Governor General of Canada facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Governor General of Canada |
|
|---|---|

Flag of the governor general
|
|

Badge of the governor general
|
|
| Style | |
| Abbreviation | GG |
| Residence |
|
| Appointer | Monarch of Canada
on the advice of the prime minister
|
| Term length | At His Majesty's pleasure (generally 3 to 7 years) |
| Formation | 1 July 1867 |
| First holder | The Viscount Monck |
| Deputy | Deputies of the governor general
|
| Salary | $342,100 annually |
The governor general of Canada (French: gouverneure générale du Canada) is the King's representative in Canada. The King of Canada is also the head of state for 14 other countries in the Commonwealth of Nations. He lives in the United Kingdom.
The King appoints a governor general to help run the government of Canada. This appointment is usually for about five years. Since 1959, it has been a tradition to choose someone who speaks French and then someone who speaks English.
The 30th and current governor general is Mary Simon. She started her role on July 26, 2021. Mary Simon is an Inuk leader from Nunavik, Quebec. She is the first Indigenous person to hold this important job.
The governor general performs daily duties for the King. These duties include both constitutional and ceremonial tasks. Constitutional duties involve appointing important officials like lieutenant governors and senators. They also sign official documents and call elections. Ceremonial duties include giving speeches and handing out awards. The governor general usually acts on the advice of the prime minister.
This important office started in the 17th century. Back then, the French King appointed governors for the colony of Canada. After the British took over in 1763, the British King appointed governors. The current role of governor general began when Canada became a country in 1867. This happened with the British North America Act, 1867.
At first, the governor general also represented the government of the United Kingdom. Over time, the role became more Canadian. By 1931, with the Statute of Westminster, 1931, the governor general became the direct representative of the Canadian King. This meant Canada had its own separate monarchy. The governor general also became the commander-in-chief of Canada's military. In 1947, King George VI allowed the governor general to use almost all of the King's powers in Canada.
Contents
Choosing the Governor General
The job of governor general is set out in Canada's laws. These include the Constitution Act, 1867 and the Letters Patent, 1947. The Canadian King appoints the governor general. This happens after the Canadian prime minister recommends someone. The appointment document is prepared in Canada.
Before 1952, the King's signature and seal were used. Since then, the Great Seal of Canada is used. The person chosen is called the governor general-designate until they are officially sworn in.
There is no exact rule for how the swearing-in ceremony happens. However, the person usually travels to Ottawa. They get an official welcome and move into 7 Rideau Gate. They meet with important officials to prepare for their new role. The King also meets with the person chosen. He makes them a Companion of the Order of Canada. They also become a Commander of the Order of Military Merit and the Order of Merit of the Police Forces.
The governor general usually serves for at least five years. This is a tradition, but it can be longer. The governor general serves "at His Majesty's pleasure". This means the prime minister can ask the King for them to stay longer. Some governors general have served for more than seven years. No special steps are needed for this extension. The governor general stays until they die, resign, or a new one is appointed.
If a governor general dies, resigns, or leaves the country for over a month, the chief justice of Canada takes over. They become the administrator of the government. They perform all the duties of the governor general.
How the Governor General is Selected
From 1867 to 1931, the British government chose the governor general. They would consult with the Canadian government. However, this was not always followed.
In 1926, the Balfour Declaration of 1926 changed things. It said the governor general was a direct representative of the King. They were no longer a stand-in for the British government. In 1930, it was decided that Canadian ministers would advise the King. This meant the King would appoint the governor general only on the advice of the Canadian prime minister. This rule became law in 1931.
The prime minister can suggest one or more names to the King. There are usually informal talks between the prime minister and the King. This happens before the official advice is given.

Only once was the leader of the opposition consulted. This happened in 1935 when Lord Tweedsmuir was chosen.
Until 1952, all governors general were British. They were often from noble families or were former military officers. They usually had not spent much time in Canada before their appointment. The idea of a Canadian governor general came up as early as 1919. But it was not until Vincent Massey was appointed in 1952 that a Canadian-born person held the job. The prime minister at the time, Louis St. Laurent, said that any Canadian could represent the King if they were qualified. Massey said that a Canadian governor general made it easier to see the King as "our own."
This practice continued until 1999. That year, Queen Elizabeth II appointed Adrienne Clarkson. She was born in Hong Kong and came to Canada as a refugee. Also, the tradition of switching between French-speaking and English-speaking Canadians began. This started with Georges Vanier, a francophone, who followed the anglophone Massey. All people suggested for the role are checked by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police.
Governors general are supposed to be neutral while in office. However, many were former politicians. Adrienne Clarkson was the first governor general without a political or military background. She was also the first Asian-Canadian and the second woman. The third woman to hold the position was Michaëlle Jean. She was also the first Caribbean-Canadian governor general.
There have been ideas to change how the governor general is chosen. Some people suggest a public vote. Others propose a parliamentary committee. However, many experts believe that not electing the governor general helps them stay neutral. This neutrality is important for the job.
In 2010, a new way was used to choose David Johnston. Prime Minister Stephen Harper created a special committee. This committee looked for a non-political candidate. They talked to over 200 people across Canada. In 2012, this committee became permanent. It was called the Advisory Committee on Vice-Regal Appointments. However, the next prime minister, Justin Trudeau, ended this committee in 2017. He later formed a new group to select Mary Simon.
The Swearing-in Ceremony

The swearing-in ceremony starts at 7 Rideau Gate. A government minister goes with the governor general-designate to Parliament Hill. There, a Canadian Forces guard of honour greets them. They are then led to the Senate chamber. Many important people are there, including Supreme Court justices and members of Parliament.
The King's official document for the governor general is read aloud. Then, the chief justice or another Supreme Court justice gives the appointee three oaths. These are the Oath of Allegiance, the Oath of Office as Governor General, and the Oath as Keeper of the Great Seal of Canada. Once they sign these oaths, they are officially the governor general.
At that moment, the flag of the governor general of Canada is raised on the Peace Tower. The "Vice Regal Salute" is played, and a 21-gun salute is fired. The governor general then gives a speech. They talk about the causes they will support during their time in office.
What the Governor General Does

Canada shares its King with 14 other countries. The King lives in the United Kingdom. So, the governor general's main job is to perform the King's duties in Canada. They carry out "the government of Canada on behalf and in the name of the sovereign."
The governor general works within Canada's parliamentary democracy. They ensure stable government. They also act as a neutral protector against power abuse. Most of the King's powers are used by elected officials. This leaves the governor general to do many ceremonial duties. If the King is in Canada, the governor general steps back from public view.
A past governor general, John Campbell, said the job needs "the patience of a saint." Another, the Earl of Dufferin, said the governor general is "a representative of all that is august, stable, and sedate." They are above political arguments.
Constitutional Duties
All government power in Canada belongs to the King. The governor general can use most of this power in the King's name. This is allowed by the Constitution Act, 1867 and other official documents. The 1947 documents state that the governor general can use "all powers and authorities lawfully belonging to Us in respect of Canada." However, the governor general does not have these powers on their own. They use them with the King's permission. The King alone appoints the governor general.
The governor general can also appoint deputies. These are usually Supreme Court justices. They can perform some duties if the governor general is away. If the governor general dies or resigns, the chief justice of the Supreme Court takes over.

