San Joaquin River facts for kids
Quick facts for kids San Joaquin River |
|
|---|---|

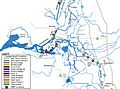
San Joaquin River near Vernalis
|
|
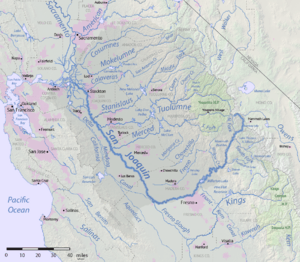
Map of the San Joaquin River watershed
|
|
| Native name | Spanish: Río San Joaquín |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Cities | Fresno, Modesto, Stockton |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Thousand Island Lake Ansel Adams Wilderness, Sierra Nevada 9,839 ft (2,999 m) 37°43′56″N 119°10′34″W / 37.73222°N 119.17611°W |
| River mouth | Suisun Bay Antioch, Contra Costa/Solano Counties 0 ft (0 m) 38°04′00″N 121°51′04″W / 38.06667°N 121.85111°W |
| Length | 366 mi (589 km) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 15,600 sq mi (40,000 km2) |
| Tributaries |
|
The San Joaquin River is a major river in California, United States. It is about 330 miles (530 km) long. This makes it the second longest river in California, right after the Sacramento River. The river starts in the western Sierra Nevada Mountains. It then flows west and north. Finally, it reaches San Francisco Bay at the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta.
The area drained by the river, called its basin, is huge. It covers about 32,000 square miles (82,879 square kilometers). Most of this land is farmland. The San Joaquin River provides drinking water for over 22 million people in California. Its three biggest rivers that flow into it, called tributaries, are the Merced, Tuolumne, and Stanislaus rivers.
This river was once home to many plants and animals. It was one of the richest river ecosystems in California. But now, more than 60 miles (97 km) of the river is often dry. Water is taken out for irrigation to grow crops. Below Friant Dam, a dam built in the 1940s, 95 percent of the river's water is gone. Also, much of the river is polluted. This has harmed the chinook salmon, which used to live here. Pesticides and other harmful materials flow from the San Joaquin into San Francisco Bay.
Good news! A big project has started to help the San Joaquin River. On September 13, 2006, a group called the Natural Resources Defense Council made an agreement. They worked with people who use water from Friant Dam and the United States Department of the Interior. This agreement aims to bring water back to the river below the dam. It also helps reduce pollution.
Contents
Journey of the San Joaquin River
Where the River Starts
The San Joaquin River begins high up in the Sierra Nevada Mountains. Three smaller rivers, called forks, join together to form the main river. These meeting points are named Balloon Dome and Junction Butte.
- The North Fork starts at a lake in Madera County. This spot is very high up, at 11,090 feet (3,380 m) above sea level.
- The Middle Fork begins at a beautiful lake called Thousand Island Lake.
- The South Fork flows out of Martha Lake. This lake is also very high, at 11,004 feet (3,354 m) above sea level. The river flows through Madera and Fresno counties.
Flowing Through California's Central Valley
The river then flows west into the Central Valley of California. Many other rivers from the Sierra Nevada mountains join it here. The biggest of these are the Stanislaus River, Tuolumne River, and Merced River. Both the Tuolumne and Merced rivers flow out of Yosemite National Park.
As the San Joaquin River moves north and west, it gets water from many other tributaries:
- Mokelumne River
- Cosumnes River
- Calaveras River
- Stanislaus River
- Tuolumne River
- Merced River
- Bear Creek
- Hospital Creek
- Ingram Creek
- Chowchilla River
- Ash Slough
- Berenda Slough
- Fresno River
The San Joaquin River system also includes many lakes and reservoirs. These include:
- Pardee Reservoir
- Camanche Reservoir
- New Hogan Reservoir
- New Don Pedro Reservoir
- Lake McClure
- Eastman Lake
- Hensley Lake
- Mendota Pool
- Millerton Lake
- Pine Flat Reservoir
- Lake Kaweah
- Lake Success
- Florence Lake
- Mammoth Pool Reservoir
People have also built channels to help manage the river's water. Some of these are:
- Stockton Deep Water Ship Channel
- Grant Line Canal
- Eastside Bypass
- Chowchilla Bypass
- San Luis Drain
- Madera Canal
- Friant-Kern Canal
Meeting the Bay
The San Joaquin River eventually meets the Sacramento River. Together, they form the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta. This delta is one of the largest estuaries (where a river meets the sea) in the United States. It is close to the city of Antioch. In this area, the San Joaquin River splits into two parts: the Old River and the Middle River. Sometimes, fish get confused and swim into the Old River. To help them, a wall is built between the San Joaquin River and the Old River.
How People Use and Change the River
River Life Before Development
Before people built many towns and farms in the Central Valley (around the 1850s), the San Joaquin River was full of life. It was one of the richest places for living things in California. In winter, the river would flood the valley. This created wetlands, which are like marshy areas. These wetlands were perfect homes for many birds and other animals. Rare animals like the San Joaquin Kit Fox and the riparian brush rabbit also lived near the river.
Friant Dam and Its Impact
In 1942, a large dam called Friant Dam was built on the San Joaquin River. This dam changed the river a lot. It took away much of the river's water. This water was used to irrigate crops, provide drinking water, and make electricity. The dam also harmed the salmon that lived in the river. It stopped the natural flooding that created the important wetlands.
The Friant Dam is a very large structure:
- It is 319 feet (97 m) tall.
- It stretches 3,488 feet (1,063 m) long.
- Its base is 267 feet (81 m) thick.
- The top of the dam is 20 feet (6.1 m) thick.
- It was built using 2,135,000 cubic yards of concrete.
Boats and Shipping on the River
The San Joaquin River has been used for shipping goods by boats and ships for a long time. This is called navigation. People first used the river for navigation during the California Gold Rush in 1849. Boats carried people over 200 miles (320 km) up the river. They were going to look for gold in the mountains.
Today, there is a special channel that goes all the way up to the city of Stockton. This channel allows big ships to sail far into the river. However, mud and sand have filled up much of the river channel past Stockton. This stops large ships from going any farther upstream.
Images for kids
-
Crossings of California State Route 99 and the Union Pacific Railroad along the northern border of Fresno. The early stages of construction of California High-Speed Rail's San Joaquin River Viaduct is also visible.
-
The San Joaquin at Mendota Pool during the high flows of April 2006
-
Headwaters of the Middle Fork San Joaquin River, just downstream of Thousand Island Lake
-
Mariposa Indian Encampment by Albert Bierstadt, c. 1872
-
Mount Diablo (background), where Juan Crespí first gazed upon the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta in 1772, with Suisun Bay in the foreground
-
Mammoth Pool Dam, the principal dam of the Big Creek Hydroelectric Project, completed in 1959
-
Millerton Lake, the reservoir of Friant Dam and the largest on the San Joaquin mainstem
-
A road in the San Luis National Wildlife Refuge, one of the few remaining wetland areas along the San Joaquin River
See also
 In Spanish: Río San Joaquín para niños
In Spanish: Río San Joaquín para niños