East Germany facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
German Democratic Republic
Deutsche Demokratische Republik
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949–1990 | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Motto: Proletarier aller Länder, vereinigt Euch!
English: Workers of the world, unite! |
|||||||||||
|
Anthem: Auferstanden aus Ruinen
"Risen from Ruins" |
|||||||||||
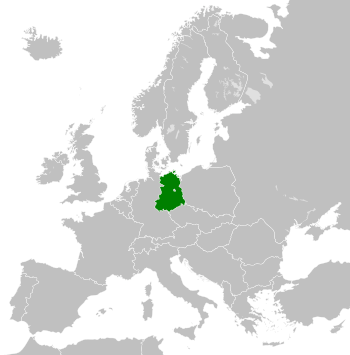
The German Democratic Republic in 1990.
|
|||||||||||
| Status | Satellite State of the Soviet Union | ||||||||||
| Capital | East Berlin | ||||||||||
| Common languages | German Sorbian (only in parts of Dresden and Cottbus districts) |
||||||||||
| Government | Marxist–Leninist one-party state (until Nov. 1989) Parliamentary republic (after Nov. 1989) |
||||||||||
| General Secretary | |||||||||||
|
• 1949–1950
|
Wilhelm Pieck | ||||||||||
|
• 1949–1950
|
Otto Grotewohl | ||||||||||
|
• 1950–1971
|
Walter Ulbricht | ||||||||||
| Head of State | |||||||||||
|
• 1949–1960
|
Wilhelm Pieck (first) | ||||||||||
|
• 1990
|
Sabine Berg.-Pohl (last) | ||||||||||
| Head of Government | |||||||||||
|
• 1949–1964
|
Otto Grotewohl (first) | ||||||||||
|
• 1990
|
Lothar de Maizière (last) | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Volkskammer | ||||||||||
|
• State Chamber
|
Länderkammer | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||
|
• Constitution adopted
|
7 October 1949 | ||||||||||
|
• Uprising of 1953
|
16 June 1953 | ||||||||||
|
• Berlin Crisis
|
4 June 1961 | ||||||||||
|
• Peaceful Revolution
|
13 October 1989 | ||||||||||
| 12 September 1990 | |||||||||||
| 3 October 1990 | |||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 1990 | 108,333 km2 (41,828 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
|
• 1950
|
18388000 | ||||||||||
|
• 1970
|
17068000 | ||||||||||
|
• 1990
|
16111000 | ||||||||||
| Currency | 1949–1964: Deutsche Mark 1964–1967: Mark der Deutschen Notenbank, (1967–1990) Mark der DDR (Three different names for the same currency) Deutsche Mark (from 1 July 1990) |
||||||||||
| Calling code | 37 | ||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .de | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
|
The initial flag of East Germany adopted in 1948 was identical to that of West Germany. In 1959, the East German government issued a new version of the flag bearing the national emblem, serving to distinguish East from West.
Dissolved by the Volkskammer on 8 December 1958. Population statistics according to Statistisches Bundesamt. Although .de was reserved as corresponding ISO code for East Germany, it was not entered to the root before the country was reunited with the west. |
|||||||||||
The German Democratic Republic (GDR), often called East Germany, was a country that existed from 1949 to 1990. It was formed on October 7, 1949, after World War II. East Germany was created from the part of Germany that the Soviet Union controlled, including a section of Berlin.
East Germany was a separate country until 1990. In that year, it joined with West Germany to become one united country again. The country was mainly ruled by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED).
Contents
A Look Back: East Germany's Story
After World War II, Germany was split into four areas. Each area was looked after by a different country. These countries were France, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union. Later, the French, American, and British parts joined to form West Germany. The Soviet part became East Germany.
Leaders and the Berlin Wall
Walter Ulbricht, who led the SED party, held a lot of power. When President Wilhelm Pieck died in 1960, Ulbricht became the "Chairman of the State Council." This made him the country's main leader.
On August 13, 1961, the famous Berlin Wall was built. The East German government said the wall was to keep "Western Capitalists" out. But its real purpose was to stop East Germans from leaving their country. Many people tried to escape, and some were stopped.
Changes and the Fall of the Wall
In the late 1980s, the Soviet Union's leader, Mikhail Gorbachev, started new policies called glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring). This inspired many people in East Germany to want changes too. In 1989, large demonstrations for democracy and human rights took place. In Leipzig, people gathered every Monday to protest. These were known as "Monday Demonstrations."
The East German leader, Erich Honecker, hoped the Soviet army would stop these protests. But the Soviet Union had its own problems and decided not to control Eastern Europe anymore. Honecker was forced to step down on October 18, 1989.
Egon Krenz took over as leader. He tried to show he wanted change, but people didn't trust him. On November 9, 1989, the government announced that East Germans could travel to West Berlin. A spokesman mistakenly said the new rule would start right away. People rushed to the Berlin Wall checkpoints. The guards, without clear orders, eventually opened the gates. Thousands of East Germans poured into West Berlin. The fall of the Berlin Wall was a huge moment.
On December 1, 1989, the government removed the law that gave the SED party the right to rule. This officially ended communist rule in East Germany.
Reunification of Germany
On March 18, 1990, East Germany held its first free election. A group of parties called the "Alliance for Germany," which wanted to unite East and West Germany, won. This period of change is known in Germany as the Wende.
In 1990, East Germany officially joined West Germany. This process is called the German reunification. East Germany's regions were reorganized into new states, like Berlin, Brandenburg, and Saxony. After this, East Germany no longer existed as a separate country.
Even today, people from former West Germany sometimes call people from former East Germany "Ossi." This word comes from "Osten," which means "East" in German. It's not always used in a friendly way.
How East Germany Was Run
The leading role of the SED party was written into East Germany's constitution. There were other political parties, but they were called Blockparteien ("block parties"). Their main job was to follow what the SED said. Some of these parties included:
- CDU (Christlich-Demokratische Union Deutschlands; "Christian Democratic Union of Germany") – This party later joined with the West German CDU.
- LDPD (Liberal-Demokratische Partei Deutschlands; "Liberal Democratic Party of Germany") – This party later joined with the West German FDP.
- NDPD (National-Demokratische Partei Deutschlands; "National Democratic Party of Germany") – This party also joined with the FDP.
- DBD (Demokratische Bauernpartei Deutschland; "Democratic Farmer's Party of Germany") – This party joined with the CDU before reunification.
The Stasi: State Security
The Ministry for State Security (in German: Ministerium für Staatssicherheit), often called the "MfS" or "Stasi," was East Germany's security service. Its job was to find people who were against the state or the SED party. The Stasi had many informants who reported on anyone who said or did something against the government. There was a large Stasi prison in the town of Bautzen.
East Germany's Place in the World
East Germany was a member of the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance of communist countries. It was closely linked to the Soviet Union. However, in the late 1980s, Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev started reforms that allowed East Germany more freedom. This was part of what was called the "Sinatra Doctrine."
Economy and Daily Life
East Germany had a planned economy. This meant the government controlled most of the country's businesses and factories. They were officially called Volkseigentum, or "people's property." Only a few small businesses and shops were privately owned.
A well-known car from East Germany was the "Trabant" or Trabi. It was a small, low-powered car that many families owned.

Sports in East Germany
Until 1964, East and West Germany competed together in the Olympic Games as one team. From 1968 onwards, they had their own separate teams.
East German athletes were very successful, especially in sports like athletics, cycling, boxing, and winter sports. Some famous East German sports stars include Täve Schur (cycling), Waldemar Cierpinski (athletics), Heike Drechsler (athletics), Olaf Ludwig (cycling), Katarina Witt (ice skating), and Jens Weißflog (ski jumping).
A famous cycling race was the Peace Race (in German: Friedensfahrt).
The East Germany national football team was not as successful. They only played in one FIFA World Cup, which was the 1974 FIFA World Cup held in West Germany. On June 22, 1974, East Germany played against West Germany. Jürgen Sparwasser scored a goal, and East Germany won 1-0.
Famous Athletes from East Germany
- Uwe Ampler, racing bicyclist
- Karin Büttner-Janz, gymnast
- Ernst Degner, racing motorcyclist
- Thomas Doll, footballer
- Heike Drechsler, athlete
- Mikhail Grabovski, hockey player
- Marita Koch, athlete
- Olaf Ludwig, racing bicyclist
- Uwe Raab, racing bicyclist
- Jürgen Sparwasser, footballer
- Jens Weissflog, skier
- Katarina Witt, ice skater
Holidays in East Germany
| Date | English Name | German Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January | New Year's Day | Neujahr | |
| Moveable feast | Good Friday | Karfreitag | |
| Moveable feast | Easter Sunday | Ostersonntag | |
| Moveable feast | Easter Monday | Ostermontag | Not an official Holiday after 1967. |
| 1 May | May Day | Tag der Arbeit | International Workers' Day |
| 8 May | Victory in Europe Day | Tag der Befreiung | Means "Day of Liberation" |
| Moveable feast | Father's Day / Ascension Day | Vatertag / Christi Himmelfahrt | Thursday after the 5th Sunday after Easter. Not an official Holiday after 1967. |
| Moveable feast | Whitmonday | Pfingstmontag | 50 days after Easter Sunday |
| 7 October | Republic Day | Tag der Republik | National holiday |
| 25 December | First Day of Christmas | 1. Weihnachtsfeiertag | |
| 26 December | Second Day of Christmas | 2. Weihnachtsfeiertag |
See also
 In Spanish: República Democrática Alemana para niños
In Spanish: República Democrática Alemana para niños
Images for kids
-
Early leaders of East Germany: President Wilhelm Pieck and Prime Minister Otto Grotewohl in 1949.
-
Walter Ulbricht, who led the SED party from 1950 to 1971.
-
Erich Honecker was the head of state for East Germany from 1971 to 1989.
-
Leaders signing the Helsinki Accords. From left: West German Chancellor Helmut Schmidt, East German Chairman Erich Honecker, U.S. President Gerald Ford, and Austrian Chancellor Bruno Kreisky.
-
A large demonstration on Alexanderplatz in East Berlin on November 4, 1989, showing people's desire for change.
-
The Uni-Riese (University Giant) building in Leipzig in 1982. It was part of the University of Leipzig.
-
East German soldiers from the National People's Army during a changing-of-the-guard ceremony in East Berlin.
-
Angola's leader José Eduardo dos Santos visiting East Berlin.
-
A Catholic meeting in Dresden in 1987, with religious leaders including Pope Benedict XVI (then Joseph Ratzinger).
-
Playwright Bertolt Brecht (1898–1956), a famous writer.
-
Gerhard Behrendt with a character from Sandmännchen, a popular children's stop-animation TV series.
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |