IBM facts for kids

Logo since 1972, designed by Paul Rand
|
|

IBM CHQ in Armonk, New York, in 2014
|
|
|
Trade name
|
IBM |
|---|---|
|
Formerly
|
Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (1911–1924) |
| Public | |
| Traded as | |
| ISIN | ISIN: [https://isin.toolforge.org/?language=en&isin=US4592001014 US4592001014] |
| Industry | Information technology |
| Predecessors |
|
| Founded | June 16, 1911 (as Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company) Endicott, New York, U.S. |
| Founders |
|
| Headquarters | 1 Orchard Road,
,
United States
|
|
Area served
|
177 countries |
|
Key people
|
|
| Products | Automation Robotics Artificial intelligence Cloud computing Consulting Blockchain Computer hardware Software Quantum computing |
| Brands |
|
| Services |
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
270,300 (2024) |
| Subsidiaries | Pre-WW2 list of subsidiaries |
International Business Machines Corporation, known as IBM and nicknamed Big Blue, is a huge technology company. It started in the United States but now works in over 175 countries around the world. IBM is one of the biggest companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average, which tracks major US companies.
IBM is famous for its research. It has 19 research centers in many countries. For 29 years in a row, from 1993 to 2021, IBM earned the most US patents each year compared to other businesses. This means they invented and officially registered more new things than anyone else!
IBM began in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR). This company brought together several smaller businesses that made machines for keeping records and measuring things. In 1924, its name changed to "International Business Machines." Soon, it became the top maker of punch-card tabulating systems.
In the 1960s and 1970s, IBM's mainframes, like the IBM System/360, were the most important computers in the world. IBM made 80% of computers in the US and 70% worldwide. The System/360 was special because it was the first computer family designed to handle all kinds of tasks, from small to very large.
In 1981, IBM entered the microcomputer market with the IBM Personal Computer. Its software, made by Microsoft, became the foundation for most personal computers we use today. Later, IBM also had success with its ThinkPad portable computers. Since the 1990s, IBM has focused on computer services, software, supercomputers, and scientific research. They sold their personal computer division to Lenovo in 2005. IBM still builds mainframes, and its supercomputers are among the most powerful in the world.
IBM has created many important inventions. These include the Automated Teller Machine (ATM), DRAM (a type of computer memory), the floppy disk, the hard disk drive, the magnetic stripe card (used in credit cards), the relational database, the SQL programming language, and the Universal Product Code (UPC) barcode. The company also works on advanced computer chips, quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and data infrastructure. IBM employees have won many awards for their work, including six Nobel Prizes and six Turing Awards.
Contents
IBM's Journey Through Time
Early Days: From Scales to Computers (1910s–1950s)
IBM's story started with several cool inventions from the late 1800s. People like Julius E. Pitrap invented a computing scale in 1885. Alexander Dey created a dial recorder in 1888. Herman Hollerith patented his Electric Tabulating Machine in 1889. And Willard Bundy invented a time clock in 1889 to track when workers arrived and left.
On June 16, 1911, these four companies joined together in New York. They formed a new company called the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR). This company had 1,300 employees and offices in several cities.
CTR made many different machines. These included commercial scales, time recorders, meat slicers, and machines that used punched cards. In 1914, Thomas J. Watson, Sr. became the general manager of CTR. He brought new ideas about sales and customer service. His famous slogan, "THINK", became a motto for all employees.
Watson wanted a better name for the company. On February 14, 1924, CTR was renamed "International Business Machines," or IBM. By 1933, most of the smaller companies had merged into one big IBM.
During World War II, IBM helped the US military. They produced about 346,500 M1 Carbine rifles. IBM also built the Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator, an early electromechanical computer. In 1952, IBM offered its first commercial computer that could store programs, the IBM 701. In 1956, the IBM 305 RAMAC introduced the hard disk drive, which was a big step forward for storing data.
IBM started using transistors in their computers in 1958. This made computers smaller and faster. In 1956, an IBM scientist named Arthur L. Samuel created a program that could play checkers and actually learn from its mistakes. This was an early example of artificial intelligence. In 1957, the FORTRAN programming language was developed, which was very important for science.

The Rise of Computing (1960s–1980s)
In 1961, IBM created the SABRE reservation system for American Airlines. They also introduced the very popular Selectric typewriter. That same year, an IBM computer, the IBM 7094, created the first song sung completely by a computer: "Daisy Bell."
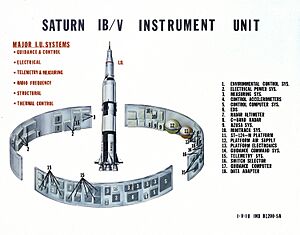
IBM helped NASA track the flights of the Mercury astronauts in 1963. A year later, IBM moved its main office to Armonk, New York. IBM continued to support space exploration, helping with the Gemini flights in 1965 and the Apollo lunar mission in 1969. IBM even built the guidance computers for the Saturn V rocket.
On April 7, 1964, IBM launched the IBM System/360. This was a family of computers that could handle all kinds of business and science tasks. Companies could easily upgrade to more powerful models without rewriting their software. The System/360 and its successor, the IBM System/370 (from 1970), made IBM's mainframes the most important computers in the industry for many years.
In 1969, an IBM engineer named Forrest Parry invented the magnetic stripe card. This invention is now used everywhere for credit cards, debit cards, and ID cards. In 1974, another IBM engineer, George J. Laurer, developed the Universal Product Code (UPC), which is the barcode you see on almost every product.
IBM entered the microcomputer market in the 1980s with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM 5150). This computer became one of IBM's best-selling products and greatly influenced how personal computers developed. However, because IBM didn't protect its ideas well enough, other companies quickly started making "compatible" PCs, and IBM lost some of its market lead.
In 1985, IBM worked with Microsoft to create a new operating system called OS/2. But they had disagreements, and Microsoft went on to develop Windows, which became much more popular than OS/2.
Focusing on Software and Services (1990s–2000s)
In the 1990s, IBM started to change. They began to sell off some of their divisions to make the company easier to manage. For example, Lexmark, which makes printers, became a separate company.
In 1992, IBM created the IBM Personal Computer Company (IBM PC Co.) to focus on personal computers. This happened after IBM saw a big drop in profits because of price wars in the PC market. The IBM PC Co. introduced the ThinkPad computers, which became very popular notebook computers.
In 1993, IBM had a huge financial loss. Lou Gerstner was hired as CEO to help the company recover. In 1995, IBM bought Lotus Software, known for its Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheet program.

By 1999, IBM stopped selling its computers in regular stores because companies like Compaq and Dell had taken over that market. The IBM PC Co. was then merged into IBM's other divisions.
In 2002, IBM bought PwC Consulting, a large consulting firm. This helped IBM grow its Global Services business. In 2004, IBM sold its entire personal computer business to a Chinese company called Lenovo. This showed IBM's shift away from making hardware like PCs and towards software and services.
In 2009, IBM bought the software company SPSS Inc.. Also in 2009, IBM's Blue Gene supercomputing program received the National Medal of Technology and Innovation from the US President.
Modern Innovations (2010s–Present)
In 2011, IBM's Watson artificial intelligence program became famous. It competed on the TV game show Jeopardy! and won against human champions. That same year, IBM celebrated its 100th anniversary.
In 2014, IBM sold its x86 server division to Lenovo. IBM also started many big partnerships with other companies like Apple Inc., Twitter, Facebook, and Microsoft.
In 2015, IBM made its chip division focus on designing semiconductors rather than making them. They also bought several companies, including Merge Healthcare and Cleversafe Inc., and the digital assets from The Weather Company, which includes Weather.com.
In 2018, IBM announced it would buy Red Hat, a major open-source software company, for $34 billion. This deal was completed in 2019.
In 2020, IBM announced it would create a new public company called Kyndryl from its managed infrastructure services unit. This was a big change for IBM, allowing it to focus more on its core businesses.
In 2022, IBM announced it would sell Watson Health. Also, after the start of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, IBM suspended all its business operations in Russia.
In 2023, IBM bought Manta Software Inc. to improve its data and AI tools. In December 2023, IBM announced it would buy parts of Software AG for a large sum. In February 2024, IBM finalized the sale of The Weather Company to Francisco Partners.
How IBM Works
Business Overview
IBM is a very large company. In May 2024, its value was over $153 billion. It's the seventh largest technology company by how much money it makes.
Here's a quick look at IBM's business over the last few years:
| Year | Revenue (US$ bn) |
Net income (US$ bn) |
Employees |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 77.1 | 9.4 | 352,600 |
| 2020 | 73.6 | 5.5 | 345,900 |
| 2021 | 57.3 | 5.7 | 282,100 |
| 2022 | 60.5 | 1.6 | 288,300 |
| 2023 | 61.8 | 7.5 | 282,200 |
| 2024 | 62.8 | 6.0 | 270,300 |
Main Offices and Locations
IBM's main headquarters is in Armonk, New York. People sometimes call the company the "Colossus of Armonk" because it's so big. The main building is a large glass and stone building on a former apple orchard.
IBM has offices in 174 countries. Besides Armonk, they have big offices in places like Austin, Texas; Research Triangle Park, North Carolina; and Silicon Valley, California.
Around the world, IBM has offices in many famous buildings. These include 1250 René-Lévesque in Montreal, Canada, and Pangu Plaza in Beijing, China. IBM India, a big part of the company, has offices in many Indian cities like Bangalore and Chennai.
What IBM Makes and Does
Computer Hardware
Mainframe Computers
Since 1954, IBM has sold mainframe computers. These are very powerful computers used by large organizations. The newest model is the IBM z17, released in 2024.
Microprocessors
In 1990, IBM released its Power microprocessors. These chips were used in many popular gaming systems, including Xbox 360, PlayStation 3, and Nintendo's Wii U. IBM also developed TrueNorth in 2014, a special chip designed to work like the human brain.
Quantum Computing

In January 2019, IBM showed off its first commercial quantum computer, called IBM Q System One. Quantum computers are a new type of computer that can solve very complex problems much faster than regular computers. In March 2020, IBM announced it would build Europe's first quantum computer in Germany, which opened in 2024.
Software
IBM owns SPSS, a software program used for statistical analysis in many fields. IBM also used to own The Weather Company, which provides weather forecasts and includes weather.com. This was sold in 2024.
Cloud Services
IBM Cloud offers many services over the internet. These include infrastructure as a service (IaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and platform as a service (PaaS). This means companies can use IBM's computing power, software, or tools without having to buy and maintain their own equipment. For example, IBM Bluemix helps developers quickly build websites. IBM SoftLayer hosts many servers for thousands of customers.
In May 2022, IBM and Amazon Web Services (AWS) agreed to make IBM software available on AWS Marketplace. This makes it easier for companies to use IBM's tools with AWS.
Artificial Intelligence
IBM Watson is a special technology that uses natural language processing and machine learning. It can understand human language and find important information in huge amounts of data. Watson became famous in 2011 when it won on Jeopardy!.
Watson is now used in many areas, like business and healthcare. For example, it helps doctors at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center consider treatment options for cancer patients. Some companies use Watson to help or even replace customer service agents in call centers.
In June 2020, IBM announced it was stopping its facial recognition business. IBM's CEO said it was time to talk about how this technology should be used by police.
In May 2023, IBM introduced Watsonx, a set of tools for Generative AI. This is powered by IBM's own Granite models, which can create new text, images, or other data. In October 2024, IBM made its Granite 3.0 models available for public use.
Consulting Services
IBM Consulting is one of the largest consulting companies in the world. As of 2024, it has 160,000 consultants globally. They help businesses with their strategies, designs, technology, and operations.
IBM's Research and Inventions

Research has been a key part of IBM since it started. Their first lab was founded in 1945 at Columbia University. Today, IBM Research is the biggest industrial research group in the world, with 12 labs on 6 continents. The main research center is the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in New York.
IBM spends billions of dollars on research and development every year. They have invested in areas like Watson and new semiconductors.
IBM has been a big supporter of open source software. They started supporting Linux in 1998 and have invested a lot in it. IBM has also released its own code as open source, like the Eclipse software framework.
Many famous inventions and developments came from IBM. These include the automated teller machine (ATM), Dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), the floppy disk, the hard disk drive, the magnetic stripe card, the relational database, SQL, the Universal Product Code (UPC) barcode, and the virtual machine. In 1990, IBM scientists even used a special microscope to arrange 35 individual atoms to spell out "IBM."
IBM is known for getting many patents. Since its first patent for a traffic signaling device, IBM has been one of the companies with the most patents in the world. In 2021, they held the record for the most US patents for 29 years in a row.
Patents
As of 2021, IBM held the record for the most annual U.S. patents generated by a business for 29 years in a row. In 2001, IBM was the first company to get over 3,000 patents in one year. By 2008, they had over 4,000 patents in a single year. As of 2022, the company had 150,000 patents in total.
IBM's Brand and Public Image

IBM is called Big Blue because of its blue logo and color scheme. Also, in the past, employees often wore white shirts with blue suits. The company's logo has changed over the years. The current "8-bar" logo was designed in 1972 by Paul Rand.
IBM has a very valuable brand because of its long history and marketing. Since 1996, IBM has been the technology partner for the Masters Tournament in golf. They created the first Masters website and the first iPhone app with live streaming for the event. IBM is also a big sponsor in professional tennis, supporting events like the U.S. Open and Wimbledon.
Environmental Efforts
IBM has been working to reduce its impact on the environment. In February 2021, IBM promised to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. This means they aim to remove as much greenhouse gas from the atmosphere as they put into it.
People and Culture at IBM
Employees
IBM is one of the largest employers in the world. In 2022, it had over 297,900 employees globally. About 160,000 of these employees are tech consultants.
IBM has special programs for its employees, like Extreme Blue, an internship program. They also have the IBM Fellow award, given to employees for their amazing technical achievements.
Famous People from IBM
Many people who worked at IBM became famous in other fields. For example, Tim Cook, the CEO of Apple Inc., used to work at IBM. So did Lisa Su, the CEO of Advanced Micro Devices (AMD).
In government, Patricia Roberts Harris became the first African American woman to serve in the United States Cabinet. Julie Payette, a Canadian astronaut and former Governor General, also worked at IBM.
Five IBM employees have won the Nobel Prize for their scientific work. Six IBM employees have won the Turing Award, which is like the Nobel Prize for computer science.
Workplace Culture
IBM employees are often called "IBMers." The company's culture has changed a lot over the years. In the past, employees had a strict dress code, but this became more relaxed in the 1990s.
The company has a slogan, "THINK", which encourages employees to be creative and solve problems.
IBM's Leaders
President
- Thomas J. Watson, 1911–1949
- John George Phillips, 1949–1951
- Thomas J. Watson Jr., 1951–1961
- Albert Lynn Williams, 1961–1966
- T. Vincent Learson, 1966–1971
- Frank T. Cary, 1971–1974
- John R. Opel, 1974–1983
- John Fellows Akers, 1983–1989
- Jack Kuehler, 1989–
- Samuel J. Palmisano, 2000–2012
- Ginni Rometty, 2012–2020
- Arvind Krishna, 2020–present
Chairman of the Board
- George Winthrop Fairchild, 1915–1949
- Thomas J. Watson, 1949–1961
- Thomas J. Watson Jr., 1961–1971
- T. Vincent Learson, 1971–1972
- Frank T. Cary, 1972–1983
- John R. Opel, 1983–1986
- John Fellows Akers, 1986–1993
- Lou Gerstner, 1993–2002
- Samuel J. Palmisano, 2003–2012
- Ginni Rometty, 2012–2020
- Arvind Krishna, 2020–present
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: IBM para niños
In Spanish: IBM para niños