2020 California wildfires facts for kids
Quick facts for kids 2020 California wildfires |
|
|---|---|
|
From top to bottom, and left to right;
September 10 satellite image of the wildfires burning in California and Oregon; The Aurora Fire on June 26, 2020; The Bobcat Fire burning in the San Gabriel mountains near Monrovia; Smoke from the North Complex over the Bay Bridge at noon on September 9; An orange sky over Eureka on Sept 9; The CZU Lightning Complex fires along Butano Ridge on August 18; The Loyalton Fire near Calpine; The Hennessey and Spanish Fires burn towards Lake Berryessa on August 18, 2020 |
|
| Statistics | |
| Total fires | 8,648 |
| Total area | 4,304,379 acres (1,741,920 ha) |
| Cost | >$12.079 billion (2020 USD) (Third-costliest on record) |
| Date(s) | February 15, 2020–January 5, 2021 |
| Buildings destroyed | 11,116 (Cal Fire) 9,211 (NIFC) |
| Deaths | 33 |
| Non-fatal injuries | 37 |
| Map | |
 A map of wildfires in California in 2020, using Cal Fire data |
|
| Season | |
|
← 2019
2021 →
|
|
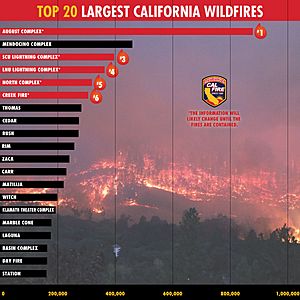
The 2020 California wildfire season was a year with a huge number of wildfires in California. It was part of the larger 2020 Western United States wildfire season. During 2020, 8,648 fires burned over 4.3 million acres. This is more than four percent of California's total land.
This made 2020 the biggest wildfire season ever recorded in California's recent history. One fire, the August Complex fire, was so large it was called the first "gigafire." It burned over 1 million acres, which is bigger than the state of Rhode Island. These fires destroyed more than 10,000 buildings. They also cost over $12 billion in damages and fighting the fires.
Experts believe the many fires happened because of two main reasons. First, for over a century, forests were not managed well. Second, higher temperatures from climate change made conditions worse.
On August 18, 2020, Governor Gavin Newsom declared a state of emergency. This meant the state needed extra help to deal with the fires. Many fires started on August 16–17 from strong thunderstorms. These storms were caused by moisture from a tropical storm. Fighting the fires and helping people evacuate was harder because of a heatwave and the COVID-19 pandemic.
In early September 2020, very strong winds and a heatwave made the fires grow quickly. The August Complex fire became the largest fire ever recorded in California. The Creek Fire trapped hundreds of campers. The North Complex grew fast, threatening the city of Oroville. This fire caused many people to leave their homes and led to 16 deaths.
Contents
Understanding California's Wildfire Season
What Causes Wildfires in California?
Wildfires are a natural part of California's environment. But in recent years, they have become much larger and more dangerous. Scientists say that before the 1850s, fires burned even more land each year. Native American tribes used to set controlled fires. This helped clear out dead plants and reduce the risk of huge wildfires.
How Land Management Affects Fires
For a long time, people have tried to stop all wildfires. This has caused a lot of dead plants and trees to build up in forests. This buildup acts like fuel, making fires much bigger and harder to control when they do start. Many scientists agree that we need more "controlled burns." These are small, planned fires that clear out fuel safely.
More people are also building homes in areas where fires are common. This means more buildings are at risk when a wildfire happens.
The Role of Climate Change

Climate change makes wildfires in California worse. It causes higher temperatures and increases the risk of droughts. Droughts mean less rain, making plants and trees very dry and easy to burn. Experts say that the heatwaves and lightning storms that started many fires in 2020 were made worse by global warming.
David Romps, a science expert, said that global warming made the heat, lightning, and dry plants much worse. Another expert, Friederike Otto, agreed. She said there is "absolutely no doubt" that the very high temperatures were higher because of human-caused climate change.
Fires Started by People
Some fires are started by people, sometimes by accident. For example, the El Dorado Fire in 2020 was started by a device at a gender reveal party. Other fires are suspected to have been started on purpose. For instance, a person was investigated for starting the Dolan Fire. Another person was investigated for starting the Markley Fire.
When Do Wildfires Usually Happen?
The peak of California's wildfire season is usually from July to November. This is when the weather is hot and dry. Strong, dry winds, like the Santa Ana winds, also happen often during this time. These winds can spread fires very quickly. The fire season usually ends when the first big autumn rainstorm arrives. This is usually in October in Northern California and November in Southern California.
How Wildfires Affect Nature
Wildfires have a big impact on California's natural environment. A study from 2023 looked at how the 2020 and 2021 fires affected ecosystems. It found that these two years saw a huge amount of land burn.
The fires destroyed parts of the homes of many animal and plant species. For example, 30% of the habitat for 50 different species was burned. For 100 other species, at least 10% of their homes were affected. Some areas burned very severely, meaning almost everything was destroyed.
Major Wildfires of 2020
Here is a list of some of the largest fires in California during 2020. These fires either burned more than 1,000 acres or caused a lot of damage or injuries.
| Name | County | Acres | Start date | Containment date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interstate 5 | Kings | 2,060 | May 3 | May 7 | |
| Range | San Luis Obispo | 5,000 | May 27 | May 28 | |
| Scorpion | Santa Barbara | 1,395 | May 31 | June 1 | |
| Quail | Solano | 1,837 | June 6 | June 10 | 3 buildings destroyed |
| Wood | San Diego | 11,000 | June 8 | June 12 | Burned on a military base |
| India | San Diego | 1,100 | June 8 | June 14 | Burned on a military base |
| Soda | San Luis Obispo | 1,672 | June 10 | June 11 | 2 buildings destroyed |
| Grant | Sacramento | 5,042 | June 12 | June 17 | 1 building damaged |
| Walker | Calaveras | 1,455 | June 16 | June 20 | 2 buildings destroyed |
| Grade | Tulare | 1,050 | June 22 | June 26 | |
| Pass | Merced | 2,192 | June 28 | June 30 | |
| Bena | Kern | 2,900 | July 1 | July 3 | |
| Crews | Santa Clara | 5,513 | July 5 | July 13 | 1 building destroyed; 1 damaged; 1 injury. People had to leave their homes. |
| Soledad | Los Angeles | 1,525 | July 5 | July 15 | 1 injury, started by fireworks |
| Mineral | Fresno | 29,667 | July 13 | July 26 | 7 buildings destroyed |
| Coyote | San Benito | 1,508 | July 15 | July 18 | |
| Hog | Lassen | 9,564 | July 18 | August 8 | 2 buildings destroyed |
| Gold | Lassen | 22,634 | July 20 | August 8 | 13 buildings destroyed; 5 damaged; 2 firefighters injured |
| July Complex 2020 | Modoc, Siskiyou | 83,261 | July 22 | August 7 | 1 building destroyed; 3 other structures destroyed |
| Blue Jay | Mariposa, Tuolumne | 6,922 | July 24 | November 20 | Started by lightning, 1 building destroyed. |
| Red Salmon Complex | Humboldt, Siskiyou, Trinity | 144,698 | July 26 | November 17 | Started as two separate fires that later joined. |
| Branch | San Luis Obispo | 3,022 | July 28 | August 1 | |
| Apple | Riverside | 33,424 | July 31 | November 18 | 4 buildings destroyed; 8 other structures destroyed; 4 injuries |
| Pond | San Luis Obispo | 1,962 | August 1 | August 8 | 1 building destroyed; 1 damaged; 13 other structures destroyed |
| North | Lassen | 6,882 | August 2 | August 10 | Part of this fire also burned in Nevada. |
| Stagecoach | Kern | 7,760 | August 3 | August 16 | 23 buildings destroyed; 4 damaged; 25 other structures destroyed; 2 damaged; 1 firefighter died |
| Wolf | Tuolumne | 2,057 | August 11 | November 19 | Started by lightning |
| Lake | Los Angeles | 31,089 | August 12 | September 28 | Started by lightning, 33 buildings destroyed; 6 damaged; 21 other structures destroyed; 2 injuries |
| Ranch 2 | Los Angeles | 4,237 | August 13 | October 5 | Started by a person, possibly on purpose |
| Hills | Fresno | 2,121 | August 15 | August 24 | Started by lightning; 1 death |
| Loyalton | Lassen, Plumas, Sierra | 47,029 | August 15 | September 14 | Started by lightning, caused the first ever "Fire Tornado Warning"; 5 homes, 6 other structures destroyed |
| Beach | Mono | 3,780 | August 16 | August 28 | Started by lightning |
| River | Monterey | 48,088 | August 16 | September 4 | Started by lightning; 30 buildings destroyed; 13 damaged; 4 injuries |
| Dome | San Bernardino | 43,273 | August 16 | September 14 | Started by lightning, burned in a national preserve; 6 buildings destroyed and over 1.3 million Joshua trees killed |
| CZU Lightning Complex | San Mateo, Santa Cruz | 86,509 | August 16 | September 22 | Several lightning-started fires that joined together; 1,490 buildings destroyed; 140 damaged; 1 injury; 1 death. |
| SCU Lightning Complex | Santa Clara, Alameda, Contra Costa, San Joaquin, Merced, Stanislaus | 396,624 | August 16 | October 1 | Many fires started by a lightning storm that combined; 222 buildings destroyed; 26 damaged; 6 injuries. This was the third-largest group of fires in California history. |
| August Complex | Glenn, Mendocino, Lake, Tehama, Trinity, Shasta | 1,032,648 | August 16 | November 12 | Originally 38 separate fires that later joined to become California's largest recorded wildfire. 1 firefighter died; 2 injuries; 935 buildings destroyed; 5 damaged. |
| Rattlesnake | Tulare | 8,419 | August 16 | December 29 | Lightning started a slow-moving fire in hard-to-reach areas. |
| LNU Lightning Complex | Colusa, Lake, Napa, Sonoma, Solano, Yolo | 363,220 | August 17 | October 2 | Many fires started by lightning that combined; 1,491 buildings destroyed; 232 damaged; 5 injuries; 6 deaths. This was the fifth-largest group of fires in California history. |
| Holser | Ventura | 3,000 | August 17 | September 6 | Cause unknown |
| Butte/Tehama/Glenn Lightning Complex (Butte Zone) | Butte | 19,609 | August 17 | October 17 | Lightning started 34 fires; 14 buildings destroyed; 1 damaged; 1 injury |
| North Complex | Plumas, Butte | 318,935 | August 17 | December 3 | Lightning started, included other fires; 2,342 buildings destroyed; 113 damaged; 16 deaths; 13 injuries. This was the sixth-largest fire in California history. |
| Jones | Nevada | 705 | August 17 | August 28 | Lightning started, 21 buildings destroyed, 3 damaged, 7 injuries |
| Sheep | Plumas, Lassen | 29,570 | August 17 | September 9 | Lightning started, 26 buildings destroyed, 1 injury |
| Salt | Calaveras | 1,789 | August 18 | August 24 | Lightning started |
| W-5 Cold Springs | Lassen, Modoc | 84,817 | August 18 | September 14 | Lightning started. Spread into Nevada. |
| Carmel | Monterey | 6,905 | August 18 | September 4 | Lightning started, 73 buildings destroyed; 7 damaged |
| Dolan | Monterey | 124,924 | August 18 | December 31 | Cause not officially known; however, a person was investigated in connection to the fire; 19 buildings destroyed. |
| Woodward | Marin | 4,929 | August 19 | October 2 | Lightning started |
| SQF Complex | Tulare | 174,178 | August 19 | January 5 | Lightning started, included other fires; 228 buildings destroyed; 12 damaged; 15 injuries |
| Moc | Tuolumne | 2,857 | August 20 | August 30 | Cause: Equipment |
| Moraine | Fresno, Tulare | 1,316 | August 21 | December 29 | Lightning started |
| Slink | Alpine, Mono | 26,759 | August 29 | November 8 | Lightning started |
| Creek | Fresno, Madera | 379,895 | September 4 | December 24 | 856 buildings destroyed, 71 damaged; 15 injuries; At the time, it was the fourth-largest fire and the largest single fire in California history. |
| El Dorado | San Bernardino, Riverside | 22,744 | September 5 | November 16 | Started by a device at a party. 10 buildings destroyed, 5 damaged; 1 firefighter died; 13 injuries. |
| Valley | San Diego | 16,390 | September 5 | September 24 | 61 buildings destroyed, 11 damaged, 3 injuries |
| Bobcat | Los Angeles | 115,997 | September 6 | December 18 | Cause unknown, 171 buildings destroyed. One of the largest fires in Los Angeles County's history. |
| Oak | Mendocino | 1,100 | September 7 | September 14 | Cause unknown, 25 buildings destroyed, 20 damaged |
| Slater / Devil | Siskiyou, Del Norte | 166,127 | September 7 | November 16 | Included two fires. 2 deaths; 440 buildings destroyed. Spread into Oregon. |
| Fork | El Dorado | 1,673 | September 8 | November 9 | Cause unknown |
| Bullfrog | Fresno | 1,185 | September 9 | November 9 | Cause being investigated |
| Willow | Yuba | 1,311 | September 9 | September 14 | 41 buildings destroyed, 10 damaged |
| Fox | Siskiyou | 2,188 | September 14 | September 29 | Started by a person |
| Snow | Riverside | 6,254 | September 17 | October 6 | Cause unknown |
| Glass | Napa, Sonoma | 67,484 | September 27 | October 20 | Cause unknown; 1,555 buildings destroyed; 280 damaged |
| Zogg | Shasta | 56,338 | September 27 | October 13 | 204 buildings destroyed; 27 damaged; 4 deaths, 1 injury; the historic town of Ono was destroyed |
| Silverado | Orange | 12,466 | October 26 | November 7 | Started by a power line; 2 firefighters badly injured; over 90,000 people had to leave their homes; 5 buildings destroyed, 9 damaged |
| Blue Ridge | Orange, San Bernardino, Riverside | 13,694 | October 26 | November 7 | Started by a power line; 1 building destroyed, 10 damaged; at least 30,000 people had to leave their homes |
| Laura 2 | Lassen | 2,800 | November 17 | November 24 | Cause unknown; 48 buildings destroyed; 4 damaged |
| Mountain View | Mono, Alpine | 20,385 | November 17 | December 11 | Cause unknown; 81 buildings destroyed; 1 death |
| Airport | Riverside | 1,087 | December 1 | December 12 | Cause unknown |
| Bond | Orange | 6,686 | December 2 | December 10 | Started by a house fire; 31 buildings destroyed; 21 damaged; 2 firefighter injuries |
| Sanderson | Riverside | 1,933 | December 13 | December 14 | Cause unknown |
| Creek 5 | San Diego | 4,276 | December 23 | December 31 | Cause unknown; over 7,000 people had to leave their homes on a military base |
See Also
- List of California wildfires
- 2020 Western United States wildfire season
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |