New Development Bank facts for kids
 |
|

NDB headquarters in Shanghai, China
|
|
| Abbreviation | NDB |
|---|---|
| Formation | July 2014 (Treaty signed) July 2015 (Treaty in force) |
| Type | International financial institution |
| Legal status | Treaty |
| Headquarters | Shanghai, China |
|
Membership
|
|
|
Official language
|
English |
|
President
|
Dilma Rousseff |
|
Parent organization
|
BRICS |
The New Development Bank (NDB), also known as the BRICS Development Bank, is a special bank created by the BRICS countries. These countries are Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. The bank helps fund big projects, both public and private. It offers loans, guarantees, and other ways to help financially. The NDB also works with other international groups and provides technical help for projects.
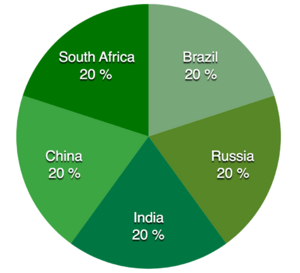
The bank started with a lot of money, about $100 billion. This money was divided equally among the five founding countries. Each founding country has one vote, and no country has a special veto power.
The main office of the bank is in Shanghai, China. The NDB also has offices in other places. These include Johannesburg, South Africa (opened in 2016), São Paulo in Brazil, Ahmedabad in India, and Moscow in Russia.
Contents
History of the NDB
How the Bank Started
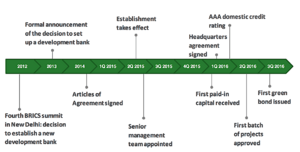
The idea for this bank came from India in 2012. This was at the 4th BRICS summit in New Delhi. The BRICS leaders thought a new bank would make it easier for their countries to trade and lend money to each other. It would also help them rely less on the US dollar and the Euro.
So, at the 5th BRICS summit in Durban, South Africa, in March 2013, they agreed to create the bank. On July 15, 2014, at the 6th BRICS summit in Fortaleza, Brazil, the five countries signed the agreement. This made the bank official. They also set up a special fund of $100 billion to help each other in emergencies.
Key Moments for the NDB
On May 11, 2015, K. V. Kamath from India became the bank's first president. In January 2016, the bank approved its first rules for how it would work. On February 27, 2016, the NDB signed an agreement to set up its main office in Shanghai.
In July 2016, the NDB made its first "green financial bond." This was a special type of loan that helps fund environmentally friendly projects. It raised 3 billion Chinese Yuan. The first yearly meeting of the NDB's leaders also happened in Shanghai in July 2016. They talked about the bank's future and were happy with its progress.
By the end of 2016, the NDB approved its first projects in all member countries. The bank signed its first loan agreement on December 21, 2016. In August 2018, the NDB received high credit ratings. This means it is seen as a very reliable bank.
In April 2020, the NDB created an Emergency Assistance Facility. This fund helped countries fight the Coronavirus and deal with its economic effects. The bank planned to provide up to $10 billion for this.
In March 2022, the NDB paused all new projects with Russia. This was due to "sound banking principles." Even though the NDB acted quickly, its credit rating was still lowered. In May 2022, the NDB opened a new office in Gujarat, India. This office helps fund and watch over projects in India and Bangladesh. In May 2023, Saudi Arabia said it wanted to join the NDB. Algeria officially joined the NDB in September 2024.
How the NDB Works
Bank Leadership
The NDB has three main parts that help it run:
- The Board of Governors
- The Board of Directors
- The President and Vice-Presidents
The NDB president is chosen from one of the founding countries. This role rotates among them. There are also four vice presidents, one from each of the other four founding countries.
K. V. Kamath was the first president. Then, Marcos Prado Troyjo from Brazil took over on July 7, 2020. Since March 24, 2023, Dilma Rousseff from Brazil has been the president.
Bank Money
The New Development Bank started with $50 billion in subscribed capital. It also had $100 billion in authorized capital. The first $50 billion was shared equally among the founding members. Each member pays their share over seven payments.
No member can increase their share of money without all other four members agreeing. The bank can let new countries join. However, the original BRICS countries must always own at least 55% of the bank's capital.
What the NDB Aims To Do
The bank wants to help countries with their development plans. It focuses on projects that are good for society, the environment, and the economy. Here are its main goals:
- Help build infrastructure and support projects that have a big positive impact in member countries.
- Work with other international banks and national development banks around the world.
- Choose a good mix of projects. This includes looking at where they are, how much money they need, and other important factors.
Who Are the Members?
| Members | Joined |
|---|---|
| 2015 | |
| 2021 | |
| 2023 | |
| 2024 | |
| 2025 | |
The agreement to create the New Development Bank became official in July 2015. All five original BRICS countries signed it. The NDB's rules say that any country that is part of the United Nations can join. But the original BRICS countries must always have at least 55% of the total votes. Right now, the original five members have more than 90% of the votes.
In 2016, some experts thought it was important for the NDB to add more members. This would help the bank grow and do more business. The bank's plan for 2017-2021 said it would add new members slowly. This helps make sure the bank can still work well and make decisions easily.
In September 2021, Bangladesh, the United Arab Emirates, and Uruguay joined the NDB. In December 2021, Egypt also became a new member. Algeria asked to join after its president visited China in 2023. Algeria was accepted as a member in 2024.
Other countries that might join in the future include Honduras and Zimbabwe.
The New Development Bank started with 1 million shares. Each share was worth $100,000. Each of the five founding members bought 100,000 shares. This meant each founding member put in $10 billion.
