Economics facts for kids
Economics is a social science that helps us understand how people make choices. It looks at how we produce, share, and use goods and services. Think of it as studying how our world manages its resources.
Economics explores how individuals, businesses, and governments make decisions. It also examines how these decisions affect each other. We learn how different parts of an economy work together.
There are two main parts of economics. Microeconomics studies the small picture. It looks at choices made by individuals, families, and companies. It also examines how they interact in markets. Macroeconomics studies the big picture. It looks at the economy as a whole. This includes things like total production, economic growth, and unemployment. It also covers how public policies can influence these big trends.
Economics helps us understand many different parts of life. It can be used in business, health care, and even to understand education. It helps us make smart choices about our resources and our future.
Contents
What is Economics?
The word "economics" comes from ancient Greek. It means "managing a household." For a long time, it was called "political economy." This meant managing a country or state.
Over the years, many smart thinkers have tried to define economics. Adam Smith, a Scottish philosopher, wrote about the "wealth of nations" in 1776. He looked at how countries become rich. He also studied how to provide for people and fund public services.
Later, Alfred Marshall said economics is "a study of man in the ordinary business of life." He meant it's about how people earn and use their money. This definition helped us look at economics on a smaller scale.
Today, a common definition comes from Lionel Robbins. He said economics studies how people make choices. This happens when they have limited resources but many different things they want to do. For example, you have limited time, but many activities you want to do. You have to choose!
This idea of scarcity is very important. It means there are not enough resources for everyone to have everything they want. So, economics helps us understand how we make choices. It shows how we use our limited resources wisely.
History of Economic Ideas
Economics has a long history, with ideas about managing resources going back to ancient times.
Early Economic Thinking

In ancient Greece, thinkers like Aristotle wrote about how households should manage their resources. Later, in Europe, two main groups of thinkers emerged.
The first group was called the "mercantilists." They believed a country's wealth came from having lots of gold and silver. They thought countries should sell many goods to other nations. They also believed in limiting imports to keep gold and silver within their borders.
The second group was the "physiocrats" in 18th-century France. They thought that only farming created real wealth. They believed in less government involvement in the economy. This idea was called laissez-faire, meaning "let do."
Classical Economics and Adam Smith
The year 1776 was a big one for economics. That's when Adam Smith published his famous book, The Wealth of Nations. Many people see this as the start of economics as a separate field.
Smith said that a nation's wealth comes from its land, labor, and capital. He explained how dividing up work (specialization) can make production much more efficient. He also talked about the "invisible hand." This idea suggests that when people act in their own best interest, it can also benefit society as a whole.
Other classical economists followed Smith. David Ricardo looked at how income is shared among landowners, workers, and business owners. He also explained comparative advantage. This means countries should focus on producing what they are relatively best at. Then they can trade with others for goods they are not as good at making.
Different Economic Schools
Over time, many different ways of thinking about economics developed.
Marxian Economics

Karl Marx was a German philosopher who wrote about economics in the 1800s. He focused on how labor creates value. He also looked at how workers were paid only a part of the value they created. His ideas led to what is known as Marxian economics.
Neoclassical Economics
Around the late 1800s, "neoclassical economics" became popular. This approach used more math and science ideas. It focused on how supply and demand work together to set prices. It also looked at how individuals and businesses make choices to get the most out of their resources.
Keynesian Economics
During the Great Depression in the 1930s, John Maynard Keynes introduced new ideas. He wrote The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. Keynes believed that sometimes, the economy might not fix itself. He suggested that governments and central banks could step in. They could use policies to help the economy grow and reduce unemployment.
Modern Economic Ideas
After World War II, economists continued to build on these ideas. Some focused on how money supply affects the economy (monetarism). Others looked at how people's expectations influence economic outcomes. Today, many economists combine different ideas. They use models that include both individual choices and the bigger picture of the economy.
How Economists Study the World
Economists use special methods to understand how economies work.
Building Theories
Economists create models to explain how things happen. These models are like simplified maps of the real world. They help economists make predictions. For example, a model might predict how a price change affects how much people buy.
Economists try to make their models simple but accurate. They want to understand how people make choices. They also want to see how these choices lead to certain results in the economy.
Using Data and Experiments
Economists also test their theories using real-world information. This is called empirical research. They use statistics to look at economic data. This data can be about prices, jobs, or how much people spend.
Sometimes, economists even do experiments. They set up situations to see how people make decisions. This helps them understand human behavior better. By combining theories and data, economists learn more about our complex world.
Microeconomics: The Small Picture


Microeconomics looks at the choices made by individuals and businesses. It studies how they interact in specific markets.
Producing Goods and Services
Production is about turning inputs into outputs. Inputs are things like labor, capital (tools and machines), and land. Outputs are the goods and services we use.
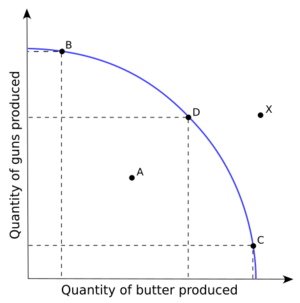
Economists also think about opportunity cost. This is what you give up when you choose one thing over another. For example, if a factory makes more cars, it might have to make fewer trucks. The trucks given up are the opportunity cost of making more cars.
Economic efficiency means using resources in the best way possible. It means getting the most output from the inputs you have.
Why We Specialize
Specialization means focusing on making one type of good or service. Imagine one person is great at baking, and another is great at building. If they both specialize, they can make more of what they're good at. Then they can trade with each other.
This idea applies to countries too. Countries can specialize in what they produce best. Then they trade with other countries. This leads to more goods and services for everyone. This is called gains from trade.
Supply and Demand
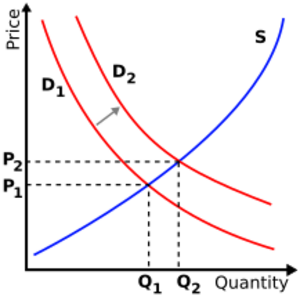
Supply and demand is a core idea in microeconomics. It explains how prices are set in a market.
Demand is how much of a good buyers want at different prices. Usually, if the price of something goes up, people want to buy less of it. If the price goes down, they want to buy more.
Supply is how much of a good sellers are willing to offer at different prices. Usually, if the price of something goes up, sellers want to produce and sell more. If the price goes down, they offer less.
The market equilibrium is where the amount buyers want equals the amount sellers offer. This is where the price settles.
Businesses and Firms
Most goods and services are made by firms or businesses. These can be small shops or large corporations. Firms combine labor and capital to produce things. They try to do this in the most efficient way to make a profit.
Dealing with Uncertainty
Life is full of unknowns, and so is economics. Uncertainty means we don't always know what will happen. Economists use tools like game theory to study how people make choices when they are uncertain. This helps understand decisions in business, negotiations, and even in daily life.
When Markets Don't Work Perfectly
Sometimes, markets don't work as well as they should. This is called market failure.
- Externalities: These are effects on others that are not included in the price. For example, pollution from a factory is a negative externality. Education can be a positive externality because it benefits all of society.
- Public goods: These are things that everyone can use, and it's hard to stop anyone from using them. Examples include national defense or streetlights. Markets often don't provide enough public goods.
Governments often step in to fix market failures. They might tax pollution or fund public goods.
Macroeconomics: The Big Picture
Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole. It studies big topics that affect everyone.
Economic Growth
Economic growth means an increase in the total amount of goods and services a country produces over time. When an economy grows, people generally have more opportunities and a higher standard of living. Economists study what makes countries grow faster. This includes things like new technologies and investments.
Ups and Downs of the Economy
Economies don't always grow smoothly. They have business cycles, which are periods of growth (booms) and slowdowns (recessions). During a recession, businesses might produce less, and some people might lose their jobs. Economists try to understand these cycles. They also look for ways to make them less severe.
Understanding Unemployment
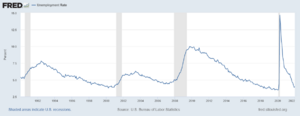
Unemployment happens when people who want to work cannot find jobs. The unemployment rate is the percentage of people in the workforce who are looking for a job but don't have one.
There are different types of unemployment. Some people are temporarily unemployed while looking for a new job (frictional). Others might lack the skills for available jobs (structural). Sometimes, unemployment rises when the economy slows down (cyclical).
Money and How It's Managed
Money is what we use to buy things. It makes trading much easier than bartering. Money includes physical cash and money in bank accounts.
Monetary policy is how central banks manage the amount of money in the economy. They often do this by changing interest rates. This affects how much people borrow and spend. The goal is to keep prices stable and help the economy grow.
Government Spending and Taxes
Fiscal policy is how governments use spending and taxes to influence the economy. When the economy is slow, governments might spend more on projects. They might also cut taxes to encourage people to spend more. This can help boost demand and create jobs.
However, there are debates about how effective fiscal policy is. Some worry that government spending might "crowd out" private spending.
Economic Inequality
Economic inequality refers to the differences in wealth and income among people. Some people have much more money and assets than others. Economists study why inequality happens and how it affects society. They also look at how government policies, like taxes, can influence income distribution.
Other Areas of Economics
Economics is a very broad field. Here are a few other areas:
- Public economics: Studies how governments make economic decisions. It looks at taxes, government spending, and public services.
- International economics: Focuses on trade between countries. It also looks at how money moves across borders.
- Labour economics: Studies how labor markets work. It looks at wages, employment, and working conditions.
- Development economics: Examines how lower-income countries can grow and improve their economies.
Economics and Other Subjects
Economics connects with many other subjects:
- Law and economics: Uses economic ideas to understand laws and legal systems.
- Political economy: Studies how politics and economic systems influence each other.
- Energy economics: Looks at the supply and demand for energy resources.
- Economic sociology: Studies how economic activities affect society and culture.
The Economics Profession
Many people work as economists. They work in universities, businesses, and for governments. Economists use math, statistics, and computer science in their work. They help make important decisions about our economy.
Women in Economics
Many women have made important contributions to economics. Harriet Martineau helped popularize classical economic ideas. Joan Robinson was a key post-Keynesian economist. Anna Schwartz co-authored a major work on the monetary history of the United States.
More recently, women like Elinor Ostrom, Esther Duflo, and Claudia Goldin have won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. This shows the growing impact of women in the field.
See also
 In Spanish: Economía (ciencia económica) para niños
In Spanish: Economía (ciencia económica) para niños
- Asymmetric cointegration
- Critical juncture theory
- Democracy and economic growth
- Economic democracy
- Economic ideology
- Economic union
- Economics terminology that differs from common usage
- Free trade
- Glossary of economics
- Happiness economics
- Humanistic economics
- Index of economics articles
- List of academic fields § Economics
- List of economics awards
- Outline of economics
- Socioeconomics
- Solidarity economy
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |