Cathode ray tube facts for kids
The cathode ray tube or CRT was a very common type of screen for many years. It was used in almost all computer monitors and televisions. You would have seen CRTs in older, bulky TVs before LCD and plasma screens became popular.
Contents
What is a Cathode Ray Tube?
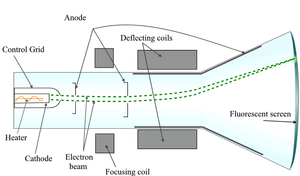
A CRT is a special kind of vacuum tube. It has a part called an electron gun. This gun shoots out tiny particles called electrons.
How the Electron Gun Works
The electron gun has a cathode. This is a metal part that gets hot. When it heats up, it sends out electrons. Inside the glass tube, there's also an anode. This anode is like a magnet for electrons. It pulls the electrons towards the front of the tube. This makes the electrons shoot out in a straight line, creating a "cathode ray."
Creating a Vacuum
To make sure the electrons travel in a straight line without hitting air molecules, all the air is taken out of the tube. This creates a vacuum.
Making the Picture Glow
The electrons hit the front of the tube, which is covered with a special material called phosphor. When electrons hit the phosphor, it lights up.
Controlling the Image
You can aim the electrons by using a magnetic field. By carefully controlling where the electrons hit the phosphor, a bright picture appears on the screen. If this picture changes very quickly, about 30 times every second, it looks like the picture is moving. This is how old TVs and computer monitors showed videos.
Why CRTs Were Heavy
Because there's a vacuum inside, the glass tube had to be very strong and thick. This was to stop the outside air pressure from crushing it. That's why large CRT televisions were often very heavy!
History of the Cathode Ray Tube
The cathode ray tube was invented in 1897 by Karl Ferdinand Braun. At first, it was used in a machine called an oscilloscope. An oscilloscope shows waves, like sound waves or electrical signals.
Later, in the 1920s, the CRT was used by Philo T. Farnsworth to create the first modern electronic television. For many decades, the CRT was the main type of screen for TVs. However, in the early 2000s, liquid crystal display (LCD) screens became popular. They were much thinner and lighter, and soon replaced CRTs in most homes.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A cathode-ray tube as found in an oscilloscope
-
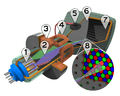
Cutaway rendering of a color CRT: 1. Three electron emitters (for red, green, and blue phosphor dots) 2. Electron beams 3. Focusing coils 4. Deflection coils 5. Connection for final anodes (referred to as the "ultor" in some receiving tube manuals) 6. Mask for separating beams for red, green, and blue part of the displayed image 7. Phosphor layer (screen)with red, green, and blue zones 8. Close-up of the phosphor-coated inner side of the screen
-
Typical 1950s United States monochrome television set
-
Snapshot of a CRT television showing the line of light being drawn from left to right in a raster pattern
See also
 In Spanish: Tubo de rayos catódicos para niños
In Spanish: Tubo de rayos catódicos para niños