The governor general appoints people to the King's Privy Council for Canada. This group advises the King and governor general. By tradition, the governor general must choose a prime minister from this group. This is usually the person who has the support of the House of Commons. The prime minister then advises the governor general to appoint other members to the Cabinet. The King and governor general usually follow the Cabinet's advice. This is called the governor-in-Council.
The governor-in-Council appoints lieutenant governors for the provinces. They also appoint senators and judges. They appoint ambassadors too. The governor general's role is mainly to advise, encourage, and warn the prime minister.
The King and governor general can use special "reserve powers" in rare cases. These powers are a final check against abuse of power. For example, in 1925, Prime Minister Mackenzie King asked Governor General Byng to call an election. Byng refused because an election had just happened. This event led to changes in how the governor general's role was understood.
After 1926, governors general stopped taking advice from British ministers. They only took advice from Canadian ministers. It was also decided that the governor general should be fully informed about government business.

The governor general also calls Parliament together. They read the speech from the throne, which outlines the government's plans. They can also end or dissolve Parliament. The governor general gives royal assent to bills. This makes them laws. They have three choices: approve the bill, reject it, or send it to the King for his decision. No governor general has ever rejected a bill.
Ceremonial Duties
Since most constitutional duties are handled by the Cabinet, the governor general mainly performs ceremonial tasks. They host members of Canada's royal family and foreign leaders. They also represent Canada on state visits to other countries. The governor general also issues official documents for Canadian ambassadors. They receive similar documents from foreign ambassadors.
The governor general also helps promote national unity and pride. They travel across Canada and meet with people from all backgrounds. This tradition started in 1869. The governor general also presents national honours and medals. They give out the Governor General's Awards and other awards. During an election, the governor general reduces public duties. This is to avoid looking like they are involved in politics.
The King is the Commander-in-Chief of Canada's military. But the governor general acts in his place. They are called the Commander-in-Chief in and over Canada. This role involves visiting military bases. They take part in military ceremonies and encourage the troops. The governor general is also an honorary Colonel of three special regiments. Since 1910, the governor general has also been the Patron Scout for Canada.
Homes and Staff
Rideau Hall in Ottawa is the official home of the Canadian King and the governor general. It is also where the governor general's staff works. Since 1872, governors general have also stayed at the Citadel in Quebec City, Quebec for part of the year.
The governor general's staff helps them with their duties. This staff is managed by the secretary to the governor general. The Chancellery of Honours is also located at Rideau Hall. It is managed by the governor general. This office grants coats of arms to Canadians.
The staff includes aides, press officers, and financial managers. There are also speech writers, event planners, and chefs. This entire office is often called Government House. Its costs are covered by the federal budget. The governor general's salary is also paid this way.
The governor general travels by special aircraft. These jets are used for travel within Canada and abroad.
Symbols and Rules
The governor general is second only to the King in Canada's order of importance. They are more important than other members of the royal family. The governor general is also more important than provincial lieutenant governors at federal events. However, at provincial events, the lieutenant governor is more important. The governor general and their spouse are called His or Her Excellency. The governor general also gets the title the Right Honourable for life.
Until 1952, all governors general were British nobles. Since then, Canadian citizens have been appointed.
The governor general is the head of the Order of Canada. They are also the head of the Order of Military Merit and the Order of Merit of the Police Forces. They also become a Knight or Dame of the Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem. They also receive the Canadian Forces' Decoration. They keep all these honours after leaving office.
The Viceregal Salute is played when the governor general arrives or leaves official events. It is made up of parts of "God Save the King" and "O Canada". The governor general's flag is flown to show their presence. This flag was adopted in 1981. It is more important than all other flags in Canada, except the King's flag. When the governor general travels abroad, the national flag is usually used.
The crest of the Royal Arms of Canada is the governor general's badge. It appears on their flag and other items. This is the fourth version of the badge since Canada became a country.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1901 | 1921 | 1931 | 1953 | 1981 |
The governor general can also wear a special military uniform. It has unique badges and markings.
| Royal Canadian Navy | Canadian Army | Royal Canadian Air Force | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Board | Sleeve | Board | Sleeve | Board | Sleeve |
History of the Role
Early Governors in Colonies
French settlement in North America began in the 1580s. Aymar Chaste was appointed Viceroy of Canada in 1602. Samuel de Champlain was the first unofficial governor of New France. In 1636, Charles Huault de Montmagny became the first formal governor. Later, King Louis XIV appointed Augustin de Saffray de Mésy as the first governor general in 1663.

After the Treaty of Paris in 1763, France gave most of its North American lands to Great Britain. King George III then created the Office of the Governor of Quebec. Other colonies like Nova Scotia and New Brunswick had their own governors. In 1786, a "governor-in-chief" role was created. Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester was the first. He directly governed Quebec.
In 1791, Quebec was split into Upper and Lower Canada. The King's representative then became known as the Governor General. He directly governed Lower Canada. Other colonies were managed by lieutenant governors.
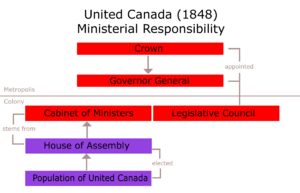
Responsible Government and Canadian Control
The Rebellions of 1837 led to big changes. The British government gave "responsible government" to Canadian provinces. This meant that elected lawmakers and their leaders (premiers) had more power. The governor general became more of a symbolic head. This was first tested in 1849. Governor General James Bruce, 8th Earl of Elgin approved a bill he disagreed with.
This system continued after Upper and Lower Canada joined in 1840. It also continued when Canada became a Dominion in 1867. The governor general performed many duties of a constitutional monarch. These included approving laws and taking advice from the Canadian Privy Council. However, the governor general was still a link to the British government.
In 1880, Canada created the role of Canadian high commissioner to the United Kingdom. This person started to take over the governor general's role as a link between Canada and Britain. This made the governor general more of a personal representative of the King. The governor general had to stay politically neutral.
Canada's Growing Independence

During the First World War, the governor general's role changed. It became more about military support and boosting morale. Governor General Prince Arthur wore his military uniform. He inspected army camps and saw troops off to Europe.
After the war, Canadians wanted more independence from Britain. The governor general's role began to focus more on Canadian affairs. They started making official international visits for Canada. The first was by the Marquess of Willingdon to the United States. He was treated like a head of state.
The King–Byng affair in 1926 was another big moment. Prime Minister Mackenzie King asked Governor General Byng to call an election. Byng refused. This led to discussions about the governor general's role. It resulted in the Balfour Declaration of 1926. This declaration said that Canada and other Dominions were fully independent. These changes became law in 1931. The governor general became solely the King's representative in Canada. They no longer represented the British government.

The first governor general chosen under this new system was John Buchan (Lord Tweedsmuir). He was British-born. However, he strongly supported the idea of a unique Canadian identity. He traveled all over Canada, including the Arctic. He said that a Canadian's first loyalty was to Canada and Canada's King. This upset some people who wanted closer ties to Britain.
During Tweedsmuir's time, people started asking for a Canadian-born governor general. But Tweedsmuir died in office in 1940. Canada was in the middle of the Second World War. So, King George VI appointed his nephew, the Earl of Athlone, for the war.
Modern Era and Challenges

In 1952, Vincent Massey became the first Canadian-born governor general since 1755. He was also the first not to be a noble. This was a big change. Massey was known for his loyalty and dignity.
As Massey's term ended, it was decided that a French-speaking Canadian should follow him. So, Georges Vanier was chosen. He was appointed by Queen Elizabeth II herself. This started the tradition of alternating between French and English speakers. However, this did not stop the growing Quebec nationalist movement. They sometimes criticized the monarchy and federal institutions.
Vanier's successor, Roland Michener, was the last to follow many old traditions. These included wearing special court uniforms. He also started new practices, like meeting regularly with lieutenant governors. He oversaw Canada's centennial celebrations in 1967. He was with French president Charles de Gaulle when he made his famous "Vive le Québec libre" speech in Montreal.
With Canada's growing role in the world, the governor general became more active. They made more state visits. The use of television also helped bring their role into public view.
In 1978, a proposal was made to change the governor general's role. It suggested renaming the position "First Canadian." But this idea was stopped by the provinces. In 1982, when Canada's constitution was brought home, a new rule was set. Any changes to the King's role, including the governor general, need approval from all provinces and the federal Parliament.
In 1984, Jeanne Sauvé became Canada's first female governor general. She created the Canadian Heraldic Authority. She also supported youth and world peace.
Recent Governors General

After Jeanne Sauvé, there were several appointments that were seen as less impactful. This led to the office being less noticed by the public.
However, when Queen Elizabeth II appointed Adrienne Clarkson in 1999, things changed. Clarkson was the first governor general without a political or military background. She was a television journalist. She was also the first from a visible minority (Chinese background). Clarkson helped bring the office back into public attention. She toured the country more than her predecessors. She gave inspiring speeches and supported the military.
Her time in office also brought some criticism. There were concerns about increased spending. Some also felt she presented the governor general as the head of state above the Queen. This caused some debate.
Prime Minister Paul Martin then recommended Michaëlle Jean as Clarkson's successor. Jean was also a woman, a refugee, and a journalist. Her appointment initially faced some questions. But she gained praise for her support of the Canadian Forces and indigenous peoples in Canada. She also played a role in a parliamentary dispute in 2008-2009.
The appointment of David Johnston in 2010 emphasized learning and innovation. Johnston was a former university president. He focused on making Canada a society that innovates. His knowledge of constitutional law was also important. This was after some debates about the governor general's role in Parliament.
In late 2021, the governor general's office had a cyber incident. Officials could not tell how much information was accessed. Security experts thought another country might be responsible. The Canadian Centre for Cyber Security is investigating.
After the Role Ends
Former governors general often step back from public life. Some take on other public roles. For example, Edward Schreyer became the Canadian High Commissioner to Australia. Michaëlle Jean became a special envoy for UNESCO. She later became the secretary-general of La Francophonie. Schreyer was also the first former governor general to run for elected office in Canada.
Before 1952, some former governors general returned to politics in the United Kingdom. They served in the British Parliament or Cabinet. Others became governors in different countries. For example, the Earl of Dufferin and the Earl of Willingdon both served as Viceroy of India.
An outgoing governor general might leave behind a special award. Examples include the Stanley Cup, the Clarkson Cup, the Vanier Cup, or the Grey Cup. They might also start an organization. Georges Vanier founded the Vanier Institute of the Family. Adrienne Clarkson founded the Institute for Canadian Citizenship.
As of 2021, former governors general receive a lifetime pension. They can also claim expenses each year.
| Institution | Founded by |
|---|---|
| Royal Society of Canada | John Campbell, Marquess of Lorne |
| Canada's first anti-tuberculosis association | The Earl of Minto |
| The Battlefields Park | The Earl Grey |
| King George V Silver Jubilee Cancer Fund for Canada | The Earl of Bessborough |
| Vanier Institute of the Family | Georges Vanier |
| Sauvé Foundation | Jeanne Sauvé |
| Governor General Ramon John Hnatyshyn Education Fund | Ray Hnatyshyn |
| International Council for Canadian Studies | |
| The Hnatyshyn Foundation | |
| Institute for Canadian Citizenship | Adrienne Clarkson |
| Michaëlle Jean Foundation | Michaëlle Jean |
| Rideau Hall Foundation | David Johnston |
How the Title is Spelled
The official spelling of the title is governor general, without a hyphen. This is different from some other countries. When there is more than one, it is spelled governors general.
See also
 In Spanish: Gobernador general de Canadá para niños
In Spanish: Gobernador general de Canadá para niños
- Armorial of the governors general of Canada
- Governor General's Awards
- Governor-general
- List of awards presented by the governor general of Canada
- List of governors general of Canada
- Monarchy of Canada and the Canadian Armed Forces
- Royal Canadian Air Force VIP aircraft
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |