Economic growth facts for kids
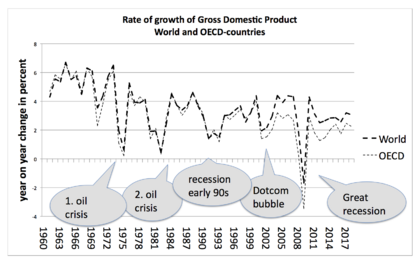
In economics, economic growth happens when a country produces more goods and services than it did in the past. Think of it as the country's economy getting bigger. This is often measured by looking at the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which is the total value of everything a country makes in a year.
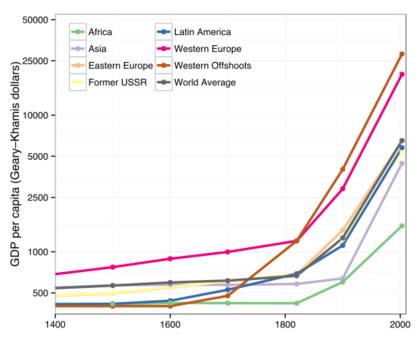
To see if people are actually better off, we often look at the real GDP per capita. This means we take the total GDP, adjust it for price changes (inflation), and then divide it by the number of people in the country. If this number goes up, it usually means that, on average, each person has more goods and services available to them.
Economic growth can happen in two main ways. Extensive growth is when an economy grows because it's using more resources, like having more workers or using more land. Intensive growth is when an economy grows by becoming more efficient—using technology and better methods to get more out of the same resources.
Contents
What Makes an Economy Grow?
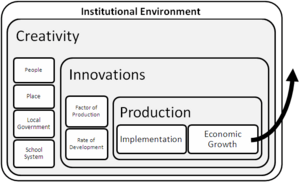
Several key ingredients help a country's economy grow over time. These factors work together to increase how much a country can produce.
Better Tools and Technology (Productivity)
The most important source of economic growth is an increase in productivity. Productivity means producing more goods and services with the same amount of effort, time, or resources.
Imagine a baker who can make 20 loaves of bread in a day. If she gets a new, better oven, she might be able to make 40 loaves in the same amount of time. Her productivity has doubled!
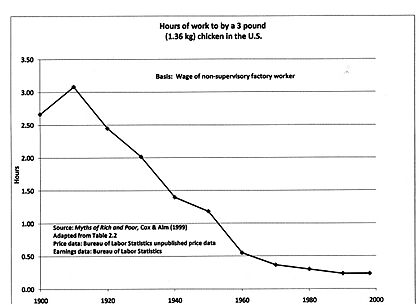
Throughout history, new inventions have boosted productivity. During the Industrial Revolution, machines started doing work that was once done by hand. Later, electricity, computers, and the internet allowed businesses to produce things much more efficiently. This is why many products that were once expensive, like phones or cars, are much cheaper and more common today.
More Tools and Equipment (Physical Capital)
Physical capital includes all the man-made things that help workers produce goods and services. This includes factories, machines, computers, roads, and office buildings.
When a country invests in more and better capital, its workers can become more productive. For example, a construction worker with a power drill can work much faster than one with only a screwdriver. Having good roads and ports also helps businesses move their goods around more easily, which helps the economy grow.
Skilled and Healthy People (Human Capital)
Human capital refers to the skills, knowledge, and health of a country's workforce. When people are well-educated and healthy, they can do their jobs better, come up with new ideas, and adapt to new technologies.
Countries that invest in schools, universities, and healthcare often see faster economic growth. A population of skilled engineers, doctors, scientists, and creative thinkers is one of the most valuable resources a country can have. When people are healthy, they can work more consistently and effectively.
Good Rules and Stable Government
For an economy to grow, it needs a stable and fair environment. This is where political institutions come in. When a government protects private property, it means people can own things and be sure they won't be taken away unfairly. This encourages them to invest and build businesses.
Fair laws, a reliable justice system, and a government that supports trade and commerce create a good foundation for economic growth. When people trust that the rules are fair and won't suddenly change, they are more willing to take risks, like starting a new company, which creates jobs and wealth.
The Power of Long-Term Growth
Even a small rate of economic growth can make a huge difference over a long time. This is because of compounding, where growth builds on top of previous growth.
A handy trick to see how long it takes for something to double is the Rule of 72. You just divide 72 by the growth rate.
- If an economy grows at 2% per year, it will double in size in about 36 years (72 / 2 = 36).
- If it grows at 4% per year, it will double in just 18 years (72 / 4 = 18).
This shows why countries are so focused on increasing their growth rate, even by a small amount. Over a person's lifetime, a slightly faster growth rate can lead to a much higher standard of living.
| Country | Period | Real GDP per person at beginning of period | Real GDP per person at end of period | Real annualized growth rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 1890–2008 | $1,504 | $35,220 | 2.71% |
| Brazil | 1900–2008 | $779 | $10,070 | 2.40% |
| Mexico | 1900–2008 | $1,159 | $14,270 | 2.35% |
| Germany | 1870–2008 | $2,184 | $35,940 | 2.05% |
| Canada | 1870–2008 | $2,375 | $36,220 | 1.99% |
| China | 1900–2008 | $716 | $6,020 | 1.99% |
| United States | 1870–2008 | $4,007 | $46,970 | 1.80% |
| Argentina | 1900–2008 | $2,293 | $14,020 | 1.69% |
| United Kingdom | 1870–2008 | $4,808 | $36,130 | 1.47% |
| India | 1900–2008 | $675 | $2,960 | 1.38% |
| Indonesia | 1900–2008 | $891 | $3,830 | 1.36% |
| Bangladesh | 1900–2008 | $623 | $1,440 | 0.78% |
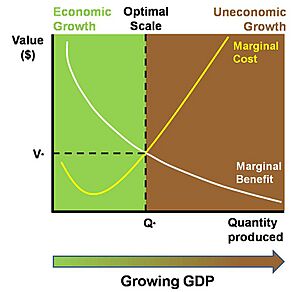
Is Economic Growth Always Good?
While economic growth can bring many benefits, like reducing poverty and improving lives, it also has some downsides and challenges that people are concerned about.
Quality of Life
Does a bigger economy always mean happier people? Not necessarily. Studies show that once people have enough money to meet their basic needs (like food, housing, and safety), getting more money doesn't always make them much happier.
Also, economic growth doesn't automatically benefit everyone. Sometimes, the gap between the rich and the poor, known as economic inequality, can increase. If only a small group of people benefits from growth, many others might be left behind. For growth to truly improve a society, its benefits need to be shared widely.
Impact on the Environment
One of the biggest concerns about economic growth is its effect on the planet. Producing more goods and services often means using more natural resources like water, trees, and minerals. It can also lead to more pollution and the release of greenhouse gases, which contribute to climate change.
This has led many people to argue for sustainable development. This is the idea that we should find ways for our economies to grow without causing permanent damage to the environment. This could mean switching to clean energy sources like solar and wind power, reducing waste, and protecting natural habitats. The goal is to improve people's lives today without making life harder for future generations
See also
 In Spanish: Crecimiento económico para niños
In Spanish: Crecimiento económico para niños
- Agrowth
- American exceptionalism
- Civilizing mission
- Climate change
- Critique of political economy
- Degrowth
- Development theory
- Economic development
- Export-oriented industrialization
- Debt-to-GDP ratio
- Greed
- Green growth
- Green new deal
- Growth accounting
- Hindu rate of growth
- The Limits to Growth
- List of countries by productivity growth.
- Manifest destiny
- Orthodox Development
- Post-growth
- Productivism
- Progress
- Propaganda
- Prosperity Without Growth
- Status quo
- Sufficiency economy
- Sustainability
- Sustainable development
- Thermoeconomics
- Uneconomic growth
- Unified growth theory
- Universal basic income
- Wealth redistribution
- The White Man's Burden
- World view
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |