Lake Mead facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Lake Mead |
|
|---|---|

Satellite image of Lake Mead in July 2022 during a big drought.
|
|
| Location | Clark County, Nevada and Mohave County, Arizona |
| Coordinates | 36°15′N 114°23′W / 36.25°N 114.39°W |
| Lake type | Reservoir |
| Primary inflows | Colorado River, Virgin River |
| Primary outflows | Colorado River |
| Basin countries | United States |
| First flooded | September 30, 1935 by the Hoover Dam |
| Max. length | 120 mi (190 km) |
| Surface area | 247 sq mi (640 km2) |
| Max. depth | 532 ft (162 m) |
| Water volume | Maximum: 26,134,000 acre⋅ft (32.236 km3) |
| Shore length1 | 759 mi (1,221 km) |
| Surface elevation | Maximum: 1,229 ft (375 m) |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
Lake Mead is a huge man-made lake, also called a reservoir. It was created by the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River in the Southwestern United States. This important lake is located in Nevada and Arizona, about 24 mi (39 km) east of Las Vegas.
Lake Mead is the largest reservoir in the U.S. when it's full of water. It supplies water to millions of people in Arizona, California, Nevada, and parts of Mexico. This water helps nearly 20 million people and many farms.
When Lake Mead is completely full, it stretches 112 miles (180 km) long. It can be 532 feet (162 m) deep at its deepest point. The water surface is 1,229 feet (375 m) above sea level, covering an area of 247 square miles (640 km2). At this size, it holds a massive 28.23 million acre-feet (34.82 km3) of water.
However, the lake has not been full since 1983. This is because of long periods of drought and more people needing water. In May 2022, Lake Mead was only about 26% full. Its water level had dropped to a new low. By December 2024, thanks to water-saving efforts, the lake's water levels had risen by 16 feet over two years.
Contents
How Lake Mead Was Formed
Long ago, before Lake Mead existed, Ancestral Puebloans lived in this area. Many of their ancient sites were covered by water when the lake was made. One famous site is called the "Lost City."
The lake is named after Elwood Mead. He was in charge of the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation from 1924 to 1936. This was during the time when the Boulder Canyon Project was planned and built. This project created both the Hoover Dam and Lake Mead.
In 1936, the area around Lake Mead became the Boulder Dam Recreation Area. The National Park Service managed it. In 1947, its name changed to the Lake Mead National Recreation Area. Later, Lake Mohave and the Shivwits Plateau were added to its care. Both lakes and their surroundings offer fun activities all year.
When the Hoover Dam was built, the rising water forced people to leave their homes. The town of St. Thomas, Nevada was one of these places. Its last resident left in 1938. Today, you can sometimes see the ruins of St. Thomas. This happens when Lake Mead's water level is very low. The lake also covered other old river crossings and towns.
You can often see a white line on the rocks around Lake Mead. This is called the high-water mark. It shows how high the water used to be. The white color comes from minerals left behind on the rocks.
Exploring Lake Mead's Geography
There are nine main ways to get to Lake Mead. Three roads from the Las Vegas metropolitan area lead to the west side. From the northwest, you can take Interstate 15. This route goes through Valley of Fire State Park and the Moapa River Indian Reservation. It leads to the Overton Arm part of the lake.
The lake is made up of several different sections. The largest section, closest to the Hoover Dam, is Boulder Basin. A narrow channel, once called Boulder Canyon, connects Boulder Basin to Virgin Basin. The Virgin River and Muddy River flow into the Overton Arm. This arm connects to the northern part of the Virgin Basin. Further east are Temple Basin and Gregg Basin.
When the lake levels are very high, other areas get flooded. These include Grand Wash Bay and about 55 miles (89 km) of the Colorado River. However, as of February 2015, some of these smaller basins remain dry.
Sharp mountain ranges surround the lake. They create beautiful views, especially when the sun sets. The River Mountains and Muddy Mountains are visible from Boulder Basin. Bonelli Peak is to the east of Virgin Basin.
Las Vegas Bay is where the Las Vegas Wash ends. This wash carries water out of the Las Vegas Valley.
Drought and Water Challenges
Lake Mead gets most of its water from melting snow. This snow falls in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado, Wyoming, and Utah. The Glen Canyon Dam controls how much water flows into Lake Mead. It must release about 8.23 million acre-feet (10,150,000 Ml) of water each year.
