Red Sea crisis facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Red Sea crisis |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Iran–Israel proxy war, the Middle Eastern crisis (2023–present), and the Yemeni civil war (2014–present) | |||||||
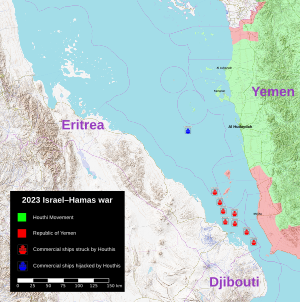 Map of Houthi activity near the Yemeni coast: Houthi-controlled Yemen (SPC) Government of Yemen (PLC) Houthi attacks (red) and hijackings (blue) |
|||||||
|
|||||||
The Red Sea crisis is a conflict that began on 19 October 2023. A group from Yemen called the Houthis started launching missiles and armed drones at Israel. They also began attacking ships in the Red Sea. The Houthis said they were doing this because of the Gaza war. They demanded that Israel stop its military actions in the Gaza Strip.
In response, the United States, the United Kingdom, and other countries began military operations to protect ships. They also launched airstrikes against Houthi targets in Yemen. The crisis has caused major problems for global shipping and trade.
The Houthis control a large part of Yemen along the Red Sea coast. They say they will target any ship connected to Israel, the US, or the UK. However, they have attacked ships from many different countries, even those with no link to Israel. To stay safe, hundreds of ships have had to take a much longer and more expensive route around Africa.
Contents
Background of the Conflict
Who are the Houthis?
The Houthi movement is a political and military group that controls large parts of Yemen, including the capital city, Sanaa. They are not the official government of Yemen recognized by other countries. The Houthis have been fighting in a civil war since 2014. This long war has caused a serious humanitarian crisis in Yemen. The Houthis are supported by Iran.
Why the attacks started
The attacks in the Red Sea are linked to the Gaza war, which began after an attack on Israel on 7 October 2023. The Houthis, along with other groups in the Middle East supported by Iran, showed support for the Palestinians.
The Houthi leader, Abdul-Malik al-Houthi, warned the United States not to get involved in the war. The Houthis have said their attacks on ships will not stop until there is a ceasefire in Gaza.
Weapons used in the attacks
The Houthis use a variety of weapons, many of which are believed to come from Iran, Russia, or China. These weapons include:
- Long-range surface-to-surface missiles that can travel over 1,800 kilometers.
- Cruise missiles that can fly long distances to reach their targets.
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones. These are aircraft without a pilot on board. Some are used for surveillance, while others are packed with explosives.
- Naval drones, which are remote-controlled boats filled with explosives.
Bab-el-Mandeb transits by cargo vessels
over 10,000 deadweight tonnage (approx.)
Before attacks
After first Houthi ship seizure/attack (19 November 2023)
After naval protection operation started (18 December 2023)
After US/UK attack on Yemen mainland (12 January 2024)
What are the Effects of the Crisis?
Effects on the World's Economy
The Red Sea is one of the world's most important routes for shipping. Many large shipping companies, like Maersk and Evergreen Marine Corporation, stopped sending their ships through the Red Sea because of the attacks. Oil and gas companies like BP and Shell also suspended shipments.
Instead of using the Red Sea and the Suez Canal, ships have to travel all the way around Africa and the Cape of Good Hope. This longer journey adds about three weeks to the trip, uses much more fuel, and costs a lot more money. These extra costs can cause prices for goods in stores to go up.
The crisis also caused problems for factories. For example, the car companies Tesla and Volvo Cars had to temporarily stop production at their European factories because parts they needed were delayed.
Effects on Israel and Egypt
The attacks have severely hurt trade with Israel. The Israeli Port of Eilat saw its activity drop by 85%. In July 2024, the port declared bankruptcy, and by July 2025, it had shut down completely.
The crisis has also been very bad for Egypt. Egypt earns billions of dollars each year from ships paying to use the Suez Canal. With fewer ships passing through, Egypt's income from the canal has dropped significantly.
Problems for Aid Shipments
The crisis has also made it harder to deliver humanitarian aid. Shipments of food and medicine for countries like Sudan, where there is an ongoing conflict and risk of famine, have been delayed for months. This is because the aid ships also have to take the longer, safer route around Africa.
How Countries Have Reacted
International Military and Political Response
Many countries have responded to the attacks. In December 2023, the United States formed a naval group called Operation Prosperity Guardian. Warships from the US, UK, and other countries began patrolling the Red Sea to protect commercial ships. The European Union also started its own naval mission called Operation Aspides.
Starting in January 2024, the US and UK began launching air and missile strikes on Houthi targets inside Yemen. They said this was to reduce the Houthis' ability to attack ships.
On 10 January 2024, the UN Security Council passed a resolution that condemned the Houthi attacks. It stated that countries have the right to defend their ships and called for freedom of navigation in the Red Sea.
Involvement of Other Countries
It is widely believed that Iran provides the Houthis with weapons, training, and intelligence for the attacks. US officials have said that members of Iran's military are in Yemen helping to direct the attacks.
Other countries have also been involved. The US government said that some companies in China have supplied materials that the Houthis use to build their weapons.
False Information Online
During the crisis, a lot of disinformation, or false information, has been spread online. Supporters of the Houthis have shared false claims about their attacks to make them seem more successful.
For example, old photos and videos of ship fires or sinkings have been posted online, claiming they show recent Houthi attacks. Some people have even used clips from the video game Arma 3 and presented them as real footage of the conflict. This makes it difficult for people to know what is really happening.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Crisis del mar Rojo para niños
In Spanish: Crisis del mar Rojo para niños
- Closure of the Suez Canal (1967–1975)
- Tanker war
- Guanbi policy