The table below shows how the shares are currently divided among the NDB member countries.
| Country | SHARES (NUMBER) Shares subscribed |
SHARES (NUMBER) Exercisable votes |
SUBSCRIBED CAPITAL Amount (billion USD) |
SUBSCRIBED CAPITAL % of total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100,000 | 100,000 | 10.000 | 18.45 | |
| 100,000 | 100,000 | 10.000 | 18.45 | |
| 100,000 | 100,000 | 10.000 | 18.45 | |
| 100,000 | 100,000 | 10.000 | 18.45 | |
| 100,000 | 100,000 | 10.000 | 18.45 | |
| 9,420 | 9,420 | 0.942 | 1.74 | |
| 15,000 | 15,000 | 1.5 | 2.77 | |
| 11,960 | 11,960 | 1.196 | 2.21 | |
| 5,560 | 5,560 | 0.556 | 1.03 | |
| ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Unallocated Shares | 458,060 | 458,060 | 45.806 | |
| Grand Total | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 100.000 | 100.00% |
What the NDB Does
Projects the Bank Funds
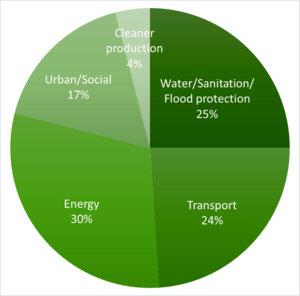
The NDB's main goal from 2017 to 2021 was to support projects that build sustainable infrastructure. About two-thirds of its money in its first five years went to this area.
The bank wants to fund projects that use renewable energy. It also wants to work with other groups to increase "green" financing. This means funding projects that protect the environment.
The NDB is interested in funding projects that meet high environmental standards. This includes projects in energy, railways, and highways. The bank also wants to fund projects that are profitable and bring benefits to local people and the environment.
The leaders of the member countries want the bank to find many good projects. They also want the bank to respond quickly to what its members need.
As of March 6, 2019, the NDB had approved 30 projects. These projects received loans totaling about $8 billion.
The bank has also started lending money directly to companies and organizations, not just governments. This includes loans in Brazil, South Africa, and Russia. In May 2024, the NDB announced it would give $1.115 billion to Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. This money is for rebuilding after the 2024 floods.
Bonds the Bank Issues
In March 2016, the NDB said it would issue a bond in China. This would help it raise money within China. The bank issued its first green financial bond on July 18, 2016. It raised 3 billion Chinese Yuan. The money from this bond is used for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in member countries. The NDB was the first international financial group to issue a green bond in China.
In February 2019, the bank successfully issued another bond in China. It raised 3 billion Chinese Yuan. On May 18, 2022, the NDB issued a 7 billion Chinese Yuan bond. This was the largest bond ever made by a foreign issuer in China.
Working with Other Banks
NDB's Approach
The NDB was created to work with other international and regional financial groups. It wants to help global growth and development. The bank can also work with other international organizations and national groups, both public and private. This includes other international financial institutions and national development banks.
The NDB President, K.V. Kamath, has said that the bank sees other international financial groups, like the IMF and World Bank, as partners, not rivals.
Asian Development Bank
In July 2016, the NDB and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed an agreement. They agreed to work together on projects. This includes sharing money and knowledge. They will focus on sustainable development projects. These include renewable energy, clean transportation, and water management.
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
The NDB and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) are similar in many ways. They both focus on developing infrastructure and sustainable projects. However, the NDB focuses more on BRICS countries. Even though they have some similar goals, there is enough need for both banks to exist.
In February 2016, the NDB president said there was no need to worry about the NDB and AIIB having too much overlap.
World Bank
The World Bank Group (WBG) has also said it wants to work with the NDB. In September 2016, the NDB and the World Bank Group signed an agreement to work together. Their main focus will be on infrastructure projects.
Partnerships and Agreements
With Other Development Banks
- World Bank
- Inter-American Development Bank (IDB)
- Financial Fund for the Development of the River Plate Basin (FONPLATA)
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB)
- Caribbean Development Bank (CDB)
- Eurasian Development Bank (EDB)
- International Investment Bank (IIB)
- Development Bank of Latin America and the Caribbean (CAF)
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Islamic Development Bank (IsDB)
- European Investment Bank (EIB)
With National Development Banks
- Development Bank of Southern Africa (DBSA)
- Agricultural Development Bank of China (ADBC)
- Exim Bank of China
- China Development Bank (CDB)
- Brazilian National Bank for Economic and Social Development (BNDES)
Logo and What It Means
The New Development Bank's logo is based on a mathematical idea called a Möbius strip. This shape shows the idea of constant change. It means the bank wants to improve the current system from within.
The logo has a triangle moving at one end. This shows balanced growth. The other end moves in the opposite direction, like a propeller. This stands for speed and energy. These two parts are held together by a wireframe, which looks like the basic structure of buildings. The logo is green, which means sustainability. This constant movement shows the bank's values: being quick, creative, and always changing for the better.
List of NDB Presidents
| # | Portrait | Name | Term | Term of office | Nationality | Background | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
K. V. Kamath | May 11, 2015 – May 27, 2020 | 5 years, 16 days | Has an MBA from Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad; was chairman of Infosys Limited; was chairman of ICICI Bank |
First New Development Bank president | |
| 2 |  |
Marcos Prado Troyjo | May 27, 2020 – March 24, 2023 | 2 years, 362 days | A diplomat, economist, and sociologist; founded BRICLab at Columbia University; was Brazil's Deputy Economy Minister for Foreign Trade & International Affairs |
First Brazilian to lead a big international development group | |
| 3 |  |
Dilma Rousseff | March 24, 2023 – present | 2 years, 273 days | An economist from Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul; was President of Brazil; was Chief of Staff of the Presidency in Brazil; was Minister of Mines and Energy in Brazil. |
First woman to lead the New Development Bank | |
| References: | |||||||
See also
- BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Policy bank
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |