Sudan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of the Sudan
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: النصر لنا
an-Naṣr lanā "Victory is ours" |
|
|
Anthem: نحن جند اللّٰه، جند الوطن
Naḥnu jund Allah, jund al-waṭan "We are Soldiers of God, Soldiers of the Homeland" |
|
Location of the Republic of the Sudan Territory claimed but not controlled
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Khartoum |
| Capital-in-exile | Port Sudan |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Sudanese |
| Government | Federal republic under a military junta |
|
|
|
|
| Legislature | Vacant |
| Formation | |
| 2500 BC | |
| 1070 BC | |
| c. 350 | |
|
• Tunjur, Funj, and Darfur Sultanates
|
c. 1500 |
| 1820 | |
| 1885 | |
| 1899 | |
| 1 January 1956 | |
| 25 May 1969 | |
| 6 April 1985 | |
|
• Secession of South Sudan
|
9 July 2011 |
| 19 December 2018 | |
|
• 2019 Draft Constitutional Declaration effective
|
20 August 2019 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
1,886,068 km2 (728,215 sq mi) (15th) |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
50,467,278 (30th) |
|
• Density
|
21.3/km2 (55.2/sq mi) (202nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2014) | ▼ 34.2 medium |
| HDI (2022) | low · 170th |
| Currency | Sudanese pound (SDG) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (CAT) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +249 |
| ISO 3166 code | SD |
| Internet TLD | .sd سودان. |
Sudan is a large country located in Africa. Its official name is the Republic of Sudan. The capital city of Sudan is Khartoum.
As of 2024, about 50 million people live in Sudan. The country covers a huge area of 1,886,068 square kilometers (728,215 square miles). This makes it the third-largest country in Africa by size. It is also the third-largest country in the Arab League.
Contents
What Does the Name Sudan Mean?
The name Sudan comes from an Arabic phrase, bilād as-sūdān. This means "The Land of the Blacks". This name was historically used for a large region in Africa called the Sahel.
Before this, the area was known by other names like Nubia. Sometimes, people also call it North Sudan today. This helps to tell it apart from South Sudan, which became a separate country in 2011.
A Brief Look at Sudan's History
The land of Sudan has a very long history, going back thousands of years. Many ancient cultures and kingdoms existed here.
Early Kingdoms and Empires
Around 2500 BC, the Kingdom of Kerma was powerful. Later, the Kingdom of Kush rose around 1070 BC. After Kush fell, the Nubians formed three Christian kingdoms: Nobatia, Makuria, and Alodia.
Arab Migration and Sultanates
Between the 14th and 15th centuries, many Arab nomads moved into Sudan. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, different sultanates ruled. The Funj sultanate controlled central and eastern Sudan. The Darfur sultanate ruled the west.
Foreign Rule and Independence
In the 19th century, Egypt conquered all of Sudan. Later, a religious uprising known as the Mahdist War took place. British and Egyptian forces eventually defeated the Mahdists.
In 1899, Sudan became a shared territory between Egypt and the United Kingdom. This was called the Anglo-Egyptian Condominium. However, Britain mostly controlled it.
Sudan gained its independence on January 1, 1956. This was a major step for the country.
Challenges After Independence
After independence, Sudan faced many challenges. Differences in language, religion, and power led to a civil war. This war was fought between the government and southern rebels.
This conflict eventually led to South Sudan becoming an independent country in 2011. From 1989 to 2019, Sudan was ruled by a military government. This period saw many difficulties for the people.
Currently, Sudan is experiencing a civil war. This conflict is between two main groups: the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF).
Where is Sudan Located?
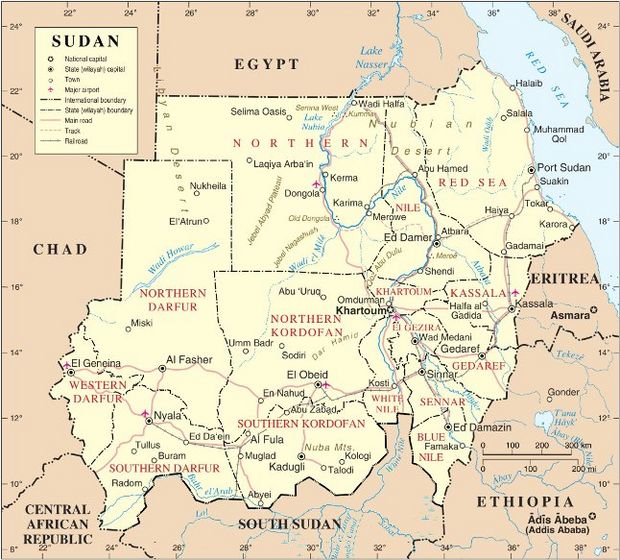
Sudan is in northern Africa. It has a coastline of about 853 kilometers (530 miles) along the Red Sea. Sudan shares borders with several countries. These include Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, South Sudan, the Central African Republic, Chad, and Libya.
The country's land is mostly flat plains. However, there are also several mountain ranges. The highest point in Sudan is the Deriba Caldera. It is 3,042 meters (9,980 feet) high and is located in the Marrah Mountains. The Red Sea Hills are in the east.
Rivers and Dams
The Blue Nile and White Nile rivers meet in Khartoum. They form the mighty Nile River, which then flows north into Egypt. The Blue Nile flows for almost 800 kilometers (500 miles) through Sudan.
There are several dams on these rivers. Examples include the Sennar Dam and Roseires Dam on the Blue Nile. The Jebel Aulia Dam is on the White Nile. There is also Lake Nubia near the border with Egypt.
Natural Resources
Sudan has many valuable mineral resources. These include gold, copper, iron, and oil. Other resources found here are natural gas, silver, and uranium.
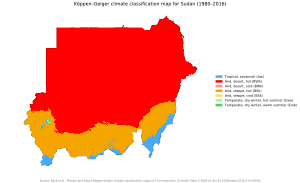
Sudan's Climate
Sudan's climate varies across the country. The northern and central parts are very dry deserts. These include the Nubian Desert and the Bayuda Desert. In the south, there are grasslands and tropical savannas.
The rainy season is short in the north, from June to September. In the south, it lasts longer, from May to October. Dry regions often experience sandstorms called haboob. These storms can make the sky very dark.
In the desert areas, people often move around with their herds of sheep and camels. Near the Nile River, farms use irrigation to grow crops.
How Sudan is Divided
Sudan is divided into 18 states. These states are then further divided into 133 districts.
- Gezira
- Al Qadarif
- Blue Nile
- Central Darfur
- East Darfur
- Kassala
- Khartoum
- North Darfur
- North Kordofan
- Northern
- Red Sea
- River Nile
- Sennar
- South Darfur
- South Kordofan
- West Darfur
- West Kordofan
- White Nile
Sudan's Economy
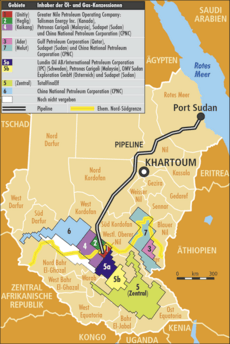
Oil used to be Sudan's main export. Production grew a lot before South Sudan became independent in 2011. After South Sudan separated, most of the major oilfields were no longer under Sudan's control.
South Sudan still needs to use pipelines in Sudan to export its oil. In 2012, Sudan and South Sudan agreed on a deal for this.
China is a big trading partner for Sudan. China owns a large share in the company that handles oil operations.
Agriculture is also very important to Sudan's economy. It employs 80 percent of the workers and makes up 39 percent of the country's total economic output. However, many farms depend on rainfall and can be affected by dry weather.
The Merowe Dam is a very large construction project in northern Sudan. It is about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Khartoum. The main goal of this dam is to create electricity. It is one of the biggest hydropower projects in Africa. The dam was finished in 2008 and provides electricity to most of the population.
Major Cities in Sudan
Here are some of the largest cities in Sudan by population:
- Omdurman - 1,849,659 people
- Khartoum - 1,410,858 people
- Khartoum North - 1,012,211 people
- Nyala - 492,984 people
- Port Sudan - 394,561 people
- El-Obeid - 345,126 people
- Kassala - 298,529 people
- Wad Madani - 289,482 people
- El-Gadarif - 269,395 people
- Al-Fashir - 217,827 people
People and Languages of Sudan
Sudan is home to many different groups of people. About 70% of the population are Arab people. Many of them are Arabized Nubians. Other groups include Beja, Nuba, and Fur.
Sudan has about 597 different groups that speak over 400 languages and dialects. Most people speak Sudanese Arabic. Some Arab tribes speak other Arabic dialects.
Many Arab tribes came to Sudan in the 12th century. They married local people and introduced Islam. There are also many non-Arabic groups in Sudan. These include the Masalit, Zaghawa, and Fulani.
Languages Spoken
Around 70 languages are native to Sudan. Before 2005, Arabic was the only official language. Now, both Arabic and English are official languages in Sudan. About 70.2% of the population can read and write.
Religion in Sudan
After South Sudan became a separate country in 2011, over 97% of the people in Sudan follow Islam. Most Muslims belong to two main groups: Sufi and Salafi Muslims.
Sudanese Culture
Sudanese culture is a mix of many different groups. There are about 578 ethnic groups, and they speak many different languages. The country has varied landscapes, from deserts to tropical forests.
Traditional Clothing
Many Sudanese people wear traditional clothes. For men, a common outfit is the jalabiya. This is a loose, long-sleeved, ankle-length garment. It is often worn with a large turban and a scarf.
For women, the most common dress is the thobe or thawb. This is a long, one-piece cloth. Women wrap it around their inner clothes, usually covering their head and hair.
Popular Sports
Football is the most popular sport in Sudan, just like in many other countries. The Sudan Football Association was started in 1936. This makes it one of the oldest football associations in Africa.
Famous football clubs like Al-Hilal Omdurman and Al-Merrikh helped make football popular. The Khartoum League was the first national football league in Sudan.
Since 2019, there has been an official national league for women's football clubs. In 2021, the Sudan women's national football team played in the 2021 Arab Women's Cup for the first time.
Sudan also has a national beach volleyball team. In 2022, Patricia Seif El Din El Haj became the first Sudanese woman wrestler to compete in an African championship. She is training for the 2024 Summer Olympics.
More About Sudan
- List of rivers of Sudan
- Sudan at the Olympics
- Sudan national football team
- Muhammed Ahmed, the Mahdi
Images for kids
-
Nubian pyramids in Meroë.
-
Muhammad Ahmad ruler of Sudan, 1881–1885.
-
The Flight of the Khalifa after his Defeat at the Battle of Omdurman.
-
The Mahdist War was fought between a group of Muslim dervishes, called Mahdists, who had over-run much of Sudan, and the British forces.
-
A map of Sudan. The Hala'ib Triangle has been under Egyptian administration since 2000.
-
JEM rebels in Darfur. Both the government and the rebels have been accused of atrocities.
-
Darfur refugee camp in Chad, 2005
-
Student from Khartoum
-
The Arabic-speaking Rashaida came to Sudan from Arabia about 170 years ago.
-
Minaret in Port Sudan
-
Sudanese tourists by the Meroë pyramids in various types of clothing.
See also
 In Spanish: Sudán para niños
In Spanish: Sudán para niños