Las Vegas Valley facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Las Vegas Valley
|
|
|---|---|
|
Left-right from top: Las Vegas Strip, Stratosphere Tower, Fremont Street Experience, Waldorf Astoria Las Vegas, Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area, The District at Green Valley Ranch
|
|
| Country | United States |
| State | Nevada |
| Largest city | Las Vegas |
| Other major cities |
|
| Area | |
| • Urban | 500 sq mi (1,400 km2) |
| • Metro | 1,600 sq mi (4,100 km2) |
| Population
(2024 estimate)
|
|
| • Metropolitan Statistical Area | 2,421,685 |
| GDP | |
| • MSA | $160.7 billion (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| Area code(s) | 702 and 725 |
The Las Vegas Valley is a large urban area in Nevada, a state in the United States. It's the second biggest metropolitan area in the Southwestern United States. Since 2003, the Las Vegas Metropolitan Statistical Area has included all of Clark County, Nevada.
The Valley is a big basin of about 600 square miles. Mountains surround it on all sides. This area is home to Nevada's three largest cities: Las Vegas, Henderson, and North Las Vegas. There are also eleven smaller towns that are part of Clark County.
People often use the names Las Vegas and Vegas to talk about the whole Valley, the famous Strip, or just the city of Las Vegas. Many people from Hawaii call the Valley the Ninth Island. This is because many Hawaiians live in or visit Las Vegas often.
The Las Vegas Valley has grown very quickly since the 1990s. Its population more than tripled from 741,459 in 1990 to 2,421,685 in 2024. It is still one of the fastest-growing areas in the U.S. Las Vegas is known worldwide for business, development, and entertainment. It is also one of the most visited places for tourists. In 2014, over 41 million people visited the area. This brought in more than $100 billion.
Contents
- History of Las Vegas Valley
- Where is the Las Vegas Valley?
- Geography and Environment of Las Vegas
- Economy of Las Vegas
- Culture and the Arts
- Communities in Las Vegas Valley
- Media in Las Vegas
- Transportation in Las Vegas
- Sports in Las Vegas
- Recreation
- Education
- Venues in Las Vegas
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Las Vegas Valley
The first non-Native American to visit the Las Vegas Valley was a Mexican scout named Raphael Rivera in 1829. He was part of a group traveling along the Old Spanish Trail. They named the area Las Vegas, which means "the meadows" in Spanish. This was because there were green, grassy areas fed by natural springs.
Mormon farmers settled here in 1854. Later, in 1864, the United States Army built a fort. This started a long connection between southern Nevada and the U.S. military. Since the 1930s, Las Vegas has been known as a place for entertainment and resorts, mainly for adults.
Nellis Air Force Base is in the northeast part of the Valley. The land used by the military and other government groups limits how much the Valley can grow.
In the late 1960s, businessman Howard Hughes bought many hotels and media stations. Over time, large companies also started buying hotels. This helped change the area. Money from tourists and new federal funds from Nellis Air Force Base helped the area grow even more. Today, Las Vegas is still a top entertainment spot in the world.
Where is the Las Vegas Valley?
The Las Vegas Valley is a landform that includes the cities of Las Vegas, North Las Vegas, and Henderson. It also includes towns like Summerlin South, Paradise, Spring Valley, Sunrise Manor, Enterprise, Winchester, and Whitney. The larger metropolitan area covers all of Clark County, even parts outside the Valley.
Clark County has an "Urban Planning Area" for Las Vegas. This is a rectangular area, about 20 miles from east to west and 30 miles from north to south. Some areas like Red Rock and Mount Charleston are not included in this planning area.
The Las Vegas Metropolitan Police Department is the largest police force in the Valley. They patrol the city of Las Vegas, the smaller towns, and other areas in Clark County. Other cities like North Las Vegas and Henderson have their own police forces.
Geography and Environment of Las Vegas
The Las Vegas Valley is located in the Mojave Desert. It is a large basin surrounded by mountains. U.S. Route 95 runs through the northwest part of the Valley.
The Valley is about 1600 square miles. Most of its edges are surrounded by hills or mountains. The Valley is a basin formed by fault lines and filled with alluvial deposits (sediment carried by water).
There are several underground water sources called aquifers in the Valley. These water sources have been used a lot. Because of this, the ground in Downtown Las Vegas has sunk by about 6.2 feet. The ground along The Strip has sunk by about 2.9 feet. This sinking is due to pumping water from these aquifers.
Climate in Las Vegas
The Las Vegas Valley has a hot-desert climate. It gets less than 5 inches of rain each year.
In summer (July and August), daytime temperatures are usually between 100°F and 110°F. Nights are cooler, from 72°F to 80°F. The air is very dry, which makes the heat feel less intense. However, it's still important to stay hydrated. Cars can get very hot and be dangerous for children and pets. Surfaces exposed to the sun can cause burns. Sometimes in July and August, there is a "monsoon season." Moist winds from the Gulf of California bring thunderstorms. These storms can cause flash floods.
Winter days (December and January) are usually mild and sunny. Highs are typically between 52°F and 60°F. Nights are colder, from 34°F to 42°F. The mountains around the Valley get snow, but it rarely snows in the city itself. When it does snow, it's usually a small amount.
Spring and fall are generally dry with hot, sunny days and cool nights.
| Climate data for Las Vegas, Nevada | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 80 (27) |
89 (32) |
96 (36) |
102 (39) |
114 (46) |
117 (47) |
120 (49) |
116 (47) |
114 (46) |
103 (39) |
89 (32) |
91 (33) |
120 (49) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 57.9 (14.4) |
62.2 (16.8) |
69.9 (21.1) |
77.9 (25.5) |
88.0 (31.1) |
98.0 (36.7) |
103.8 (39.9) |
101.4 (38.6) |
93.4 (34.1) |
80.2 (26.8) |
66.4 (19.1) |
56.3 (13.5) |
79.6 (26.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 37.1 (2.8) |
41.0 (5.0) |
46.8 (8.2) |
53.3 (11.8) |
63.2 (17.3) |
71.7 (22.1) |
77.8 (25.4) |
76.3 (24.6) |
68.0 (20.0) |
56.0 (13.3) |
44.3 (6.8) |
36.6 (2.6) |
56.0 (13.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 8 (−13) |
10 (−12) |
16 (−9) |
26 (−3) |
28 (−2) |
33 (1) |
40 (4) |
46 (8) |
38 (3) |
26 (−3) |
14 (−10) |
11 (−12) |
8 (−13) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.61 (15) |
0.68 (17) |
0.60 (15) |
0.16 (4.1) |
0.25 (6.4) |
0.08 (2.0) |
0.43 (11) |
0.46 (12) |
0.31 (7.9) |
0.25 (6.4) |
0.33 (8.4) |
0.40 (10) |
4.56 (116) |
Earthquake Zones
The Las Vegas Valley is an active earthquake zone. It has several fault lines. One of these, the Frenchman Mountain Fault, is 20 miles long. It could cause a magnitude 7 earthquake.
Air Quality in Las Vegas
Being in a desert basin can cause air quality problems. Dust from the wind, smog from cars, and pollen can make the air unhealthy on some days.
Pollen can be a big issue for several weeks each year. Local governments are trying to control this by banning plants that produce a lot of pollen.
Dust problems usually happen on very windy days. They are often short and happen at certain times of the year. Big dust storms are rare.
Smog gets worse when there is no wind to clear the air. Also, in winter, a weather event called an inversion can trap air pollution in the Valley.
Las Vegas does not have many factories. Clark County is working to improve air quality. This has shown good results over the years.
Water Sources
The plants that naturally grow in the desert do not help the soil hold water. During heavy rains, dry riverbeds called washes or arroyos carry water from the mountains. This water flows into the Las Vegas Wash. The wash used to form a large natural wetland that flowed into the Colorado River.
After the Hoover Dam was built on the Colorado River, Lake Mead was created. Later, in the 1980s and 1990s, Lake Las Vegas was built. This required directing the Las Vegas Wash through tunnels under Lake Las Vegas and into Lake Mead.
Nevada gets a certain amount of water from Lake Mead each year. Las Vegas uses most of this water. About 90 percent of Las Vegas's water comes from Lake Mead.
In the past, Las Vegas relied on underground water from aquifers. Pumping too much water from these caused the ground to sink. Today, aquifers are mainly used to store water. Water is pumped in when demand is low and pumped out when demand is high.
