Yemeni Civil War (2014–present) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Yemeni civil war |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Yemeni Crisis, Arab Winter, War on terror, and the Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict | |||||||||
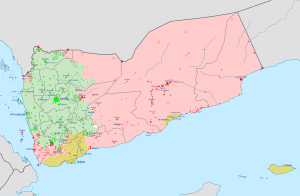 Political and military control in Yemen in October 2022 Republic of Yemen (internationally recognized), Yemeni Armed Forces and GPC allies Republic of Yemen, territories controlled by pro-government STC militias Houthi movement Local, non-aligned forces Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) Islamic State – Yemen Province (IS-YP) (For a map of the military situation in Yemen and border areas in Saudi Arabia, see the detailed map here.) |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
The Yemeni civil war is a conflict happening in the country of Yemen. It started in late 2014. This war is mainly between two groups: the Presidential Leadership Council, led by Rashad al-Alimi, and the Supreme Political Council, led by Mahdi al-Mashat. Both groups believe they are the true government of Yemen.
Contents
What Caused the Yemeni Civil War?
The civil war began in September 2014. Forces known as the Houthis took control of Sanaa, the capital city. After this, the Houthis quickly took over the government.
In March 2015, the Houthi-led Supreme Revolutionary Committee called for everyone to join their fight. Their goal was to remove then-president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi. They also wanted to expand their control into southern parts of Yemen. The Houthis, along with soldiers loyal to former President Ali Abdullah Saleh, started fighting in Lahij Governorate. By March 25, Lahij fell to the Houthis. They reached the city of Aden, where Hadi's government was based. President Hadi then left the country.
Who is Fighting in Yemen?
A group of countries led by Saudi Arabia started military actions. They used air strikes to support the former Yemeni government. Even though the Iranian government has not directly joined the fight, this conflict is part of a larger rivalry between Iran and Saudi Arabia. This is called a "proxy conflict." Iran helps the Houthis by providing weapons, training, and other support.
Saudi Arabia sees Iran's actions in Yemen as an attempt to create a friendly government there. They believe Iran wants to trap them in a difficult situation.
Currently, Houthi fighters control the capital city of Sanaa. They also control most of what used to be North Yemen. They are fighting against forces loyal to President Hadi, who are supported by Saudi Arabia.
Since 2017, the anti-Houthi side has become divided. This happened when the Southern Transitional Council (STC) was formed. The STC later took control of Aden in 2018. Now, there are often clashes between Hadi's forces (backed by Saudi Arabia) and southern separatists (backed by the United Arab Emirates).
Other groups, like Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and the Islamic State, have also attacked both sides. AQAP controls some areas in the countryside and along the coast.
Efforts to Stop the Fighting
The United Nations (UN) helped create a two-month ceasefire in April 2022. This truce allowed fuel to be brought into Houthi-controlled areas. It also allowed some flights from Sanaa International Airport to Jordan and Egypt. The UN extended this truce in June 2022.
In March 2023, it was reported that Iran agreed to stop all military support to the Houthis. This was part of a deal between Iran and Saudi Arabia, helped by China. This agreement is expected to push the Houthis to end the conflict through talks.
How the War Affects People
The Yemeni civil war is sometimes called the "world's forgotten war." It has caused a lot of suffering.
Famine and Health Issues
In 2018, the United Nations warned that 13 million people in Yemen faced starvation. They said it could become the "worst famine in the world in 100 years." By December 2020, the UN estimated that the war had caused about 230,000 deaths. Most of these deaths were from indirect causes, like not enough food, poor healthcare, and damaged infrastructure.
Between 2016 and 2019, over 2 million suspected cases of cholera were reported in Yemen. Cholera is a serious disease that causes severe diarrhea.
Impact on Education
The war has badly damaged Yemen's education system. The number of children not attending school grew to 1.8 million between 2015 and 2016. Many schools are affected:
- 68 schools are used by armed groups.
- 248 schools have serious structural damage.
- 270 schools are used to house people who have lost their homes.
The government has struggled to fix these problems. There isn't enough money to run schools or pay teachers. Materials to rebuild damaged schools are scarce, and there are problems printing textbooks.
Despite the war, the education ministry has tried to help students. They sent teams to oversee final exams for primary and secondary schools. The UNICEF organization is also working to raise money to support students and repair damaged schools.
Dangers from Mines and Airstrikes
The quality of life for people in Yemen has been severely affected. Even though landmines are banned by the government, Houthi forces have placed many anti-personnel mines. Thousands of civilians have been injured by stepping on these mines. Many have lost legs or suffered eye injuries. It is believed that over 500,000 mines have been laid by Houthi forces. The Yemeni Army has removed many of these mines in areas they have taken back.
A group of nine countries led by Saudi Arabia has launched many airstrikes against Houthi forces. Between March 2015 and December 2018, over 4,600 civilians were killed. Much of the infrastructure for producing, storing, and distributing food has been destroyed. Factories have stopped working, and many people have lost their jobs. Because less is being produced, food, medicines, and other basic goods are hard to find. Their prices have also gone up, making them too expensive for many families.
Working Towards Peace
There have been efforts to bring peace to Yemen.
Stockholm Agreement
One important step was the Stockholm Agreement in December 2018. This deal was made between the Yemeni government and the Houthi rebels. It focused on stopping the fighting in the city of Hodeida and nearby areas. The agreement also aimed to move forces away from the city and address humanitarian needs. This was seen as a big step to help the people of Yemen and encourage more talks.
Since then, the United Nations has helped with many rounds of discussions. These talks have covered finding a complete political solution, exchanging prisoners, and setting up a temporary government. The main goal is to solve the root causes of the conflict, bring people together, and make Yemen safe and stable again.
Riyadh Agreement
Another important step was the Riyadh Agreement in November 2019. This agreement was between the Yemeni government and the Southern Transitional Council (STC). It aimed to solve power struggles in southern Yemen by sharing power between the two groups. This was seen as a key part of creating a united Yemen and helping the larger peace process.
Even with these efforts, achieving peace in Yemen is still hard. There are ongoing clashes, political disagreements, and rivalries between countries in the region. Also, the humanitarian situation in Yemen remains very serious, with millions of people needing urgent help.
Related Pages
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra civil yemení (2014-presente) para niños
In Spanish: Guerra civil yemení (2014-presente) para niños

