Turbine facts for kids
A turbine is a special machine that turns the movement of a liquid or gas into useful energy. Think of it like a fancy spinning wheel! It has a central rod called a shaft with many blades attached to it. When a fluid (like water or air) pushes against these blades, they spin the shaft very fast.
This spinning motion is super important because it can be used to power other things. Most often, a turbine's spinning shaft is connected to an electric generator. This generator then uses the spinning motion to create electricity for our homes and schools! Some of the earliest turbines were simple windmills and water wheels, which people used for grinding grain or pumping water. Turbines can also work in reverse, using power to move fluids, like the propellers on some airplanes.
Sometimes, a special cover called a casing is placed around the turbine. This helps to guide the fluid and make sure the turbine works as efficiently as possible.
Contents
How Turbines Make Energy
Turbines are amazing because they use the power of moving fluids. Imagine a strong gust of wind pushing a windmill's blades, or a powerful river current spinning a water wheel. This is the basic idea!
The Spinning Blades
The blades on a turbine are designed to catch the fluid's movement. When water, steam, or air hits the blades, it pushes them, causing the shaft to rotate. The faster the fluid moves, the faster the turbine spins. This spinning is what creates mechanical energy.
From Spin to Electricity
Once the turbine's shaft is spinning, it can be connected to a generator. A generator is a device that turns mechanical energy (like spinning) into electrical energy. So, the turbine spins the generator, and the generator makes electricity! This electricity then travels through power lines to light up our cities and power our devices.
Different Kinds of Turbines
There are many types of turbines, each designed for a specific job and using different fluids to spin their blades.
Steam Turbines

Steam turbines are very common in power plants. They use superheated steam to spin their blades. Water is heated until it turns into high-pressure steam, which then rushes through the turbine, making it spin. After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled back into water and reused. This process is a key part of how much of the world's electricity is made.
Gas Turbines
Gas turbines work with hot, fast-moving gases. They are often used in jet engines for airplanes and also in some power plants. Air is sucked into the turbine, compressed, mixed with fuel, and then burned. This creates very hot, high-pressure gas that blasts through the turbine blades, making them spin.
Jet Engines
Jet engines are a type of gas turbine that creates thrust to push an airplane forward.
- Turbojet engines push air straight out the back.
- Turbofan engines have a large fan at the front that pushes most of the air around the engine, making them more fuel-efficient.
- Turboprop engines use the turbine's power to spin a propeller, like on smaller airplanes.
- Turboshaft engines use the turbine's power to spin a shaft that can be connected to helicopter rotors or other machinery.
Water Turbines
Water turbines use the power of flowing water, usually from rivers or dams, to generate electricity. This is called hydroelectric power. The water flows through the turbine, spinning its blades, which then turn a generator. There are different designs like Kaplan, Pelton, and Francis turbines, each suited for different water pressures and flows.
Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are what you see in large "wind farms." They use the power of the wind to spin large blades, which then turn a generator to create electricity. They are a great way to make clean, renewable energy.
Images for kids
-
A steam turbine with the case opened.
-
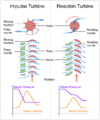
Schematic of impulse and reaction turbines, where the rotor is the rotating part, and the stator is the stationary part of the machine.
-
Turbine inlet guide vanes of a turbojet
See also
 In Spanish: Turbina para niños
In Spanish: Turbina para niños