Urban Growth
The population of the Las Vegas area has grown very quickly. Since the early 1970s, the population has doubled about every ten years. Now, nearly three million people live here. This fast growth has turned many desert lands into cities and business areas.
Economy of Las Vegas
 The main reason for Las Vegas's economy is tourism. The area has about 150,000 hotel rooms, more than any other city in the world. In the past, hotels with casinos and celebrity shows were the main attractions. Now, shopping, conventions, fine dining, and outdoor activities also bring in many tourists.
The main reason for Las Vegas's economy is tourism. The area has about 150,000 hotel rooms, more than any other city in the world. In the past, hotels with casinos and celebrity shows were the main attractions. Now, shopping, conventions, fine dining, and outdoor activities also bring in many tourists.
Las Vegas is the world headquarters for MGM Resorts International, a large gaming company. Many companies that make electronic gaming machines are also in the Las Vegas area. In the 2000s, shopping and dining became big attractions. The Las Vegas Convention and Visitors Authority promotes tourism in the area. They collect information on how many people visit and how much money they spend.

Las Vegas has always attracted people who enjoy gambling. However, it now faces more competition from other places around the world.
The Las Vegas area has seen a big increase in population and tourism. The city has grown so fast that it reaches the edges of government-owned land. This has made land more valuable, leading to more buildings closer to the city center. Chinatown was built in the early 1990s. It started with one large shopping center but has grown to include many Asian businesses. In recent years, many retired people have moved to the area. This has led to more businesses that serve them, like housing and healthcare.
The cost of housing went up a lot in 2004. However, Nevada does not have business or income taxes. This makes it an attractive place for many companies to move to or expand. Las Vegas is a city that is active 24 hours a day. Because of this, call centers often find it a good place to hire workers who are used to working at all hours.
Construction Industry
The construction industry is a big part of the Las Vegas economy. It is growing quickly with the population. In March 2011, construction employed 40,700 people. This number is expected to grow as the economy gets better. Since the large resorts began to be built in the 1970s, construction has been very important. Cranes are a common sight in the Las Vegas skyline. At any time, about 300 new homes are being built. Also, in recent years, there has been a rise in tall apartment buildings. New planned communities in the suburbs are also common.
The huge CityCenter project started building on the Strip in 2006. It cost $8.5 billion and was finished in 2009. It includes many hotels, apartments, shops, and a casino. It is the most expensive privately funded construction project in U.S. history.
The Tropicana Hotel, which opened in 1957, was taken down in April 2025. A new baseball stadium will be built there. The owner, Bally's Corporation, plans to develop the site further after the stadium is finished.
Housing in Las Vegas
Most homes in Las Vegas have traditionally been single-family detached homes. These homes are usually built on a flat concrete base. Apartments were typically two-story buildings. In the 1990s, the first tall apartment towers were built. By the mid-2000s, many more tall apartment buildings were constructed. These changed the look of the skyline around the Strip.
The Las Vegas Valley has many suburban master planned communities. These communities offer lots of fun things to do. They have lakes, golf courses, parks, bike paths, and jogging trails. Some examples include Aliante, Anthem, Cadence, Centennial Hills, Green Valley, Inspirada, Lake Las Vegas, The Lakes, Mountain's Edge, Peccole Ranch, Providence, Rhodes Ranch, Seven Hills, Skye Canyon, Southern Highlands, and Summerlin.
Technology Companies

Some technology companies have moved to Las Vegas or started there. Las Vegas has many technology companies in electronic gaming and telecommunications.
Some technology companies in southern Nevada include Bigelow Aerospace, Petroglyph, Switch Communications, US Support LLC, Fanatics, and Zappos.
In 2015, the electric car company Faraday Future chose North Las Vegas for its $1 billion car factory.
Some companies that started in Las Vegas but later sold or moved include Westwood Studios (sold to Electronic Arts), Systems Research & Development (sold to IBM), Yellowpages.com (sold to BellSouth and SBC), and MPower Communications.
Tourism in Las Vegas
The main attractions in the Las Vegas Valley are the hotel/casinos. These hotels usually have large areas for games, theaters for live shows, shops, bars, and many restaurants. There are groups of large hotel/casinos in downtown Las Vegas and on the Las Vegas Strip. The biggest hotels are mostly on the Strip, which is a four-mile part of Las Vegas Boulevard. These hotels offer thousands of rooms. Fifteen of the world's 30 largest hotels are on the Strip, with over 62,000 rooms in total. Many hotels are also in the city's downtown area, which was the first main spot for games. Many of the world's largest hotels, casinos, and resorts are on the Las Vegas Strip.
