Membrane facts for kids
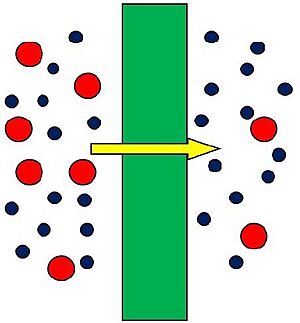
A membrane is a thin, soft layer of material. It acts like a special wall or curtain. A membrane separates two things from each other.
In biology, the study of living things, a membrane can mean two different things. It can be a tissue membrane, which is a bigger layer of cells. Or it can be the tiny membranes found inside and around a cell.
Membranes in Your Body
A tissue membrane is a thin layer of cells or tissue. This layer can cover parts of your body or an organ. It can also separate or line a body cavity.
For example, the mucous membrane is like the skin that lines the inside of your nose and mouth. It helps keep these areas moist. An epithelial membrane has two main parts. One part is epithelial tissue, and the other is connective tissue.
Membranes Inside Cells
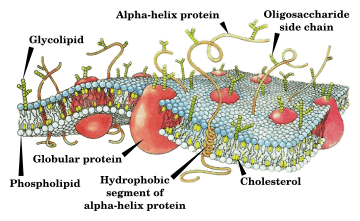
Cells are the tiny building blocks of all living things. There are many different types of membranes inside a cell. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is the outer layer that covers one whole cell.
Membranes also divide the cell into smaller spaces. These spaces are called organelles. Organelles are like tiny organs inside the cell. Each organelle does a special job. For example, the nucleus holds the cell's DNA. The mitochondria are like power plants; they make energy for the cell.
Membranes in cells are made of lipids (which are a type of fat) and proteins. The lipids help keep the inside of the cell or organelle separate from the outside. The proteins do many important things. Plasma membranes can receive messages from outside the cell. They also control what goes into and out of the cell. For example, they let things like glucose (sugar), calcium, and potassium move in and out.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Membrana (objeto) para niños
In Spanish: Membrana (objeto) para niños