Nobel Prize facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Nobel Prize |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Presented by |
|
| Country | |
| Reward | A gold-plated green gold medal, a diploma, and a monetary award of 11 million SEK |
| First awarded | 10 December 1901 |
| Currently held by | 621 prizes to 992 laureates (as of 2024[update]) |
The Nobel Prizes are super important awards given each year. They honor people and groups who have done amazing things. These achievements must have helped humanity a lot. The prizes started in 1901. They were created because of the will of Alfred Nobel.
Alfred Nobel was a Swedish inventor. He wanted his money to be used for these special awards. Originally, there were five prize areas. These were physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine (which is about biology and health), literature, and peace. Later, in 1968, a sixth prize was added. This was the Prize in Economic Sciences. It was created by Sweden's central bank.
The Nobel Prizes are seen as the most respected awards in their fields. Each winner is called a laureate. They receive a special gold medal, a diploma, and money. As of 2023, the prize money was about 11 million Swedish Krona. That's around 1 million US dollars! The medal shows Alfred Nobel's face. It also has his birth and death years. Usually, no more than three people can share one prize. But the Peace Prize can go to organizations with more members. A prize is not given if someone dies before being chosen. But if they die after being chosen, they still get the prize. Between 1901 and 2024, over 1,000 people and organizations have received a Nobel Prize. Some have even won more than once!
Contents
History of the Nobel Prizes

Alfred Nobel was born in Stockholm, Sweden, in 1833. He came from a family of engineers. Alfred grew up to be a chemist, engineer, and inventor. He bought a steel mill in 1894. He turned it into a big factory for making weapons. Nobel also invented ballistite, a type of explosive. He became very rich from his 355 inventions. His most famous invention was dynamite.
There's a famous story about Alfred Nobel. In 1888, he supposedly read his own obituary in a French newspaper. An obituary is a notice about someone's death. The newspaper mistakenly thought Alfred had died. The headline said, "The Merchant of Death Is Dead." It was actually his brother, Ludvig, who had passed away. This article made Alfred worried about his legacy. He wanted to be remembered for something good. This story might have inspired him to change his will. However, some historians think this story is just a myth.
Alfred Nobel died in Italy on December 10, 1896. He was 63 years old.
Nobel wrote several wills during his life. His last will was written in 1895. It surprised many people. He stated that most of his money should be used to create prizes. These prizes would go to those who brought "the greatest benefit on mankind." The prizes were for physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, literature, and peace. Nobel left 94% of his wealth for these five prizes. This was a huge amount of money. Because of some doubts, his will was not approved until 1897. The people in charge of his will created the Nobel Foundation. This foundation would manage the money and organize the prizes.
Nobel's will also named the Norwegian Nobel Committee. This committee would award the Peace Prize. Other organizations were chosen soon after. These included the Karolinska Institute for medicine. The Swedish Academy was chosen for literature. The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences was chosen for physics and chemistry. In 1900, the Nobel Foundation set up rules for how the prizes would be given.
The Nobel Foundation

The Nobel Foundation was officially started on June 29, 1900. It is a private organization. Its main job is to manage the money and handle the business side of the Nobel Prizes. Alfred Nobel's personal fortune funds the prizes. The foundation invests this money. This helps make sure there's always enough money for the awards.
The Nobel Foundation also promotes the prizes around the world. It handles many of the tasks related to the awards. But it does not choose the winners. The foundation is like an investment company. It invests Nobel's money to keep the prizes going. The foundation does not have to pay taxes in Sweden or the United States. By 2007, the foundation had about 3.6 billion Swedish kronor. That's a lot of money!
The foundation has a board of five people. They are Swedish or Norwegian citizens. The chairman is chosen by the Swedish King. Other members are chosen by the groups that award the prizes.
How the Foundation is Funded
Today, the Nobel Foundation invests its money in different ways. About half is in stocks. Some is in bonds. The rest is in other investments, like real estate. This mix helps the money grow.
In 2011, the total cost to run the Nobel Prizes was about 120 million kronor. About 50 million kronor was for the prize money itself. Other costs included paying the groups that choose the winners. The events during Nobel Week in Stockholm and Oslo also cost money. The cost for the Economic Sciences prize is paid by Sweden's central bank.
First Nobel Prizes
Once the Nobel Foundation was ready, the Nobel Committees started looking for nominees. They sent lists of possible winners to the prize-awarding groups.
For the first Physics Prize, Wilhelm Röntgen was chosen. He discovered X-rays. This was a huge breakthrough! For the Chemistry Prize, many scientists had done great work. The committee chose Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff. He won for his work in chemical thermodynamics.
The first Nobel Prize in Literature went to the poet Sully Prudhomme. Some people were surprised by this choice. They thought Leo Tolstoy should have won. The first Physiology or Medicine Prize went to Emil von Behring. He developed a treatment for diphtheria. This disease had caused many deaths.
The first Nobel Peace Prize was shared. One part went to Henry Dunant. He helped start the Red Cross. He also helped create the Geneva Convention. The other part went to Frédéric Passy. He was a French pacifist.
Nobel Prizes During World War II
From 1940 to 1942, no Nobel Prizes were awarded. This was because of World War II. In 1938 and 1939, Adolf Hitler's government stopped three German winners from accepting their prizes. These scientists later received their diplomas and medals after the war.
Even though Sweden was neutral, the prizes were given out less often. The Peace Prize was not awarded in 1939. During the war, some members of the Norwegian Nobel Committee had to leave Norway. The Nobel Foundation said the committee's building in Oslo was Swedish property. This kept it safe from the German military. The committee kept working, but they did not award any prizes during the occupation. In 1944, they started accepting nominations again.
The Economics Prize
After World War II, the study of economics grew a lot. It became a very important scientific field. In 1968, Sweden's central bank celebrated its 300th birthday. It gave money to the Nobel Foundation. This money was used to create a new award. It was for achievements in economic sciences. The first Prize in Economic Sciences was given in 1969. The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences chooses the economics winners. The first winners were Jan Tinbergen and Ragnar Frisch. They won for their work on economic models. The Nobel Foundation decided not to add any more new prizes after this one.
How Nobel Prizes Are Awarded
The process for choosing Nobel winners is similar for all prizes. The main difference is who can suggest names for each award.
Nominations for the Prize
Each September, the Nobel Committee sends forms to about 3,000 people. These are usually important experts in the prize fields. For the Peace Prize, they also ask governments and past winners for ideas. The deadline to send in nominations is January 31st of the award year. The Nobel Committee then picks about 300 possible winners. The names of nominees are kept secret for 50 years. Winners are not told they are being considered.
Choosing the Winners
The Nobel Committee gets advice from experts. They create a report with a list of candidates. This report goes to the groups that award the prizes. There are four main groups that choose the winners:
- Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences – for Chemistry, Physics, and Economics
- Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute – for Physiology or Medicine
- Swedish Academy – for Literature
- Norwegian Nobel Committee – for Peace
These groups meet and vote to pick the winners. Their decision is final and announced right away. A maximum of three people can share one prize. The Peace Prize can be given to organizations. The winners are announced in the first two weeks of October.
Posthumous Awards
Normally, a person must be alive when the prize is announced in October. But there have been a few exceptions. In the past, if someone died between being nominated and the decision, they could still get the prize. This happened twice, in 1931 and 1961. In 1996, William Vickrey died after the Economics Prize was announced but before he could receive it. He still got the award. In 2011, the committee didn't know that Ralph M. Steinman had died three days before the Physiology or Medicine Prize was announced. They decided to let his award stand because the decision was made when they thought he was alive.
Time Between Discovery and Award
Alfred Nobel's will said prizes should be for discoveries made "during the preceding year." But early on, some discoveries that won prizes were later found to be wrong. To avoid this, the awards now often recognize older discoveries. These are discoveries that have been proven true over time. The Nobel Assembly says "the previous year" means when the full importance of a discovery is clear.
The time between a discovery and the award can be different for each prize. The Literature Prize often honors a writer's whole life's work. The Peace Prize can also be for a lifetime of work. For example, Martti Ahtisaari won in 2008 for his work solving conflicts. But it can also be for recent events. Kofi Annan won the Peace Prize in 2001, just four years after becoming UN Secretary-General. Sometimes, scientists don't live long enough for their work to be recognized.
Award Ceremonies and Events
Most Nobel Prizes are given out in Stockholm, Sweden. This happens at the annual Award Ceremony on December 10th. This date is the anniversary of Nobel's death. The Peace Prize is given in Oslo, Norway, also usually on December 10th. These ceremonies and the parties afterward are big international events.
In Stockholm, the ceremony is at the Stockholm Concert Hall. A fancy banquet follows at Stockholm City Hall. In Oslo, the Peace Prize ceremony has been held in different places. Since 1990, it has been at Oslo City Hall. At the Stockholm ceremony, the King of Sweden gives the prizes to the winners. In Oslo, the chairman of the Norwegian Nobel Committee gives the Peace Prize. The King of Norway and the royal family are usually there.
Nobel Banquet

After the award ceremony in Sweden, there's a big dinner. It's held in the Blue Hall at the Stockholm City Hall. The Swedish Royal Family attends, along with about 1,300 guests. The Nobel Peace Prize banquet is in Norway. It's held at the Oslo Grand Hotel. About 250 guests attend this dinner.
Nobel Lecture
Every Nobel winner must give a public lecture. This lecture is about the topic of their prize. These lectures usually happen during Nobel Week. This is the week leading up to the award ceremony. But winners have up to six months to give their lecture. For example, US President Theodore Roosevelt won the Peace Prize in 1906. But he gave his lecture in 1910, after he was no longer president.
Nobel Minds
Since 2004, there has been a TV show called Nobel Minds. It's a discussion with the science prize winners. It's a co-production with BBC World News.
The Prizes Themselves
Medals

The Nobel Prize medals are made by Svenska Medalj AB in Sweden. Before 2010, they were made by the Swedish Mint. The Nobel Prize medals are special trademarks of the Nobel Foundation.
Each medal has a picture of Alfred Nobel on the front. This picture is the same for the physics, chemistry, medicine, and literature medals. The Peace Prize and Economics Prize medals have a slightly different design. The back of each medal is different. It depends on which group awarded the prize. The back of the chemistry and physics medals look the same.
Before 1980, all medals were made of 23 carat gold. Now, they are 18 carat gold plated with 24 carat gold. Each medal weighs about 175 grams. They are 66 millimeters wide. Because they are so valuable, Nobel medals can be stolen. During World War II, some German scientists' medals were sent to Denmark for safety. A chemist dissolved them in acid to hide them from the Nazis. After the war, the gold was recovered, and new medals were made.
Diplomas

Nobel winners get a diploma from the King of Sweden. For the Peace Prize, the chairman of the Norwegian Nobel Committee gives it. Each diploma is unique. It's designed by the group that gives the prize. The diploma has a picture and text in Swedish. It names the winner and usually says why they won. Peace Prize diplomas do not have a specific reason written on them.
Prize Money
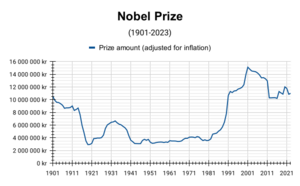
Winners also get a sum of money. The amount changes each year. It depends on how much money the Nobel Foundation has. The prize money has grown since the 1980s. In 2009, it was 10 million Swedish Krona. In 2012, it was lowered to 8 million SEK. If two people share a prize, the money is split equally. If three people share, the committee can split it equally. Or they can give half to one person and a quarter to each of the others. Many winners donate their prize money to good causes.
Interesting Nobel Prize Facts
- Youngest winner: Malala Yousafzai. She was 17 when she won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2014.
- Oldest winner: John B. Goodenough. He was 97 when he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2019.
- Only person to win two unshared Nobel Prizes: Linus Pauling. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954 and the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962.
- People who won Nobel Prizes in two different subjects:
* Marie Skłodowska-Curie: Nobel Prize in Physics (1903) and Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1911). * Linus Pauling: Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1954) and Nobel Peace Prize (1962).
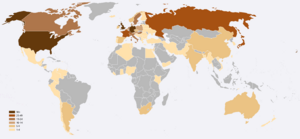
- Country with the most Nobel winners: United States. They had 403 Nobel laureates as of 2022.
- Winners who received multiple Nobel Prizes:
* Marie Skłodowska-Curie (Physics 1903, Chemistry 1911) * International Committee of the Red Cross (Peace 1917, 1944, 1963) * Linus Pauling (Chemistry 1954, Peace 1962) * John Bardeen (Physics 1956, 1972) * Frederick Sanger (Chemistry 1958, 1980) * United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (Peace 1954, 1981) * Karl Barry Sharpless (Chemistry 2001, 2022)
- Nobel Prizes given after someone died:
* Erik Axel Karlfeldt (Literature 1931) * Dag Hammarskjöld (Peace 1961) * Ralph M. Steinman (Physiology or Medicine 2011)
- Married couples who won Nobel Prizes:
* Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie (Physics 1903) * Irène Joliot-Curie and Frédéric Joliot-Curie (Chemistry 1935) * Gerty Cori and Carl Ferdinand Cori (Physiology or Medicine 1947) * Gunnar Myrdal (Economics 1974) and Alva Myrdal (Peace 1982) * May-Britt Moser and Edvard Moser (Physiology or Medicine 2014) * Esther Duflo and Abhijit Banerjee (Economics 2019)
- Years with no prizes:
* Physics: 1916, 1931, 1934, 1940, 1941, 1942 * Chemistry: 1916, 1917, 1919, 1924, 1933, 1940, 1941, 1942 * Physiology or Medicine: 1915, 1916, 1917, 1918, 1921, 1925, 1940, 1941, 1942 * Literature: 1914, 1918, 1935, 1940, 1941, 1942, 1943 * Peace: 1914, 1915, 1916, 1918, 1923, 1924, 1928, 1932, 1939, 1940, 1941, 1942, 1943, 1948, 1955, 1956, 1966, 1967, 1972
Special Nobel Laureates
Winners of Multiple Prizes

Five people have won two Nobel Prizes. Marie Skłodowska-Curie won the Physics Prize in 1903. This was for her work on radioactivity. She also won the Chemistry Prize in 1911 for isolating pure radium. She is the only person to win Nobel Prizes in two different sciences. Linus Pauling won the Chemistry Prize in 1954. This was for his research on chemical bonds. He also won the Peace Prize in 1962 for his work against nuclear weapons. He is the only person to win two unshared prizes.
John Bardeen won the Physics Prize twice. He won in 1956 for inventing the transistor. He won again in 1972 for his theory of superconductivity. Frederick Sanger won the Chemistry Prize twice. He won in 1958 for finding the structure of insulin. He won again in 1980 for a method to find DNA sequences. Karl Barry Sharpless won the Chemistry Prize in 2001 and again in 2022.
Two organizations have won the Peace Prize multiple times. The International Committee of the Red Cross won it three times. They won in 1917 and 1944 for their work during the world wars. They also won in 1963 for their 100th anniversary. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees has won the Peace Prize twice. They won in 1954 and 1981 for helping refugees.
Family Nobel Laureates
The Curie family has won the most Nobel Prizes. They have four prizes awarded to five family members. Marie Skłodowska-Curie won in Physics (1903) and Chemistry (1911). Her husband, Pierre Curie, shared the 1903 Physics prize with her. Their daughter, Irène Joliot-Curie, won the Chemistry Prize in 1935. She shared it with her husband, Frédéric Joliot-Curie. Also, Henry Labouisse, who was married to Marie Curie's other daughter, accepted the Peace Prize in 1965 for UNICEF.
Many other families have had two Nobel winners. For example, Gerty Cori and Carl Ferdinand Cori, a husband-and-wife team, won the Physiology or Medicine Prize in 1947. Another couple, May-Britt Moser and Edvard Moser, won the same prize in 2014. J. J. Thomson won the Physics Prize in 1906. His son, George Paget Thomson, won the Physics Prize in 1937. They both studied electrons.
Refusing and Restrictions
Two winners have willingly turned down the Nobel Prize. In 1964, Jean-Paul Sartre won the Literature Prize. But he refused it. He said a writer should not become an "institution." Lê Đức Thọ was chosen for the 1973 Peace Prize. He refused it because there was no real peace in Vietnam yet. George Bernard Shaw tried to refuse the prize money in 1925. But they agreed to use it to start a literary foundation.
During the time of Adolf Hitler's rule, three German winners were not allowed to accept their prizes. These were Richard Kuhn, Adolf Butenandt, and Gerhard Domagk. They all received their diplomas and medals after World War II.
In 1958, Boris Pasternak turned down his Literature Prize. He was afraid of what the Soviet Union government might do. The Swedish Academy did not accept his refusal. They said the award was still valid. Pasternak's son later accepted the prize for him in 1989.
Aung San Suu Kyi won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1991. But her children accepted it for her. She was under house arrest in Myanmar. She gave her speech 20 years later, in 2012. Liu Xiaobo won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2010. He was a political prisoner in China. He was unable to accept the prize during his lifetime.
Impact of the Nobel Prizes
Cultural Influence

The Nobel Prize is a worldwide symbol of great achievement. It is often shown in movies and TV shows. For example, the movie The Prize (1963) is about fictional Nobel winners. The TV show The Big Bang Theory also features the Nobel Prize.
There is a statue called Planet of Alfred Nobel in Ukraine. It has reliefs of 802 Nobel winners. These reliefs are made from metal from old missiles.
Sometimes, Nobel winners have believed in ideas that are not supported by science. This is sometimes called "Nobel disease."
In 2001, a college in Minnesota asked a composer to write music for the 100th anniversary of the Nobel Prizes. The Nobel Symphony highlights all the main prizes. It includes words from Nobel winners like Pablo Neruda and Martin Luther King Jr..
See also
 In Spanish: Premio Nobel para niños
In Spanish: Premio Nobel para niños
- List of Nobel laureates
- List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry
- List of Nobel laureates in Literature
- List of Nobel Peace Prize laureates
- List of Nobel laureates in Physics
- List of Nobel laureates in Physiology or Medicine
- List of Nobel Memorial Prize laureates in Economics
- List of female Nobel laureates
- List of Nobel laureates by country
- List of Nobel laureates by university affiliation
- List of Asian Nobel laureates
- List of Jewish Nobel laureates
- Nobel Prize medal
- Fields Medal
- Abel Prize
- Ig Nobel Prize
- Lindau Nobel Laureate Meetings
- List of prizes known as the Nobel of a field
- Lists of science and technology awards
- Nobel Conference
- Nobel Library
- Nobel Prize Museum
- Nobel Prize effect