BRICS facts for kids

Heads of delegations of the BRICS countries pose at 2025 BRICS Summit, Brazil
|
|
Map key
BRICS member countries BRICS partners BRICS applicants Invited to join BRICS |
|
| Named after | First five member states' initials in English |
|---|---|
| Predecessor | 2024 BRICS Summit, Russia |
| Successor | 2025 BRICS Summit, Brazil |
| Formation |
|
| Founded at |
|
| Type | Intergovernmental organization |
| Purpose | Political and economical |
| Fields | International politics |
|
Membership
|
|
|
Chairman (incumbent)
|
|
|
Formerly called
|
BRIC |
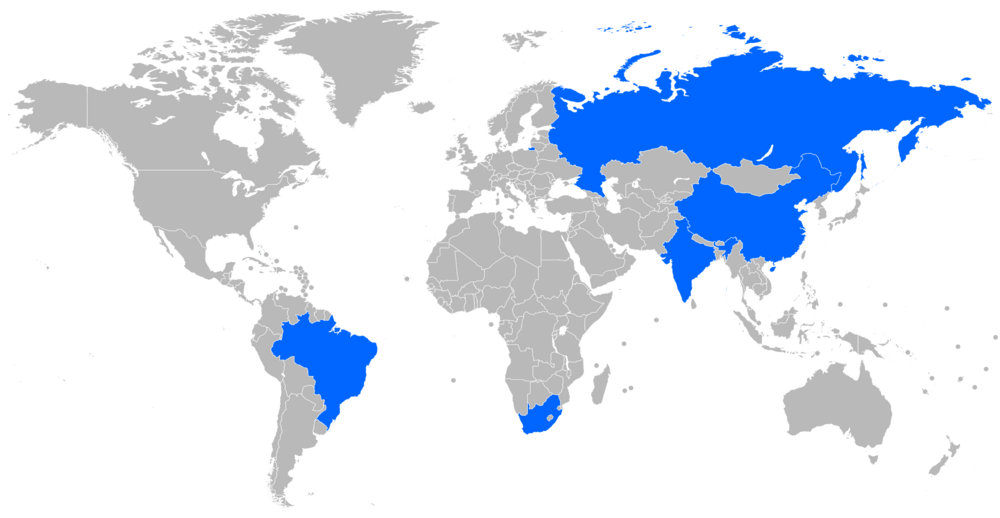
BRICS is a group of ten countries that work together on important global issues. These countries are Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates. The name BRICS comes from the first letters of the original five countries: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
The idea for a group like BRICS started with Russian foreign minister Yevgeny Primakov in the late 1990s. Later, a British economist named Jim O'Neill used the term "BRIC" in 2001 to describe these fast-growing economies. The first meeting of BRIC leaders happened in 2009. South Africa joined in 2010, changing the group's name to BRICS. In 2024, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates became members. Indonesia officially joined in early 2025.
BRICS aims to be an alternative to other powerful groups like the G7, which includes many of the world's richest countries. BRICS has created its own institutions, like the New Development Bank, to help its members. The group also works on many different topics, from trade to technology.
Contents
History
How BRICS Started
The idea for countries like Brazil, Russia, India, and China to work together began even before the term "BRIC" was created. Russia's Foreign Minister, Yevgeny Primakov, talked about this idea in 1998. Groups like RIC (Russia, India, China) and IBSA (India, Brazil, South Africa) also helped pave the way for BRIC.
The name "BRIC" was first used in 2001 by Jim O'Neill, an economist from Goldman Sachs. He used it to talk about countries that were quickly growing their economies. However, O'Neill later felt that the BRICS group didn't achieve its full potential.
The foreign ministers from Brazil, Russia, India, and China started meeting in 2006. Their first big meeting, called a summit, was held in Yekaterinburg, Russia, on June 16, 2009. The leaders discussed how to improve the global economy and make financial systems fairer, especially during the Great Recession. They also talked about how developing countries could have a bigger say in world matters.
