Vladimir Putin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Vladimir Putin
|
|
|---|---|
|
Владимир Путин
|
|

Putin in 2024
|
|
| President of Russia | |
| Assumed office 7 May 2012 |
|
| Prime Minister | |
| Preceded by | Dmitry Medvedev |
| In office 7 May 2000 – 7 May 2008 Acting: 31 December 1999 – 7 May 2000 |
|
| Prime Minister | |
| Preceded by | Boris Yeltsin |
| Succeeded by | Dmitry Medvedev |
| Prime Minister of Russia | |
| In office 8 May 2008 – 7 May 2012 |
|
| President | Dmitry Medvedev |
| First Deputy |
|
| Preceded by | Viktor Zubkov |
| Succeeded by | Viktor Zubkov (acting) |
| In office 9 August 1999 – 7 May 2000 |
|
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| First Deputy |
|
| Preceded by | Sergei Stepashin |
| Succeeded by | Mikhail Kasyanov |
| Secretary of the Security Council of Russia | |
| In office 9 March 1999 – 9 August 1999 |
|
| Chairman | Boris Yeltsin |
| Preceded by | Nikolay Bordyuzha |
| Succeeded by | Sergei Ivanov |
| Director of the Federal Security Service | |
| In office 25 July 1998 – 29 March 1999 |
|
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| Preceded by | Nikolay Kovalyov |
| Succeeded by | Nikolai Patrushev |
| First Deputy Chief of the Presidential Administration | |
| In office 25 May 1998 – 24 July 1998 |
|
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| Deputy Chief of the Presidential Administration – Head of the Main Supervisory Department | |
| In office 26 March 1997 – 24 May 1998 |
|
| President | Boris Yeltsin |
| Preceded by | Alexei Kudrin |
| Succeeded by | Nikolai Patrushev |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 7 October 1952 Leningrad, Soviet Union |
| Political party | Independent (1991–1995, 2001–2008, 2012–present) |
| Other political affiliations |
|
| Spouse | |
| Children | At least 2, Maria and Katerina |
| Relatives | Putin family |
| Residences | Novo-Ogaryovo, Moscow |
| Alma mater |
|
| Awards | Full list |
| Signature | |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | Soviet Union Russia |
| Branch/service | |
| Years of service |
|
| Rank |
|
| Commands | Supreme Commander-in-Chief |
| Battles/wars |
|
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician. He is the current president of Russia. Putin has been a leader in Russia since 1999. He has served as prime minister and president. He was prime minister from 1999 to 2000 and again from 2008 to 2012. He was president from 2000 to 2008 and has been president since 2012. He is the longest-serving Russian or Soviet leader since Joseph Stalin.
Forbes magazine named him the "World's Most Powerful Individual" from 2013 to 2016.
Contents
Early Life and Family
Vladimir Putin was born on October 7, 1952. This happened in Leningrad, Soviet Union. Today, this city is called Saint Petersburg, Russia. He was the youngest of three children. His parents were Vladimir Spiridonovich Putin and Maria Ivanovna Putina.
Putin's grandfather, Spiridon Putin, was a personal cook. He cooked for leaders like Vladimir Lenin and Joseph Stalin. Vladimir had two older brothers who died young. Albert died as a baby in the 1930s. Viktor died in 1942 during the Siege of Leningrad. This was during World War II.
Putin's mother worked in a factory. His father was a soldier in the Soviet Navy. He served in submarines in the 1930s. During World War II, his father was badly hurt. Putin's grandmother was killed by German soldiers in 1941. His uncles also disappeared during the war.
Putin went to School No. 193. When he was 12, he started learning sambo and judo. He also enjoyed reading books by famous thinkers like Karl Marx. Putin learned German in school and speaks it well.
Education and Early Career
Putin studied law at Leningrad State University. This university is now called Saint Petersburg State University.
In 1997, he earned a Ph.D. in economics. This was from Saint Petersburg Mining University.
Joining the KGB

In 1975, Putin joined the KGB. This was the main security agency of the Soviet Union. From 1985 to 1990, he worked in Dresden, East Germany. He worked there as a translator, but this was a secret identity for his KGB work.
After the Communist government in East Germany fell, Putin returned to Leningrad. He left the KGB in 1991. This happened after a failed attempt to remove Mikhail Gorbachev from power.
Political Journey
In May 1990, Putin became an advisor. He advised the mayor of Leningrad, Anatoly Sobchak, on international matters. In March 1994, he became a top official in the city government.
In June 1996, the mayor lost his election. Putin then left his job in the city.
Rising in Government
On March 26, 1997, President Boris Yeltsin gave Putin a new job. He became a deputy chief in the Presidential Staff. He kept this job until May 1998.
On July 25, 1998, Yeltsin appointed Putin as director of the Federal Security Service (FSB). The FSB is Russia's main intelligence and security agency. It is the successor to the KGB.
On August 9, 1999, Putin became acting Prime Minister. President Yeltsin also said he wanted Putin to be the next president. On December 31, 1999, Yeltsin suddenly resigned. Putin then became the Acting President of the Russian Federation. In the 2000 presidential election, Putin won with 53% of the votes.
Presidency and Key Policies



During Putin's first time as president, Russia's economy grew a lot. It grew about seven percent each year. This was due to new economic rules and a big increase in oil and gas prices. In 2012, Russia joined the World Trade Organization.
In 2014, Putin signed a deal to send natural gas to China. This project, called "Power of Siberia," started in 2019. It is expected to last 30 years.
Social and Cultural Affairs
Putin has worked closely with the Russian Orthodox Church. He supported a change to the Constitution of Russia in 2020. This change defined marriage as being between one man and one woman.
Conflicts and Foreign Relations
Putin is known for ending the Second Chechen War. This brought federal control back to the region. When he was prime minister, he oversaw a military conflict with Georgia. He also made changes to the military and police.
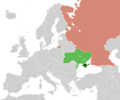
In his third term as president, Russia took control of Crimea. Russia also supported a war in eastern Ukraine. These actions led to international sanctions against Russia.
Putin has also worked to increase Russia's claims in the Arctic region. He has also increased Russia's military presence there. In 2007, a Russian expedition placed the Russian flag on the seabed at the North Pole.
Relations with Other Countries
Russia's relationship with NATO and the U.S. has changed over time. After the 9/11 attacks in 2001, Putin had good relations with U.S. President George W. Bush. He also had good relations with many European leaders. However, in 2011, a military action in Libya led to criticism from Putin and other world leaders.
In late 2013, relations between Russia and the U.S. worsened. The U.S. canceled a meeting after Putin gave safety to Edward Snowden. In 2014, Russia was removed from the G8 group. This was because Russia took control of Crimea. Putin criticized the United States. He said they were trying to control the world. In February 2023, Putin stopped Russia's part in a nuclear arms reduction treaty with the U.S.
In his fourth term, Putin started a military operation in Ukraine. This led to strong international criticism. It also led to more sanctions against Russia.
Putinisms
Putin is known for saying many memorable phrases. These are sometimes called "putinisms." Many of these came from his yearly question-and-answer sessions. During these, he answers questions from journalists and people across Russia. Putin is known for his strong and direct language. He often uses Russian jokes and folk sayings.
Personal Life
Family
On July 28, 1983, Putin married Lyudmila Shkrebneva. They lived in East Germany from 1985 to 1990. They have two daughters. Mariya Putina was born on April 28, 1985, in Leningrad. Yekaterina Putina was born on August 31, 1986, in Dresden, East Germany.
On June 6, 2013, Putin and Lyudmila announced their marriage was over. On April 1, 2014, the Kremlin confirmed their divorce was final.
Putin has two grandsons through his daughter Maria. They were born in 2012 and 2017. He also reportedly has a granddaughter through Katerina, born in 2017.
Pets
Putin has received five dogs as gifts from other leaders. Their names are Konni, Buffy, Yume, Verni, and Pasha. Konni passed away in 2014. When Putin first became president, his family had two poodles, Tosya and Rodeo. They reportedly stayed with his ex-wife Lyudmila after their divorce.
Sports and Hobbies
Putin enjoys watching football. He supports FC Zenit Saint Petersburg. He also likes ice hockey and bandy. He even played in a hockey game on his 63rd birthday.

Putin has practiced judo since he was 11. He later switched to sambo at age 14. He won competitions in both sports in Leningrad. In 2012, he earned an eighth dan black belt in judo. This made him the first Russian to reach this level. Putin also practices karate.
He helped write a book called Learn Judo with Vladimir Putin (2000). He also co-authored Judo: History, Theory, Practice in English (2004).
Awards and Honours
See also
 In Spanish: Vladímir Putin para niños
In Spanish: Vladímir Putin para niños
Images for kids
-
Putin and wife Lyudmila in New York at a service for victims of the 11 September attacks, November 2001
-
Putin, Bill Clinton, George H. W. Bush and Lyudmila Putina at the state funeral of Boris Yeltsin in Moscow, April 2007
-
Putin with Tom Brokaw before an interview on June 2, 2000
-
Putin taking the presidential oath beside Boris Yeltsin, May 2000
-
Putin as FSB director, 1998
-
Putin's Stasi "Ausweis" (identification card). He was assigned as a KGB agent in Dresden, as a mid-level liaison to the "Stasi" (East German intelligence agency) in 1985. He held a job as a translator as a "cover" for his KGB work.
-
Putin with President Boris Yeltsin on December 31, 1999, when Yeltsin announced his resignation
-
Putin with Junichiro Koizumi, Jacques Chirac, Gerhard Schröder, George W. Bush and other state leaders in Moscow during the Victory Day parade, May 9, 2005.
-
Putin with Dmitry Medvedev, March 2008
-
Putin opens the Wall of Grief, a monument to victims of Stalinist repression, October 2017
-
Putin's close associate Arkady Rotenberg is mentioned in the Panama Papers, pictured 2018
-
Putin receives Barack Obama at his residence in Novo-Ogaryovo, 2009
-
Putin in Normandy Format talks with Ukrainian president Petro Poroshenko, German chancellor Angela Merkel and French president François Hollande, October 17, 2014
-
Putin meets with U.S. president Barack Obama in New York City to discuss Syria and ISIL, September 29, 2015
-
Putin with Syrian president Bashar al-Assad in 2017
-
Putin and the newly appointed prime minister Mikhail Mishustin meeting with members of Mishustin's Cabinet, January 21, 2020
-
Putin's first deputy chief of staff Sergey Kiriyenko (left) is in charge of Russia's domestic politics.
-
Putin in a meeting with Irani president Ebrahim Raisi and supreme leader Ali Khamenei in 2022
-
Putin holds a video call with U.S. president Joe Biden on December 7, 2021
-
Pakistan's Prime Minister Imran Khan met with Putin in Moscow in 2022
-
Putin attends the Orthodox Christmas service in the village Turginovo in Kalininsky District, Tver Oblast, January 7, 2016
-
Putin with Indian prime minister Modi in New Delhi
-
Putin and Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedow, President of Turkmenistan, in October 2017
-
Putin with Italian prime minister Silvio Berlusconi and U.S. president George W. Bush at the NATO-Russia Council meeting in Rome on May 28, 2002.
-
Putin held a meeting in Sochi with German chancellor Angela Merkel to discuss Nord Stream 2 natural gas pipeline in May 2018
-
According to Putin, he and Russia have a particularly good relationship to neighboring country Finland. Picture of Putin handshaking with Sauli Niinistö, the president of Finland, in August 2019.
-
Putin and his wife Lyudmila meeting with Queen Elizabeth II, her husband Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and Prime Minister Tony Blair in 2005
-
Putin and Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro on May 22, 2015
-
Putin and Brazilian president Jair Bolsonaro at the virtual 14th BRICS Summit on June 23, 2022. Brazil and Russia are members of BRICS.
-
Putin with Iranian president Hassan Rouhani and Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, September 2018
-
Putin with Russia's long-serving minister of defense, Army General Sergey Shoygu, in the Eastern Military District, 2013
-
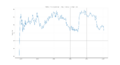
Russian GDP since the end of the Soviet Union (beyond 2014 are forecasts)
-
Putin, Lyudmila Narusova and Ksenia Sobchak at the funeral of Putin's former mentor Anatoly Sobchak, Mayor of Saint Petersburg (1991–1996)
-
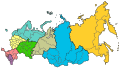
In May 2000, Putin introduced seven federal districts for administrative purposes. In January 2010, the 8th North Caucasus Federal District (shown here in purple) was split from the Southern Federal District. In March 2014, the new 9th Crimean Federal District was formed after the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation. In July 2016, it was incorporated into the Southern Federal District.