However, Hoover Dam has been releasing more water than that, over 9 million acre-feet (11,000,000 Ml) each year. This has caused Lake Mead's water levels to drop since 2000. Water also leaves the lake through evaporation. This means the lake loses about 1.2 million acre-feet (1,500,000 ML) more water than it receives each year. Farmers in California's Imperial Valley have some of the oldest water rights. They receive the largest share of water.
From the 1970s to the 1990s, there were many wet years. This filled both Lake Mead and Lake Powell to their full capacity. Lake Mead reached a record high of 1,225 feet (373 m) in the summer of 1983.
Since 2000, the Colorado River basin has faced a very long and severe drought. This is known as the southwestern North American megadrought. Because of this, Lake Mead's water levels have fallen significantly.

In June 2010, the lake was only 39% full. It hit a new record low in November 2010. After heavy snowmelt in 2011, the lake's level rose for a while. But in 2012 and 2013, the drought worsened. This caused Lake Mead's level to drop to new record lows in 2014, 2015, and 2016.
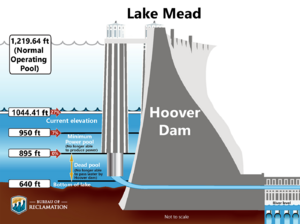
In July 2016, it reached its lowest point ever at 1,071.60 feet (326.62 m). If the lake falls below 1,075 feet (328 m) at the start of the water year (October 1), water rationing is declared. This means Arizona and Nevada would have to use less water. Luckily, the lake rose just enough in September 2016 to avoid these restrictions.
In 2017, heavy snowfall in the Rocky Mountains helped the lake recover some water. Levels rose throughout the year. However, the drought continued. From 2018 to early 2021, Lake Mead stayed above the shortage level. But by mid-2021, it dropped below it. This led to a water shortage declaration in August 2021. On July 28, 2022, the lake reached its lowest level since 1937.
The dropping water levels have caused problems for marinas and boat ramps. Many have had to move or close. This makes it harder for people to enjoy boating on the lake.
The changing weather, high evaporation, and less snowmelt are all putting pressure on Lake Mead. More people rely on it for water and for electricity from the Hoover Dam. To help with electricity, Hoover Dam was updated in 2015 and 2016. It can now generate power even with lower water levels.
If water levels keep falling, the Hoover Dam would stop making electricity below 950 feet (290 m). The lake would stabilize at 895 feet (273 m) when water reaches the dam's lowest outlet. To make sure Las Vegas can always get drinking water, a new intake tunnel was built. This 3-mile (4.8 km) tunnel is in the middle of the lake at 860 feet (260 m). It started working in late 2015.
About 6% of Lake Mead's water evaporates each year. Scientists are looking into covering parts of the lake with special floating solar panels. These panels could generate a lot of electricity. They would also reduce water loss from evaporation by up to 90%.
In December 2021, Arizona, California, Nevada, and the U.S. government agreed to spend $200 million. This money helps water users reduce their water use. This "500+ Plan" aimed to keep an extra 500,000 acre-feet (620,000,000 m3) of water in the lake. Agreements with Native American tribes also helped save water. By December 2024, California had greatly reduced its water use. Lake Mead's water levels had risen by 16 feet in two years.
However, in February 2025, experts confirmed that Lake Mead is still only about 35% full. This is still a serious situation.
Fun Activities at Lake Mead
Lake Mead offers many fun things to do for both locals and visitors. You can go boating, fishing, swimming, sunbathing, and water skiing. There are four main marinas on Lake Mead: Las Vegas Boat Harbor, Lake Mead Marina, Callville Bay, and Temple Bar. The area has many hidden coves with rocky cliffs and sandy beaches.
The lake has several small islands, depending on the water level. Oberlink Island is the largest. The Alan Bible Visitor Center has a garden with cactus and other plants from the Mojave Desert. The Grand Wash is another popular spot for recreation.
In 1971, Lake Mead hosted the first-ever B.A.S.S Bassmaster Classic. This was a secret fishing tournament. The 24 anglers didn't know where they were going until their plane was in the air! Bobby Murray won the $10,000 prize.
You can also take a cruise on the Desert Princess. This three-level boat takes passengers to the Hoover Dam five days a week.
B-29 Plane Crash
At the bottom of Lake Mead lies a Boeing B-29 Superfortress airplane. It crashed in 1948 during a test flight. The plane was testing a new missile guidance system. The wreckage of at least two other smaller airplanes are also submerged in Lake Mead.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lago Mead para niños
In Spanish: Lago Mead para niños
- List of drying lakes
- List of reservoirs and dams in the United States