The Valley's hotels with games can be found in several places. The biggest is the Las Vegas Strip, then Downtown Las Vegas, and then the smaller Boulder Strip. There are also some single hotels with games spread around the Valley.
In 2011, most tourists (55%) came from western states, with 31% from California alone. About 16% of tourists came from outside North America.
Shopping in Las Vegas
Las Vegas has become more attractive to visitors by offering many shops and malls. You can find both affordable and high-end items. Many hotels on the Las Vegas Strip also have shopping malls next to them. This means the Las Vegas area has the most shopping malls in any four-mile stretch of road. Besides the malls on the Strip, there are several other malls in Las Vegas, Henderson, and nearby areas. The monorail helps people travel north and south, with stops at several hotels and the Las Vegas Convention Center.
Major shopping places include:
- Bonanza Gift Shop
- The Boulevard Mall
- Broadacres Marketplace
- The Shops at Crystals
- Downtown Summerlin
- Galleria at Sunset
- Grand Canal Shoppes
- Fantastic Indoor Swap Meet
- Fashion Show Mall
- The Forum Shops at Caesars
- Las Vegas Premium Outlets
- Meadows Mall
- Miracle Mile Shops
- Stratosphere Tower Shops
- Tivoli Village
- Town Square
Conventions in Las Vegas
Las Vegas hosts many of the world's largest conventions each year. These include CES, SEMA, and Conexpo. The Las Vegas Convention Center is one of the biggest in the world. It has over 1.9 million square feet of exhibit space. These events bring in about $7.4 billion in revenue to the city each year. They also host over 5 million attendees.
-
The Bellagio (left) and Caesar's Palace (right)
Culture and the Arts

The "First Friday" event happens on the first Friday of each month. It shows the work of local artists and musicians. The city has a large Downtown Arts District. This area has many art galleries, film festivals, and other events.
The Shark Reef Aquarium at Mandalay Bay is the only aquarium in Nevada accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums. It has over 2,000 animals and 1,200 species in 1.6 million gallons of seawater.
The Smith Center for the Performing Arts cost $485 million and is in downtown Las Vegas. It hosts Broadway shows, concerts, opera, jazz, and dance performances.
The Bellagio Gallery of Fine Art shows high-quality art from major museums. Past exhibits have included works by Andy Warhol and Alexander Calder.
The Las Vegas Natural History Museum has robot dinosaurs, live fish, and many preserved animals. There are also "hands-on" areas where you can pet some animals.
The Atomic Testing Museum is connected with the Smithsonian Institution. It has items from the Nevada Test Site. It tells the story of the atomic age through interactive displays, films, and real equipment.
In 2019, The New York Times noted that Las Vegas had a growing literary scene. This scene is centered around the Black Mountain Institute at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas.
The Valley also has many other art galleries, orchestras, ballets, theaters, sculptures, and museums.
Festivals
- CineVegas
- Helldorado Days
- Electric Daisy Carnival
- Feast of San Gennaro
- Las Vegas Pride Festival
- The Dam Short Film Festival
- Life is Beautiful
Gardens
- Alan Bible Botanical Garden
- Ethel M Botanical Cactus Garden
- Bellagio Conservatory & Botanical Gardens
- The Gardens at the Las Vegas Springs Preserve
- UNLV Arboretum
Libraries and Bookstores
- The Writer's Block
- Architecture Studies Library
- Las Vegas–Clark County Library District
- Lied Library (at UNLV)
- North Las Vegas Library District
Museums
- Atomic Testing Museum
- Clark County Heritage Museum
- Discovery Children's Museum
- Howard W. Cannon Aviation Museum
- The Linq Auto Collection
- Las Vegas Art Museum
- Las Vegas Museum of Organized Crime and Law Enforcement
- Las Vegas Natural History Museum
- Liberace Museum
- Lost City Museum
- Madame Tussauds
- Marjorie Barrick Museum (at UNLV)
- Neon Museum
- Nevada State Museum
- Nevada Southern Railroad Museum
- Pinball Hall of Fame
- Shelby Museum
- Southern Nevada Museum of Fine Art
- Thunderbirds Museum
Parks and Attractions

- Acacia Demonstration Gardens
- The Amanda & Stacy Darling Memorial Tennis Center
- Bettye Wilson Soccer Complex
- Clark County Shooting Park
- Clark County Wetlands Park
- Floyd Lamb Park at Tule Springs
- Hoover Dam
- Lake Mead National Recreation Area
- Las Vegas Motor Speedway
- Las Vegas Springs Preserve
- Mount Charleston
- Old Las Vegas Mormon Fort State Historic Park
- Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area
- Spring Mountains National Recreation Area
- Sunset Park
- Tule Springs Fossil Beds National Monument
- Valley of Fire State Park
- Cowabunga Canyon Waterpark
Theaters
- Huntridge Theater
- Lance Burton Theatre
- Las Vegas Little Theater
- The Smith Center for the Performing Arts
- Theatre for the Performing Arts
Wildlife Attractions
Communities in Las Vegas Valley
Cities
Las Vegas Neighborhoods
- Aliante
- Anthem/Anthem Country Club
- Cadence
- Centennial Hills
- Chinatown
- Downtown Las Vegas
- Green Valley
- Lake Las Vegas
- Las Vegas Country Club
- MacDonald Highlands
- Mountain's Edge
- Paradise Palms
- Queensridge & One Queensridge Place
- Red Rock Country Club
- Rhodes Ranch
- Seven Hills
- Southern Highlands
- Southern Highlands Golf Club
- Summerlin
- Summerlin South
- The Lakes
- The Ridges
- Tuscany Village
- West Las Vegas
Census-Designated Places

Other Communities
Media in Las Vegas
Newspapers
- Las Vegas Review-Journal is the area's largest daily newspaper. It started in 1909 and is the biggest newspaper in Nevada. It is one of the top 25 newspapers in the U.S. by how many copies it sells. In 2000, the Review-Journal installed the world's largest newspaper printing press. In 2018, it won an award for its reporting on the 2017 Las Vegas shooting.
- Las Vegas Sun is a daily 8-page newspaper. It is given out as part of the Review-Journal. The Sun started in 1950. It is known for being "politically liberal." In 2009, the Sun won a Pulitzer Prize for Public Service for its stories about the high death rate of construction workers on the Las Vegas Strip.
- Las Vegas Weekly is a free newspaper published every week. It covers arts, entertainment, culture, and news in Las Vegas. It started in 1992.
Broadcast Media
Las Vegas has 22 television stations and 46 radio stations. It also has two NOAA Weather Radio transmitters for weather alerts.
- Radio stations in Las Vegas
- Television stations in Las Vegas
Magazines
- Desert Companion
- Las Vegas Weekly
- Luxury Las Vegas
Transportation in Las Vegas

Harry Reid International Airport (LAS) handles commercial flights for the Las Vegas Valley. It serves flights for people, cargo, and some private planes. Smaller airports like North Las Vegas Airport are used for general aviation.
Public transportation is provided by RTC Transit. Many bus routes cover Las Vegas, Henderson, North Las Vegas, and other areas.
The Las Vegas Monorail runs from the MGM Grand Las Vegas at the south end of the Strip to the Sahara Las Vegas at the north end.
The street numbering system is divided by certain streets. For example, Westcliff Drive and Fremont Street divide north-south block numbers. Las Vegas Boulevard divides east-west streets. All city street signs start with N, S, W, or E.
Before 1997, the Amtrak Desert Wind train used to go through Las Vegas. Now, Amtrak offers bus service instead. There have been talks about bringing back train service between Los Angeles and Las Vegas.
Airports
- Henderson Executive Airport
- Ivanpah Valley Airport (planned)
- Harry Reid International Airport
- North Las Vegas Airport
Rail and Bus Services
Las Vegas does not have passenger train service right now. However, Brightline West plans to build a high-speed train between the Las Vegas station and Rancho Cucamonga in California.
Las Vegas receives about 30 freight trains per day. Freight traffic was 179,284 cars in 2004.
Existing Services
- RTC Transit
- Las Vegas Monorail
Resort Trams
- Aria Express
- Mandalay Bay Tram
- The Mirage-Treasure Island Tram
Roads

Two major freeways, Interstate 15 and Interstate 11 (which includes US 93 and US 95), meet in downtown Las Vegas. I-15 connects Las Vegas to Los Angeles and San Diego. It also goes northeast to Salt Lake City. I-11 goes northwest to the Las Vegas Paiute Indian Reservation and southeast to Henderson. US 95 connects the city to northwestern Nevada, including Carson City (the state capital) and Reno.
A large part of the Las Vegas Beltway has been built. This includes Interstate 215 on the south and Clark County 215 on the west and north. Other important roads include SR 160 to Pahrump and SR 147 and SR 564 to Lake Mead.
Most surface streets outside downtown Las Vegas are laid out in a grid pattern. Many are maintained by the Nevada Department of Transportation (NDOT) as state highways.
- East–West Roads (North to South)
- Elkhorn Road
 Las Vegas Beltway (CC 215)
Las Vegas Beltway (CC 215)- Ann Road
 Craig Road (SR 573)
Craig Road (SR 573) Cheyenne Avenue (SR 574)
Cheyenne Avenue (SR 574)- Carey Avenue
 Lake Mead Boulevard (SR 147)
Lake Mead Boulevard (SR 147)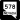 Washington Avenue (SR 578)
Washington Avenue (SR 578)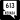 Summerlin Parkway (SR 613)
Summerlin Parkway (SR 613)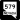 Bonanza Road (SR 579)
Bonanza Road (SR 579)
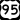 Interstate 11 and US 95
Interstate 11 and US 95
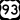
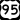 Interstate 11, US 93 and US 95
Interstate 11, US 93 and US 95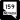 Charleston Boulevard (SR 159)
Charleston Boulevard (SR 159)- Sahara Avenue
- Desert Inn Road
- Spring Mountain Road
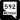 Flamingo Road (SR 592)
Flamingo Road (SR 592)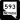 Tropicana Avenue (SR 593)
Tropicana Avenue (SR 593)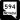 Russell Road (SR 594)
Russell Road (SR 594)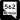 Sunset Road (SR 562)
Sunset Road (SR 562)- Warm Springs Road
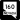 Blue Diamond Road (SR 160)
Blue Diamond Road (SR 160) Las Vegas Beltway (I-215)
Las Vegas Beltway (I-215)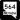 Lake Mead Parkway (SR 564)
Lake Mead Parkway (SR 564)- Horizon Ridge Parkway
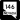 Saint Rose Parkway (SR 146)
Saint Rose Parkway (SR 146)
- North–South Roads (West to East)
 Las Vegas Beltway (CC 215)
Las Vegas Beltway (CC 215)- Durango Drive
- Buffalo Drive
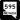 Rainbow Boulevard (SR 595)
Rainbow Boulevard (SR 595)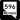 Jones Boulevard (SR 596)
Jones Boulevard (SR 596)- Decatur Boulevard
- Valley View Boulevard
- Dean Martin Drive
 Interstate 15
Interstate 15 Las Vegas Boulevard (SR 604)
Las Vegas Boulevard (SR 604) Rancho Drive (SR 599)
Rancho Drive (SR 599) Paradise Road (SR 605)
Paradise Road (SR 605)- Maryland Parkway
 Eastern Avenue (SR 607)
Eastern Avenue (SR 607)- Pecos Road

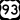
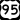 Interstate 11, US 93 and US 95
Interstate 11, US 93 and US 95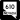 Lamb Boulevard (SR 610)
Lamb Boulevard (SR 610)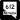 Nellis Boulevard (SR 612)
Nellis Boulevard (SR 612)
- Major Freeways
 Interstate 11
Interstate 11 Interstate 15
Interstate 15 Las Vegas Beltway (I-215)
Las Vegas Beltway (I-215) Las Vegas Beltway (CC 215)
Las Vegas Beltway (CC 215)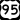 US 95
US 95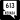 Summerlin Parkway (SR 613)
Summerlin Parkway (SR 613)
Fuel and Electricity
The Las Vegas area gets most of its gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuel from other places. It relies on the Calnev Pipeline and Unev pipeline. About 70% of the power to Southern Nevada comes from natural gas power stations. About 25% of the electricity from Hoover Dam goes to Nevada.
Sports in Las Vegas
Las Vegas is home to several sports teams. These include minor league teams and the UNLV Rebels college team. It also has three major professional teams: the Las Vegas Raiders (football), the Vegas Golden Knights (ice hockey), and the Las Vegas Aces (women's basketball). The Oakland Athletics baseball team plans to move to Las Vegas in 2028.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Since | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Raiders | Football | NFL | Allegiant Stadium (65,000) | 2020 | 3 |
| Vegas Golden Knights | Ice hockey | NHL | T-Mobile Arena (17,368) | 2017 | 1 |
| Las Vegas Aces | Basketball | WNBA | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 2018 | 2 |
| Las Vegas Aviators | Baseball | PCL | Las Vegas Ballpark (10,000) | 1983 | 2 |
| Henderson Silver Knights | Ice hockey | AHL | Dollar Loan Center (5,567) | 2021 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Lights FC | Soccer | USLC | Cashman Field (9,300) | 2018 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Desert Dogs | Box Lacrosse | NLL | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 2021 | 1 |
Recreation
Las Vegas offers many outdoor activities in nature.
There are several trail systems in the Valley. These are managed by different groups. The River Mountains Loop Trail is a 35-mile long trail. It connects the west side of the Valley with Hoover Dam and Lake Mead. Summerlin has over 150 miles of trails within its 22,500-acre community. Other trails include the 3-mile Angel Park Trail and the Flamingo Arroyo Trail.

The Las Vegas Valley also has great mountain biking. Bootleg Canyon Mountain Bike Park in Boulder City is known as one of the best "epic rides" by the International Mountain Biking Association.
Education
Primary and Secondary Schools
The Clark County School District runs all public primary and secondary schools in the county. There are also 37 public charter schools.
- Selected Private Schools
- Alexander Dawson School
- Bishop Gorman High School
- Faith Lutheran Jr/Sr High School
- The Meadows School
Colleges and Universities
The University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) is in Paradise. It is about three miles south of Las Vegas city limits. Several national colleges have campuses in the Las Vegas area. These include the University of Phoenix and Le Cordon Bleu. Nevada State College, National University, and Touro University Nevada are nearby in Henderson. The College of Southern Nevada has campuses in Las Vegas, North Las Vegas, and Henderson. Henderson is also home to DeVry University and the Roseman University of Health Sciences. Carrington College also has a location in the Las Vegas Valley.
Venues in Las Vegas
- Music venues in Las Vegas
- Sports venues in Las Vegas
- City of Rock (Las Vegas)
Images for kids
-
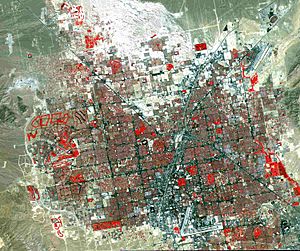
Las Vegas Valley viewed in false color, from 438 miles by TERRA satellite. Grass-covered land, such as golf courses, appears in red. The picture bottom is just south of Sunset Road and the airport, the Spring Mountains on the west and Sunrise Mountain on the east.
-
Lake Mead shown behind Hoover Dam on the Colorado River
-
The Las Vegas Strip looking south at night
-
A full-scale mockup of Bigelow Aerospace's Space Station Alpha inside their facility in North Las Vegas
-
Chanel and Giorgio Armani boutiques at Via Bellagio
-
The Bellagio (left) and Caesar's Palace (right)
-
The Smith Center for the Performing Arts located in downtown Las Vegas
-
Wildflowers in Red Rock Canyon National Conservation Area
-
The Las Vegas Strip in 2004, as seen from the top of the Rio. The Strip is largely within Paradise.
-
The entrance to Summerlin, an affluent planned community
-
The Las Vegas Monorail pulling into the Sahara station in Paradise
-
A JetBlue Airbus A320 taking off from Harry Reid International Airport
-
Las Vegas Boulevard looking south from the Stratosphere
-
T-Mobile Arena as seen from Toshiba Plaza
-
Sunset Park at dusk
See also
 In Spanish: Área metropolitana de Las Vegas para niños
In Spanish: Área metropolitana de Las Vegas para niños
- Architecture of Las Vegas
- List of Las Vegas Strip hotels
- List of people from Las Vegas
- List of restaurants in the Las Vegas Valley
- Las Vegas shows
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |