Curie family facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Curie family |
|
|---|---|
| Place of origin | Paris, France |
| Members | |
| Connected families |
|
| Distinctions | |

The Curie family is known for being a group of amazing scientists. Many members of this French family made huge discoveries in physics and chemistry. They even won several Nobel Prizes! Their work changed how we understand radioactivity and the tiny particles that make up everything.
Here are some of the most famous Curies:
- Marie Curie (1867-1934): A Polish-French chemist and physicist. She was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize and the only person to win Nobel Prizes in two different sciences (physics and chemistry).
- Pierre Curie (1859-1906): Marie's husband, a French physicist. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physics with Marie and Henri Becquerel for their work on radioactivity.
- Irène Joliot-Curie (1897-1956): Marie and Pierre's daughter, a French physicist. She won a Nobel Prize in Chemistry with her husband.
- Frédéric Joliot-Curie (1900-1958): Irène's husband, a French physicist. He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Irène.
- Ève Curie (1904-2007): Marie and Pierre's second daughter. She was a French-American writer and journalist.
Things Named After the Curies
The Curie family's discoveries were so important that many things are named after them. This shows how much they contributed to science and the world.
Some examples include:
- Curie (unit) (Ci): This is a unit used to measure radioactivity.
- Curie point: This is a special temperature where certain materials lose their magnetic properties.
- Curium (Cm): This is a chemical element, a type of atom, named in their honor.
- Curie (lunar crater): A crater on the Moon is named after them.
- Curie Institute (Paris) and Curie Institute (Warsaw): These are famous research centers for cancer treatment and scientific study.
- Two French submarines were also named Curie in the First and Second World Wars.
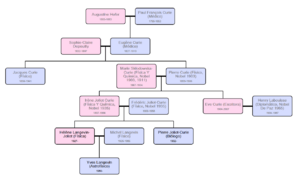
Exploring the Curie Family Tree
The Curie family tree shows how many brilliant minds were connected. It all started with Paul Curie, a doctor and humanist.
Paul Curie (1799–1853), a doctor
x Augustine Hofer (1805–1883), whose family included the famous mathematician Johann Bernoulli.
-
- Eugene Curie (1827–1910), also a doctor.
x Sophie-Claire Depouilly (1832-1897).- Paul-Jacques Curie] (1855–1941), a physicist.
- Maurice Curie (1888–1975), also a physicist.
- Paul-Jacques Curie] (1855–1941), a physicist.
- Eugene Curie (1827–1910), also a doctor.
*Daniel Curie (1927-2000), a physicist.
-
-
- Pierre Curie (1859–1906), a physicist who won the Nobel Prize in 1903.
x Marie Skłodowska Curie (1867–1934), a physicist and chemist who won Nobel Prizes in 1903 and 1911.- Irène Joliot-Curie (1897–1956), a physicist who won the Nobel Prize in 1935
x Frédéric Joliot-Curie (1900–1958), a physicist who also won the Nobel Prize in 1935.
- Irène Joliot-Curie (1897–1956), a physicist who won the Nobel Prize in 1935
- Pierre Curie (1859–1906), a physicist who won the Nobel Prize in 1903.
-
* Pierre Joliot-Curie (1932), a biologist. ** Marc Joliot (1962), a neuroscientist.
**- Alain Joliot (1964), a biologist. *
- Hélène Langevin-Joliot (1927), a nuclear physicist. ** Françoise Langevin-Mijangos **
- Yves Langevin (1951), an astrophysicist.
-
-
-
- Ève Curie (1904–2007), a writer and journalist.
x Henry Richardson Labouisse Jr. (1904–1987), an American diplomat who accepted the Nobel Peace Prize on behalf of UNICEF in 1965.
- Ève Curie (1904–2007), a writer and journalist.
-
-
-
See also
 In Spanish: Familia Curie para niños
In Spanish: Familia Curie para niños