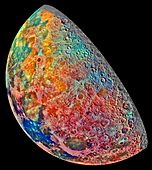False color facts for kids
False color is a way to show images using colors that aren't what you'd see with your own eyes. Imagine taking a picture where green trees show up as bright red! That's false color.
A false-color image uses colors to give you extra information about something. It's different from a true-color image, which shows things exactly as they look in real life.
When you take a photo with a regular camera, the colors in the picture match what your eyes would see. This is a true-color image. But in a false-color image, the colors are changed on purpose. These new colors help scientists and others see things that are usually invisible or hard to spot.
Contents
Why Use False Color?
False color helps us understand data better. It's like a secret code where each color means something special.
Seeing the Invisible
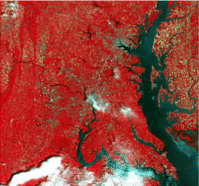
Sometimes, cameras can "see" light that our eyes can't. This includes infrared light or ultraviolet light. When a camera captures these types of light, false colors are used to make them visible to us. For example, infrared light is often used to study plants. Plants reflect a lot of infrared light. In a false-color image, areas with healthy plants might show up as bright red. This helps scientists track plant health from space.
Making Details Stand Out
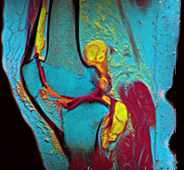
False color can also make small differences in an image much clearer. Imagine a picture of a knee from an MRI scan. In a regular MRI, different body parts might just be different shades of gray. It can be hard to tell them apart. But if you add false colors, each type of tissue (like bone, muscle, or fat) can be given a different color. This makes it much easier for doctors to see what's what.
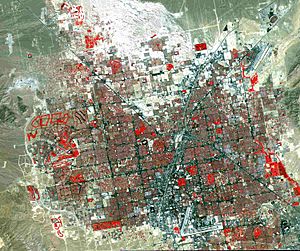
Showing Data from Space
Satellites often use false color. They collect information about Earth using different types of light. For example, a satellite might use false colors to show:
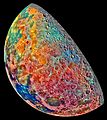
- Where different types of rocks are on the Moon.
- How much phytoplankton (tiny ocean plants) is in the sea.
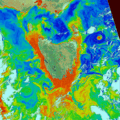
- The temperature of different areas on Earth.
By using false colors, scientists can quickly see patterns and changes that would be invisible in a normal picture. It's a powerful tool for learning more about our world and beyond!
Images for kids
-
Burns Cliff on Mars. The colors are close to what you'd see, but infrared light was used instead of red light.
-
A false-color image of Tasmania showing how much phytoplankton is in the water. Yellow, orange, and red mean more phytoplankton.
See also
 In Spanish: Falso color para niños
In Spanish: Falso color para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |