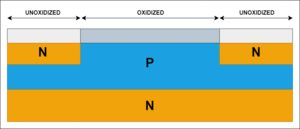
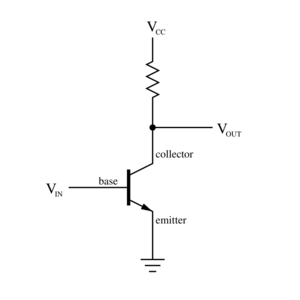
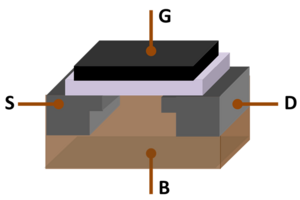
- A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) has terminals called base, collector, and emitter. A small current at the base controls a larger current between the collector and emitter.
- A field-effect transistor (FET) has terminals called gate, source, and drain. A voltage at the gate controls the current between the source and drain.
Transistor as a Switch
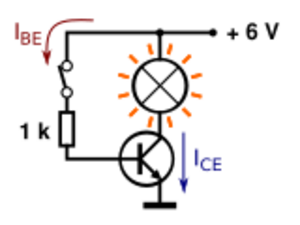
Imagine you want to turn a light bulb on or off with a tiny signal. A transistor can do this! When a small voltage is applied to the transistor's control terminal (the base for a BJT), it acts like closing a switch, allowing a larger current to flow and turn on the light. When the small voltage is removed, the switch opens, and the light turns off.
This fast switching ability is key for all digital circuits, including the ones in your computer that perform calculations.
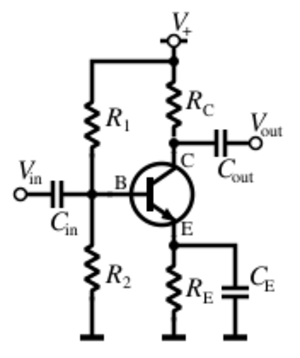
Transistor as an Amplifier
If you have a very quiet sound signal, like from a microphone, you need to make it louder to hear it through speakers. A transistor can act as an amplifier. A small change in the input signal causes a much larger change in the output signal.
This is how your phone makes music loud enough to hear, or how a radio signal can travel long distances. Transistors are essential for making signals strong enough to be useful.
Transistors vs. Vacuum Tubes
Before transistors, vacuum (electron) tubes were the main electronic components. Transistors largely replaced them because of several key advantages:
Advantages of Transistors
- Small Size: Transistors are tiny, allowing devices to be much smaller and lighter.
- Less Power: They use much less electricity, which means devices can run on batteries and don't get as hot.
- No Warm-up Time: Vacuum tubes needed time to heat up, but transistors work instantly.
- Strong and Durable: Transistors are solid-state devices, meaning they have no fragile glass parts or internal vacuums that can break.
- Mass Production: Millions or even billions of transistors can be made on a single tiny chip.
Limitations of Transistors
While transistors are amazing, vacuum tubes still have some uses:
- Some vacuum tubes are better for very high-frequency signals or extremely high voltages, like those used in powerful radio transmitters.
- Transistors can be damaged by static electricity or radiation, so special "hardened" chips are needed for spacecraft.
Types of Transistors
There are many kinds of transistors, but they generally fall into two main families:
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs): These were the first type of transistor to be mass-produced. They use two types of electrical carriers (electrons and "holes") to conduct current. BJTs are often used in amplifiers.
- Field-Effect Transistors (FETs): These transistors use an electric field to control the flow of current. They are known for having a high input resistance.
- MOSFETs: The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is the most common type of FET and the most widely used transistor in the world. It's the basic building block for almost all modern digital electronics, like computer chips.
How MOSFETs and BJTs are Used Today
The MOSFET is used in almost all digital circuits and many analog circuits. It makes up 99.9% of all transistors in the world! BJTs were very popular in the 1950s and 60s, especially for amplifiers. While MOSFETs have taken over most digital uses, BJTs are still used in some specialized analog circuits.
How Transistors Are Made
Semiconductor Materials
Transistors are made from special materials called semiconductors. The most common one is very pure silicon. Some older transistors used germanium. Other materials like gallium arsenide are used for very fast transistors in things like satellite receivers.
Silicon is great because it can handle higher temperatures and voltages than germanium. The way these materials are treated, or "doped," helps control how electricity flows through the transistor.
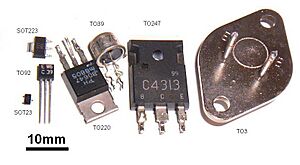
Packaging Transistors
Transistors come in many different shapes and sizes, called "packages."
- Through-hole packages have long wires that go through holes on a circuit board.
- Surface-mount packages are smaller and sit directly on the surface of the circuit board. These are used in tiny devices like smartphones.
Power transistors, which handle a lot of electricity, have larger packages. These often have metal parts that can be attached to a heat sink to keep them cool. On the other hand, some tiny transistors for very high frequencies are no bigger than a grain of sand!
Flexible Transistors
Scientists are even creating flexible transistors! These can be bent and twisted, which is useful for new technologies like flexible displays and other bendable electronics.
Images for kids
-
Soviet-manufactured KT315b transistors.
-
A Darlington transistor with its case removed, showing the two transistor chips inside.
See also
 In Spanish: Transistor para niños
In Spanish: Transistor para niños
- Digital electronics
- Moore's law
- Semiconductor device modeling
- Transistor count
- Very Large Scale Integration