After this first summit, the BRIC nations suggested that the world needed a new, more stable global currency, rather than relying mostly on the US dollar.
South Africa Joins
In 2010, South Africa wanted to join the BRIC group. China invited them, and the other BRIC countries agreed. On December 24, 2010, South Africa officially became a member. The group then changed its name to BRICS, adding the "S" for South Africa. South Africa's president, Jacob Zuma, attended his first BRICS summit as a full member in 2011 in Sanya, China.

New Development Bank
In 2012, BRICS countries promised to give $75 billion to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to help other countries, but only if the IMF changed its voting rules. In March 2013, at a summit in Durban, the BRICS members decided to create their own financial institution. This bank, called the New Development Bank (NDB), would work alongside the IMF and World Bank, which are mostly led by Western countries.
The NDB officially started in 2014. China contributed the most money to the bank, and it is headquartered in Shanghai. By 2024, the bank had approved over $32 billion for 96 projects. In 2021, Bangladesh, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, and Uruguay also joined the NDB.

Other BRICS Projects
Since 2011, the statistics offices of BRICS countries have worked together to publish yearly data. This helps them compare information and understand each other's economies better.
The BRICS group also planned to build an optical fiber submarine cable system, called the BRICS Cable, to improve communication between their countries. This was partly to avoid spying on their communications. However, this project was stopped in 2015 due to high costs.
In 2019, BRICS communication ministers agreed to work together on technology. In 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the BRICS summit was held online. They discussed how to handle the pandemic and improve global systems.
BRICS has created many different groups and forums, like the BRICS Business Council and the BRICS Think Tanks Council. These groups help members work together on various topics, from business to culture and health. In 2021, BRICS countries agreed to build a satellite system together to share data from space.
Expanding the Group
In August 2023, at the 15th BRICS summit, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa announced that six more countries were invited to join: Argentina, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. They were expected to become full members on January 1, 2024.
However, Argentina's new government decided not to join. By January 2024, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates officially became members, increasing BRICS from five to nine countries. Saudi Arabia was still deciding whether to join.
In October 2024, 13 more countries, including Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Indonesia, and Vietnam, were invited to become "partner countries." This status allows them to work with BRICS on different projects.
On January 6, 2025, Indonesia officially became a full member of BRICS, making it the 11th country to join. This was a big step for the group, as Indonesia is the first Southeast Asian country to be a full member.
Statistics
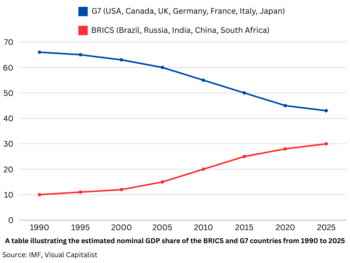
BRICS+ (including the new members) makes up about 46% of the world's population and 25% of the world's land. The economies of BRICS countries have grown a lot. In 2022, BRICS+ countries produced about 35.6% of the world's total economic output (when measured by purchasing power). Trade between BRICS countries was about $614.8 billion in 2022.
BRICS+ countries have over 1200 satellites in space and account for 40% of all internet users worldwide. They also produce a large share of the world's food, including 42% of wheat, 52% of rice, and 46% of soybeans.
Brazil, India, and China are among the world's largest countries by population, land area, and economic size. The original five BRICS members are also part of the G20, a group of the world's major economies. Together, the original five BRICS countries had a total economic output of about $28 trillion in 2024.
Experts believe that the total economic size of BRICS+ countries will become larger than the G7 group after 2045.
Economic Share in Percentage (as of 2022) G7 (43.70%) BRICS + (28.70%) Rest of world (27.6%)
Rotating BRICS Presidency
BRICS leaders meet once a year, and the host country's leader becomes the "President Pro Tempore" for that year. This means they lead the group's meetings and set priorities. Many other meetings are held throughout the year, involving ministers of foreign affairs, finance, trade, and more.
BRICS does not have a permanent office or a fixed leader. In 2019, Brazil held the presidency and focused on science, technology, and fighting crime. In 2024, Russia was the president and aimed to strengthen economies and cooperate on energy. Brazil is the current President Pro Tempore in 2025.
Leaders' Summits
BRICS has held annual meetings since 2009. The host country changes each year. The first summit with five members (including South Africa) was in 2011. The first summit with nine members (BRICS+) was in 2024 in Russia. Some recent summits were held online due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
| No. | Dates | Host country | Host leader | Location | Main Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | June 16, 2009 | Dmitry Medvedev | Yekaterinburg | Discussed the global economic crisis and future cooperation. | |
| 2nd | April 15, 2010 | Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva | Brasília | Continued talks on global recovery and cooperation. South Africa attended as a guest. | |
| 3rd | April 14, 2011 | Hu Jintao | Sanya | First summit with South Africa as a full member. Discussed global and national economies. | |
| 4th | March 29, 2012 | Manmohan Singh | New Delhi | Focused on how BRICS could grow stronger after the recession. | |
| 5th | March 26–27, 2013 | Jacob Zuma | Durban | Agreed to create the New Development Bank. | |
| 6th | July 14–17, 2014 | Dilma Rousseff | Fortaleza | Signed agreements to create the New Development Bank and a reserve fund. | |
| 7th | July 8–9, 2015 | Vladimir Putin | Ufa | Discussed global political and economic issues. | |
| 8th | October 15–16, 2016 | Narendra Modi | Benaulim, Goa | Debated topics like fighting terrorism and climate change. | |
| 9th | September 3–5, 2017 | Xi Jinping | Xiamen | Talked about the future goals of BRICS and international issues. | |
| 10th | July 25–27, 2018 | Cyril Ramaphosa | Johannesburg | Discussed growing industries within BRICS countries. | |
| 11th | November 13–14, 2019 | Jair Bolsonaro | Brasília | Focused on science, technology, and fighting crime. | |
| 12th | November 17, 2020 | Vladimir Putin | Saint Petersburg (video conference) | Discussed improving living standards and focusing on peace and economies. | |
| 13th | September 9, 2021 | Narendra Modi | New Delhi (video conference) | Held many meetings on finance, trade, and energy. | |
| 14th | June 23, 2022 | Xi Jinping | Beijing (video conference) | Discussed creating a new reserve currency. | |
| 15th | August 22–24, 2023 | Cyril Ramaphosa | Johannesburg | Invited Argentina, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates to join. | |
| 16th | October 22–24, 2024 | Vladimir Putin | Kazan | First summit of the expanded BRICS+ group. Discussed new payment systems. | |
| 17th | July 6–7, 2025 | Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva | Rio de Janeiro | ||
| 18th | 2026 | Narendra Modi | TBD |
Member states
List of Current Member States
Overview of BRICS Members
| Country | Population | GDP (Nom.) | GDP (PPP) | G20 | Economic classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7th | 10th | 7th | Newly industrialized | ||
| 9th | 11th | 4th | Emerging | ||
| 1st | 5th | 3rd | Newly industrialized | ||
| 2nd | 2nd | 1st | Newly industrialized | ||
| 23rd | 40th | 33rd | Newly industrialized | ||
| 15th | 45th | 17th | Emerging and Developing | ||
| 13th | 56th | 55th | Under developed | ||
| 17th | 36th | 23rd | Emerging and Developing | ||
| 88th | 26th | 38th | Emerging and Developing | ||
| 4th | 16th | 8th | Newly industrialized |
Partner States and Applications
BRICS does not have a formal way for countries to apply. Instead, a country needs all current members to agree to invite them. Discussions about adding new members became more common in the early 2020s.
In August 2023, six countries were invited to join. Argentina later decided not to accept the invitation. By January 2024, Egypt, United Arab Emirates, Ethiopia, and Iran officially joined. Saudi Arabia was still considering its membership.
In November 2023, Pakistan applied to join, but not all BRICS members supported this. Turkey officially applied in September 2024. Algeria, which had applied in 2023, later withdrew its application in September 2024.
After the 2024 BRICS summit, Brazil did not support Venezuela's application to join. This was due to concerns about the 2024 Venezuelan elections.
The group is now sometimes called "BRICS+" to show that it has expanded. Indonesia, which was first considered a partner, became a full member in January 2025.
Financial Architecture

China has the largest economy within the BRICS group, making up about 70% of the group's total economic output.
The main financial parts of BRICS are the New Development Bank (NDB) and the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA). These were officially created in 2014 and started working in 2015.
New Development Bank
The New Development Bank (NDB) is a bank run by the BRICS countries. Its main goal is to lend money for big projects like roads, bridges, and power plants. The bank started with $50 billion and plans to grow to $100 billion. Each of the original five BRICS countries contributed $10 billion. South Africa hosts the NDB's African office.
BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement
The BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) is like a safety net for BRICS countries. It helps protect them if their money (currency) faces problems because of global financial pressures. This is especially helpful for growing economies that can sometimes have unstable financial situations. The CRA works as an alternative to the International Monetary Fund (IMF). It was set up in 2015.
BRICS Payment System
At the 2015 BRICS summit, leaders started talking about creating a payment system that could be an alternative to the SWIFT system, which is used worldwide. The goal was to allow countries to make payments using their own currencies. This system would also provide a backup if the SWIFT system had problems.
China has its own payment system called the Cross-Border Interbank Payment System. India, Russia, and Brazil also have their own payment systems.
Potential Common Currency
BRICS countries have discussed creating a new common currency or a similar system. This would make international trade easier and cheaper for them. One idea for the currency name is "R5," based on the first letter of the original five currencies (Renminbi, Ruble, Rupee, Real, and Rand). A sample banknote was shown at the 2024 summit in Russia.
BRICS is also working on "BRICS Bridge," which would allow central banks to make international payments using their own digital currencies. This system would be independent and give each central bank control over its currency exchange rate.
Important Issues
Peace and Security
At the 16th BRICS summit in October 2024, the leaders talked about important peace and security issues. They supported efforts for a peaceful solution to the conflict in Ukraine. They also expressed deep concern about the situation in the Palestinian Territory, especially the violence in Gaza and the West Bank, which caused many people to be harmed or displaced. They called for an immediate end to fighting in Southern Lebanon. The leaders also noted that one-sided economic penalties can hurt the global economy.
At the 17th BRICS summit in Brazil, the leaders strongly condemned a terrorist attack that happened in Jammu and Kashmir in April 2025. They called for fighting terrorism in all its forms, including stopping terrorists from moving across borders and cutting off their funding. They emphasized that there should be "zero tolerance" for terrorism and that countries should not have different rules for fighting it.
Current leaders
Current leading member state representatives:
| Member | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | |||||
| Name | Lula da Silva | Vladimir Putin | Narendra Modi | Xi Jinping | Cyril Ramaphosa |
| Position | President of Brazil | President of Russia | Prime Minister of India | President of China | President of South Africa |
| Member | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | |||||
| Name | Abdel Fattah el-Sisi | Abiy Ahmed | Prabowo Subianto | Masoud Pezeshkian | Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan |
| Position | President of Egypt | Prime Minister of Ethiopia | President of Indonesia | President of Iran | President of the United Arab Emirates |
See also
 In Spanish: BRICS para niños
In Spanish: BRICS para niños
- Belt and Road Initiative
- BRICS Games
- Developing country
- East–West dichotomy
- Emerging power
- List of multilateral free-trade agreements
- MIKTA
- G7
- Potential superpowers
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
- ASEAN
- Mercosul
- BRICS PAY
- G20
- Hague Group
- Member states of BRICS
- Non-Aligned Movement
- OPEC
- List of BRICS summit attendees
- List of country groupings
- BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement
- BRICS Universities League
- Axis of Upheaval
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |