Tuberculosis facts for kids
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious infectious disease caused by tiny living things called bacteria. Long ago, people sometimes called it consumption.
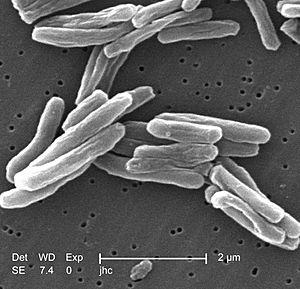
TB is usually caused by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This disease often attacks the lungs. But it can also affect other parts of your body, like your bones or kidneys.
Contents
What Causes TB?
The main cause of TB is a specific type of bacteria named Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). These bacteria are very small. They need air to live and cannot move on their own.
These bacteria grow very slowly. They divide into new bacteria every 16 to 20 hours. Other bacteria usually divide in less than an hour! In nature, MTB can only grow inside a living creature. But scientists can grow them in a lab.
How Does TB Spread?
TB bacteria can travel through the air. They spread from one person to another when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or spits.
Not everyone who gets infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. Out of 100 people who get the bacteria, only about five to ten people will show symptoms. When someone shows symptoms, we say they have active TB. If people with active TB do not get treatment, more than half of them can die from the disease.
How Doctors Find and Treat TB
To find active TB, doctors often use radiology. They might look at an X-ray of a person's chest. They also check body fluids, like spit. They grow any microbes from these fluids in a lab. Then they check if the person is infected with TB bacteria.
If someone has TB bacteria but no symptoms, it's called 'latent' TB. Doctors use a skin test called the Mantoux test to find latent TB. They also often do blood tests.
There is a vaccine that helps protect against some types of tuberculosis. It's called the bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine.
TB used to be easy to treat with antibiotics. But now, the bacteria have become very strong. They are resistant to many antibiotics. This makes treatment harder. People often need to take many different kinds of antibiotics for a long time. There are even some types of TB that are resistant to all medicines.
What Are the Symptoms of TB?
Tuberculosis can cause many different signs that someone is sick. The most common ones include:
- A cough that won't go away, especially if the person coughs up blood. This is called hemoptysis.
- Pain in the chest.
- Not feeling like eating.
- Feeling weak.
- Losing weight without trying.
- Feeling cold and shivering (chills).
- Looking very pale.
- Having tired-looking eyes.
- A Fever.
- Sweating a lot at night.
- Having trouble breathing.
- Feeling very, very tired.
People are more likely to get TB if they live close to others who have it. For example, TB can spread easily in places like homeless shelters, prisons, and crowded communities.
How Common is TB Around the World?
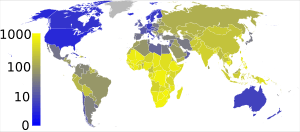
Experts believe that about one-third of all people in the world population have been infected with M. tuberculosis. New infections happen about once every second. In 2007, about 13.7 million people had active TB around the world. In 2010, about 8.8 million new cases appeared. Nearly 1.5 million people died from TB that year, mostly in poorer countries.
The number of TB cases has been going down since 2006. New cases have also decreased since 2002.
TB is not equally common everywhere. About 80% of people in many Asian and African countries test positive for TB. But only about 5 to 10% of people in the United States do.
People usually get tuberculosis when their immune system is weak. Many people with HIV and AIDS can also get tuberculosis more easily.
Interesting Facts About TB
- For many years, tuberculosis was sometimes called "the romantic disease." This was because it was linked to poets and artists who had the illness.
- Many famous artists and writers had TB or were close to people who did. These include poets John Keats and Edgar Allan Poe, composer Frédéric Chopin, and writers like Franz Kafka and Charlotte Brontë.
- The only vaccine available right now (as of 2021) is called bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG).
- People who spend a lot of time close to someone with TB are at high risk of getting infected. About 22% of them might get infected.
- Tuberculosis is often found where there is overcrowding and poor nutrition. This makes it one of the main diseases of poverty.
- About one-quarter of the world's population has been infected with M. tuberculosis. About 1% of people get new infections each year.
- Most people infected with M. tuberculosis do not get sick. About 90-95% of infections do not show any symptoms.
- It has been hard to stop the disease from spreading. This might be partly because of the shame some people feel about having TB.
- TB cases tend to increase in spring and summer. The reason for this is not fully clear. It might be linked to not getting enough vitamin D in winter.
See Also
 In Spanish: Tuberculosis para niños
In Spanish: Tuberculosis para niños