Software as a service facts for kids
Imagine you use an app on your phone or computer, but you don't actually own the software or have to install it. That's often Software as a service (SaaS). It's a way for companies to let you use their programs over the internet, like a rental service. You usually access SaaS through a web browser, like when you visit a website.
With SaaS, you don't buy the software; you just use it. The company that made it takes care of all the technical stuff, like keeping it updated and running smoothly. SaaS started becoming popular around the year 2000. By 2023, it was the most common way for people and businesses to get and use software.
Unlike old-fashioned software you install, SaaS usually has just one main version that everyone uses. These services often run on powerful computers owned by other companies (called cloud computing providers). This helps them handle many users at once and makes sure the software is always available. Because many users share the same system, the cost for each user can be lower. You usually pay for SaaS through a subscription or based on how much you use it. /sæs/
Contents
What is Cloud Computing?
SaaS is a type of cloud computing. Think of cloud computing as using computer services over the internet instead of owning all the hardware and software yourself. It's like renting a locker instead of buying a whole storage unit.
There are different levels of cloud computing:
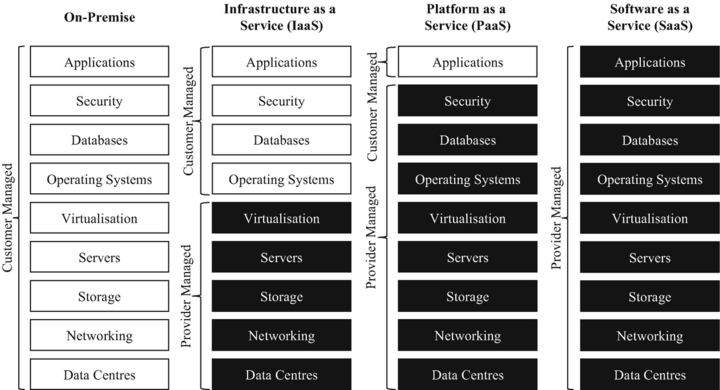
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the most basic. Here, you rent things like virtual computers and storage from a cloud provider. You still need to set up the operating system and your applications. It's like renting an empty room.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) gives you more. It includes the operating system and other tools you need to build and run apps. It's like renting a room with furniture.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) is the most complete. You just use the finished application. The provider handles everything else. It's like renting a fully furnished apartment where you just move in and live.
SaaS providers often use IaaS or PaaS to run their applications. This makes it easy for them to handle many users and keep the software running all the time. When you use a SaaS product, you don't have to worry about the complex computers or operating systems behind it. Cloud computing also makes it super easy for software companies to update their apps. Everyone gets the new features instantly!
In 2019, SaaS made up about 43% of the cloud computing market. IaaS and PaaS together made up about 25%. This shows how popular SaaS has become.
How SaaS Started
In the 1960s, computers learned to do many tasks at once, allowing several people to use a single large computer. This idea of sharing computer time became very popular.
Cloud computing, including SaaS, really started to grow in the late 1990s. Companies like Amazon (which started in 1994), Salesforce (1999), and Concur (1993) began offering applications over the internet. You would pay to use these programs, often for specific business tasks.
One of the first big consumer SaaS products was Gmail, which launched in 2004. Email services were among the first SaaS apps that many people started using. The market for SaaS grew very quickly in the early 2000s. At first, people saw it as a cool new technology. Now, it's mostly seen as a smart way for businesses to offer their software. By 2023, SaaS was the main way companies delivered their applications.
You probably use many popular SaaS products every day! These include:
- All social media websites (like TikTok, Instagram)
- Email services (like Gmail)
- Online document tools (like Google Docs Editors)
- Video chat apps (like Skype)
- Cloud storage (like Dropbox)
- Entertainment services (like Netflix and Spotify)
Businesses also use many SaaS products for things like managing customer information (like Salesforce) or planning their resources (like SAP Cloud Platform and Oracle Cloud Enterprise Resource Planning).
How SaaS Companies Make Money
SaaS companies use different ways to earn money:
- Free Services: Some offer free services that are supported by ads, or by selling data (like how some social media sites work).
- Freemium: This is very popular for apps. You get a basic version for free, but you pay for extra features or continued use. Even if you never pay, using the free version helps the company get more users. However, the company still has to pay to host all those free users.
- Demonstration (Crippleware): Sometimes, the free version is just a limited demo to show you what the full software can do.
- Transaction Fees: Online marketplaces might charge a fee on sales to cover their SaaS costs.
The most common ways SaaS companies make money are through subscriptions and pay-per-use models.
Subscriptions and Pay-Per-Use
For you, the customer, these models have advantages:
- Lower Upfront Cost: You don't have to pay a huge amount of money all at once to buy the software.
- More Flexibility: You can often cancel your subscription if you don't need the software anymore.
- Lower Overall Cost: For many, it's cheaper than buying a traditional software license that you own forever. This is especially helpful for smaller businesses that might not be able to afford expensive traditional software.
With pay-per-use, you might be charged based on how many users you have, how many tasks you complete, how much storage you use, or other things. Many people like this because they feel they only pay for what they use.
The subscription model gives the company a steady income. However, if many people cancel their subscriptions, it can be a problem for the business. Because it's easy to cancel and switch to a competitor, SaaS companies often work hard to keep their customers happy.
Why Companies Use SaaS
SaaS products are usually accessed through a web browser. This means you can use the application from almost anywhere, on any device (like a computer, tablet, or smartphone), without needing to install or update anything.
SaaS providers often make it easy to sign up for their products. They also try to quickly update their software based on what customers say they need. This makes customers feel like the product is always getting better. This can help SaaS companies attract customers who might otherwise stick with older, traditional software.
Security and Challenges
Even though cloud software can be very secure, some companies worry about security and privacy when using SaaS products. They might not trust a third-party provider to keep their sensitive information safe. SaaS companies have to protect their services from attacks, like denial-of-service attacks (where too much traffic tries to crash a system) and hacking. They use tools like access control, authentication (checking who you are), and encryption (scrambling data) to keep your information private.
The SaaS provider is responsible for all software updates, including security patches, and for protecting your data.
One challenge with SaaS is that it can be a bit slower than software installed directly on your computer. This is because the information has to travel over the internet to the cloud and back. For most uses, this isn't a problem, but for very time-sensitive tasks, it could be.
Many companies have changed how they budget for technology because of SaaS. Instead of buying expensive software and hardware (a big one-time cost), they now pay for SaaS as a regular operating expense (like a monthly bill).
How SaaS is Developed
A big challenge for SaaS companies is not knowing exactly how many users they will have at any given time. Their system needs to be strong enough to handle everyone without slowing down or crashing. But they also don't want to pay for too many resources that aren't being used. Sometimes, they offer cheaper rates during off-peak hours to spread out the usage. People expect SaaS services to always be available, so if there's an outage, it often makes the news!
There aren't special ways of writing code that are only for SaaS. However, SaaS products are often updated very frequently. This is because it's easy to roll out new features over the internet. Developers often use methods like Agile software development, which helps them release updates quickly. They also do a lot of software testing to make sure the service is always working well.
SaaS developers also need to make sure their apps work on many different devices, like desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones. Some apps are even designed as Progressive web applications, which means they can still work a bit even if your device is offline.
SaaS Architecture
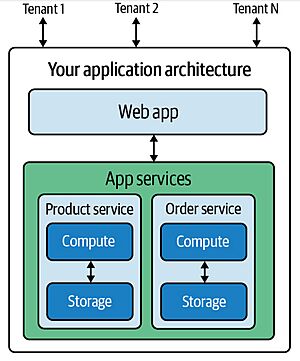
Most SaaS providers use a "multi-tenant" architecture. This means that all customers ("tenants") use the same version of the software on the same setup (computers, network, operating system). This makes it easier for the company because they don't have to support many different versions. In this setup, many computer resources can be shared among different customers.
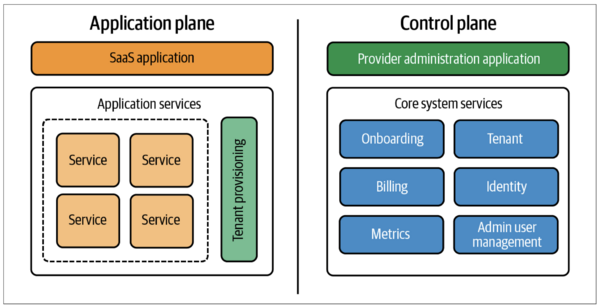
A typical SaaS application has two main parts:
- Application Plane: This is the main part of the software that you use. It handles the core features of the SaaS product.
- Control Plane: This part manages the system itself. It handles things like signing up new customers, billing, and how the SaaS provider manages the service. For example, if a SaaS product offers different levels of service for different prices, this is usually handled by the control plane.
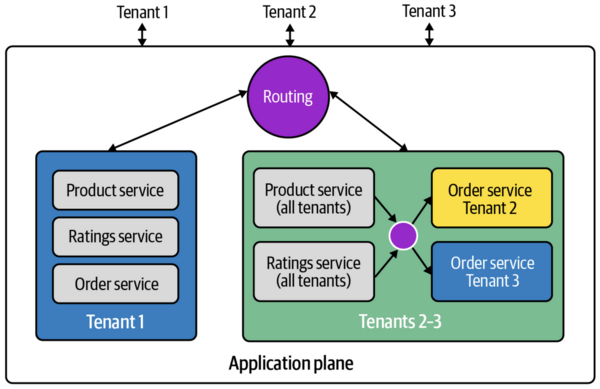
A key challenge in a multi-tenant system is making sure that different customers cannot see or change each other's data. For most SaaS apps, some parts of the system are shared, while others are kept separate for each customer. There's also a system to direct each customer's requests to the right services.
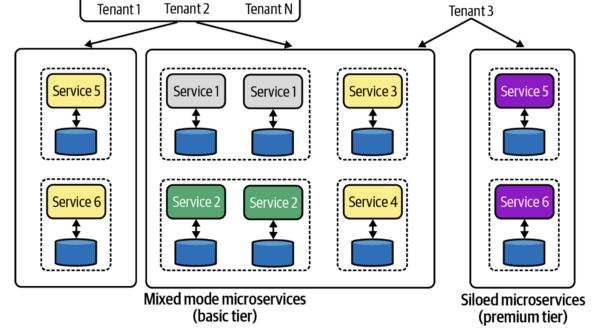
Some SaaS products keep everything completely separate for each customer. This is called "siloing." While it might not be as efficient, it can make it easier to move older software to a SaaS model. Sometimes, this "siloed" option is offered as a more expensive, premium service. Many systems use a mix of both approaches, sharing some resources and keeping others separate.
See also
 In Spanish: Software como servicio para niños
In Spanish: Software como servicio para niños