Analog television facts for kids
Analog television is the original way we watched TV shows and movies. It uses special signals, called analog signals, to send pictures and sounds to your screen. These signals are like a continuous wave that changes quickly to carry all the information for the show you're watching.
The first TV systems were only in black-and-white. Color television started to become popular in the 1950s.
Analog signals change smoothly over a wide range of values. This means that any electronic noise or interference also gets picked up by your TV. If an analog signal was weak, your TV picture would look "snowy" or have lines. But with digital TV, a weak signal can still look perfect, or it might just disappear completely.
Analog television can be sent wirelessly, like through terrestrial television (using antennas) or satellite television. It can also be sent through cable television networks using wires.
Before digital television (DTV) came along, all TV broadcasts used analog signals. Since the 2000s, most countries have been switching from analog to digital TV. This change is called the digital television transition. Digital signals use less "space" on the airwaves, which is why countries are making the switch.
Some common analog television systems were:
Images for kids
-
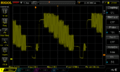
NTSC composite video signal (analog)
-
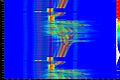
Portion of a PAL videosignal. From left to right: end of a video line, front porch, horizontal sync pulse, back porch with colorburst, and beginning of next line
-
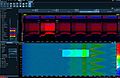
PAL video signal frames. Left to right: frame with scan lines (overlapping together, horizontal sync pulses show as the doubled straight horizontal lines), vertical blanking interval with vertical sync (shows as brightness increase of the bottom part of the signal in almost the leftmost part of the vertical blanking interval), entire frame, another VBI with VSYNC, beginning of the third frame
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |