Warsaw Pact facts for kids
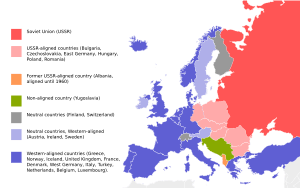
The Warsaw Pact, officially known as the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a group of countries in Central Europe and Eastern Europe. These countries were all Communist states and promised to help each other if one of them was attacked. Even though they were supposed to be equal, the Soviet Union had a lot of control over the smaller countries in the group.
The Warsaw Pact was created in 1955 in Warsaw, Poland. It was formed because West Germany had joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). The treaty was signed on May 14, 1955. It was written in Russian, Polish, Czech, and German. The Warsaw Pact lasted until 1991, near the end of the Cold War. Many members left as the Eastern Bloc changed and the Soviet Union faced political changes.
Don't confuse the Warsaw Pact with other agreements. For example, the Warsaw Convention is about money for air travel. The Treaty of Warsaw (1970) was an agreement between West Germany and Poland.
 |
|
The WTO in 1990
|
|
| Abbreviation | WTO, WAPA, DDSV |
|---|---|
| Motto | Union of peace and socialism |
| Founded | 14 May 1955 |
| Founded at | Warsaw, Poland |
| Dissolved | 1 July 1991 |
| Type | Military alliance |
| Headquarters | Moscow, Soviet Union |
|
Membership
|
|
|
Supreme Commander
|
|
|
Chief of Combined Staff
|
|
| Affiliations | Council for Mutual Economic Assistance |
Who Were the Members?
The Warsaw Pact had several member countries. The Soviet Union was the main and most powerful member.
- Soviet Union
- East Germany
- Czechoslovakia
- Bulgaria
- Hungary
- Poland
- Romania
- Albania (Albania stopped supporting the Pact in 1962 due to different ideas. It officially left in 1968.)
All the Communist countries in Central and Eastern Europe joined, except for Yugoslavia.
Images for kids
-
The Presidential Palace in Warsaw, Poland, where the Warsaw Pact was signed on May 14, 1955.
-
A meeting of seven Warsaw Pact country representatives in East Berlin in May 1987. From left to right: Gustáv Husák, Todor Zhivkov, Erich Honecker, Mikhail Gorbachev, Nicolae Ceaușescu, Wojciech Jaruzelski, and János Kádár.
-
Soviet tanks, marked with white crosses to tell them apart from Czechoslovak tanks, on the streets of Prague during the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968.
-
The Paneuropean Picnic took place on the border between Hungary and Austria.
-
How NATO grew before and after communism ended in Central and Eastern Europe.
See also
 In Spanish: Pacto de Varsovia para niños
In Spanish: Pacto de Varsovia para niños